首页 > Python资料 博客日记
基于遗传算法的CVRP建模求解(Python)
2024-05-26 12:00:05Python资料围观263次
基于遗传算法的CVRP建模求解(Python)
带容量约束的车辆路径优化问题,CVRP,对一系列装卸货点进行适当的路径规划,在满足约束条件(客户需求、车辆载重和容积、车型、车辆行驶里程、配送中心数量等限制)和目标最优化(路程最短、成本最低、使用车辆数最少、配送时间最快等)下,将客户的配送需求从配送中心送达客户点,或从客户点送回配送中心。
一、CVRP问题描述
1.1场景
单向:纯取货/纯送货;
单配送中心:只有一个配送中心/车场;
单车型:只考虑一种车型,
需求不可拆分:客户需求只能有一辆车满足;
车辆封闭:完成配送任务的车辆需回到配送中心;
车辆充足:不限制车辆数量,即配送车辆需求均能满足;
非满载:任意客户点的需求量小于车辆最大载重;
1.2要求
优化目标:最小化车辆启动成本和车辆行驶成本之和;
约束条件:车辆行驶距离约束,重量约束;
已知信息:配送中心位置、客户点位置、客户点需求、车辆最大载重、车辆最大行驶距离、车辆启动成本、车辆单位距离行驶成本;
二、CVRP数学模型
2.1符号定义

2.2数学模型

2.3参数设置
车辆启动成本 C0 =30,车辆单位距离行驶成本C1 =1
详见problem.py
三、遗传算法设计
3.1 染色体编码、解码
同TSP问题生成方式,以客户点(编号为1,2,3…)为自然数编码(不包含配送中心0)
解码:考虑车辆载重和行驶距离约束的8客户点染色体[8,4,1,5,2,3,6,7]解码为
【0,8,4,1,0】
【0,5,2,0】
【0,3,6,7,0】
3.2交叉变异
采用两点交叉、和2-opt变异,和TSP问题相同,见基于自适应遗传算法的TSP问题建模求解(Java)
四、基于遗传算法的CVRP建模求解(Python)
下载连接:https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_43276566/87554423
分为四个模块,populatioin.py、algorithm.py,problem.py 和程序运行接口run-cvrp.py。
完整代码如下:
import datetime
import heapq
import itertools
import time
import numpy as np
import math
from typing import Dict, List
from scipy import spatial
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
np.set_printoptions(
precision=2, # 显示到小数点后几位,默认是4
threshold=None, # 超过默认1000行数据,折叠显示
edgeitems=None, # 折叠显示前/后
linewidth=4000, # 换行字符长度
)
def timer(func):
def inner(*args, **kwargs):
start = time.time()
gbest = func(*args, **kwargs)
end = time.time()
print(f'程序运行时间:{round(end - start, 2)}s')
return gbest
return inner
class Population:
pop_size: int
def __init__(self, problem):
self.pop_size = 100 # 种群规模
self.problem = problem
self.chrom_matrix = np.empty(shape=(self.pop_size, 31), dtype=np.int64) # 种群染色体编码矩阵
self.phenMatrix = [] # 每条染色体的表现型
self.objV = [] # 目标函数值
self.fitV = [] # 适应度函数
def init_chrom(self):
"""
:return:初始化染色体
"""
chrom = np.arange(1, self.problem.num_customer)
np.random.shuffle(chrom)
return chrom
def initialize_pop(self):
"""初始化种群"""
# self.chrom_matrix = []
# for i in range(self.pop_size):
# chrom = self.init_chrom()
# self.chrom_matrix.append(chrom)
self.chrom_matrix = [self.init_chrom() for _ in range(self.pop_size)]
def decodePop(self):
for i in range(self.pop_size):
routes = self.decode_chrom(self.chrom_matrix[i])
self.phenMatrix.append(routes)
def decode_chrom(self, chrom: list):
problem = self.problem
capacity = 0
distance = 0
route = [0]
totalDist = 0
routes = []
i = 0
while i < len(chrom):
k = chrom[i]
if route == [0]:
# print(problem.distance, problem.vehMaxDis)
if problem.distance[0][k] < problem.vehicle_max_travel_distance:
distance += problem.distance[0][k]
capacity += problem.customer_list[k]["demand"]
route.append(k)
i += 1
else:
if distance + problem.distance[route[-1]][k] + problem.distance[k][
0] <= problem.vehicle_max_travel_distance and capacity + problem.customer_list[k]["demand"] <= problem.vehicle_capacity:
distance += problem.distance[route[-1]][k]
capacity += problem.customer_list[k]["demand"]
route.append(k)
i += 1
else:
l = route[-1]
distance += problem.distance[l][0]
route.append(0)
totalDist += distance
routes.append(route)
capacity = 0
distance = 0
route = [0]
route.append(0)
routes.append(route)
return routes
def __getitem__(self, item):
return self.chrom_matrix[item]
def __setitem__(self, key, value):
self.chrom_matrix[key] = value
def __str__(self):
s = "chrom"
for i in range(self.pop_size):
s + "%s\n".format(self.chrom_matrix[i])
print(self.chrom_matrix[i])
return s
def __repr__(self):
return self.__str__()
class CVRP:
def __init__(self, customer_list):
self.customer_list = customer_list
self.num_customer = len(customer_list)
self.distance = self.init_distance_matrix()
self.vehicle_capacity = 120
self.vehicle_max_travel_distance = 250
self.vehicle_use_cost = 30
self.vehicle_travel_cost = 1
def evaluate(self, pop: Population):
pop.decodePop()
c1: [] = self.calc_veh_travel_cost(pop)
c2: [] = self.calc_veh_use_cost(pop)
c1 = np.asarray(c1)
c2 = np.asarray(c2)
pop.objV = c1 + c2
pop.fitV = 1 / (0.5 * c1 + 0.5 * c2)
def init_distance_matrix(self):
customer_coord = [customer["coordinate"] for customer in self.customer_list]
return spatial.distance.cdist(customer_coord, customer_coord, 'euclidean')
def calc_route_distance(self, route: []):
route_distance = 0
for i, j in itertools.pairwise(route):
route_distance += self.distance[i][j]
i, j = route[-1], route[0]
route_distance += self.distance[i][j]
return route_distance
def calc_veh_travel_cost(self, pop):
a = []
for phen in pop.phenMatrix:
routes = phen
dist = self.calc_routes_distance(routes)
a.append(dist)
return a
def calc_routes_distance(self, routes: [[]]):
return sum([self.calc_route_distance(route) for route in routes])
def calc_veh_use_cost(self, pop):
a = []
for phen in pop.phenMatrix:
routes = phen
cost = len(routes) * self.vehicle_use_cost
a.append(cost)
return a
class GeneticAlgorithm:
def __init__(self, problem):
self.problem = problem # type:CVRP
self.currentGen = 0 # type: int
self.MAX_GEN = 5000 # type: int
self.pc = 0.8 # type: float
self.pm = 0.1 # type: float
self.history = {"obj": [], "solution": []} # type:Dict[str,List]
pass
def cross(self, chrom1: [], chrom2: []):
# i = np.random.randint(low=0, high=len(chrom1) - 3)
# j = i + 2
# chrom1 = chrom1.tolist()
# chrom2 = chrom2.tolist()
# key = chrom1[i:j]
# val = chrom2[i:j]
# duplicates = []
# for e in key:
# if e in val:
# duplicates.append(e)
# for e in duplicates:
# key.remove(e)
# val.remove(e)
# chrom1[i:j], chrom2[i:j] = chrom2[i:j], chrom1[i:j]
#
# for k in range(i):
# if chrom1[k] in val:
# chrom1[k] = key[val.index(chrom1[k])]
# if chrom2[k] in key:
# chrom2[k] = val[key.index(chrom2[k])]
# for l in range(j, len(chrom1)):
# if chrom1[l] in val:
# chrom1[l] = key[val.index(chrom1[l])]
# if chrom2[l] in key:
# chrom2[l] = val[key.index(chrom2[l])]
chrom_length = len(chrom1)
parent1 = chrom1
parent2 = chrom2
child = [None] * chrom_length
start = np.random.randint(low=0, high=chrom_length)
end = np.random.randint(low=start, high=chrom_length)
child[start:end] = parent1[start:end]
left = 0
right = end
for k in range(chrom_length):
if parent2[k] not in parent1[start:end]:
if left < start:
child[left] = parent2[k]
left += 1
elif right < self.problem.num_customer:
child[right] = parent2[k]
right += 1
return list(child)
def crossover(self, pop: Population):
for i in range(10, 100, 2):
if np.random.uniform(low=0, high=1) < self.pc:
chrom1 = pop[i]
chrom2 = pop[i + 1]
child = self.cross(chrom1, chrom2)
pop[i] = child
def selection(self, pop: Population):
off = Population(self.problem)
fitV = pop.fitV
if not isinstance(fitV, np.ndarray):
fitV = np.asarray(fitV)
elites_idx = heapq.nlargest(10, range(pop.pop_size), pop.fitV.__getitem__)
for i in range(0, 10):
off.chrom_matrix[i] = pop.chrom_matrix[elites_idx[i]]
# print(off)
ps = fitV / np.sum(fitV)
pc = np.cumsum(ps)
for i in range(10, 100):
r = np.random.random()
select = 0
for j in range(pop.pop_size):
if r < pc[j]:
select = j
break
off.chrom_matrix[i] = pop.chrom_matrix[select]
return off
def mutation(self, pop):
for i in range(10, 100):
if np.random.uniform(low=0, high=1) < self.pm:
r1, r2 = np.random.randint(low=0, high=len(pop.chrom_matrix[0]), size=2)
chrom = pop.chrom_matrix[i]
chrom[r1], chrom[r2] = chrom[r2], chrom[r1]
@timer
def run(self):
population = Population(self.problem)
population.initialize_pop()
self.problem.evaluate(population)
while not self.terminated(population):
offspring = self.selection(population)
self.crossover(offspring)
self.mutation(offspring)
self.problem.evaluate(offspring) # 计算目标函数值
population = offspring
return self.finish(population)
def terminated(self, population):
self.log(population)
if self.currentGen + 1 >= self.MAX_GEN:
return True
self.currentGen += 1
return False
def log(self, pop: Population):
idx = np.argmax(pop.fitV)
self.history["obj"].append(pop.objV[idx])
self.history["solution"].append(pop.phenMatrix[idx])
print("iter=%d obj=%.2f" % (self.currentGen, pop.objV[idx]))
def finish(self, pop: Population):
print("final solution:")
idx = np.argmax(pop.fitV)
routes = pop.phenMatrix[idx]
print(routes)
print("veh used:", len(routes))
self.draw(routes)
self.save(pop)
def save(self, pop: Population):
with open('final result.txt', 'a') as f:
idx = np.argmax(pop.fitV)
routes = pop.phenMatrix[idx]
f.write("veh used:%d\n" % len(routes))
f.write("%s\n" % routes)
f.write("%s\n" % pop.objV[idx])
def draw(self, routes):
customers = self.problem.customer_list
for route in routes:
X = []
Y = []
for customer_id in route:
x, y = customers[customer_id]["coordinate"]
X.append(x)
Y.append(y)
plt.plot(X, Y, '-', alpha=1, linewidth=1.2, zorder=1)
X = []
Y = []
for customer in customers:
if customer["customer_id"] == 0: continue
x, y = customer["coordinate"]
X.append(x)
Y.append(y)
plt.scatter(X, Y, marker='o', s=25, c='#000000', alpha=1, zorder=2)
depot_x, depot_y = customers[0]["coordinate"]
plt.scatter(depot_x, depot_y, marker='D', s=30, c='#0000FF', alpha=1, zorder=2)
for customer in customers:
x, y = customer["coordinate"]
customer_id = customer["customer_id"]
plt.text(x, y, f'{customer_id}')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
current_time = datetime.datetime.strftime(datetime.datetime.now(), '%Y%m%d%H%M%S')
plt.savefig("cg" + current_time, bbox_inches="tight")
plt.show()
plt.clf()
if __name__ == "__main__":
customer_list = [{'customer_id': 0, 'coordinate': (50, 50), 'demand': 0},
{'customer_id': 1, 'coordinate': (96, 24), 'demand': 16},
{'customer_id': 2, 'coordinate': (40, 5), 'demand': 11},
{'customer_id': 3, 'coordinate': (49, 8), 'demand': 6},
{'customer_id': 4, 'coordinate': (13, 7), 'demand': 10},
{'customer_id': 5, 'coordinate': (29, 89), 'demand': 7},
{'customer_id': 6, 'coordinate': (48, 30), 'demand': 12},
{'customer_id': 7, 'coordinate': (84, 39), 'demand': 16},
{'customer_id': 8, 'coordinate': (14, 47), 'demand': 6},
{'customer_id': 9, 'coordinate': (2, 24), 'demand': 16},
{'customer_id': 10, 'coordinate': (3, 82), 'demand': 8},
{'customer_id': 11, 'coordinate': (65, 10), 'demand': 14},
{'customer_id': 12, 'coordinate': (98, 52), 'demand': 7},
{'customer_id': 13, 'coordinate': (84, 25), 'demand': 16},
{'customer_id': 14, 'coordinate': (41, 69), 'demand': 3},
{'customer_id': 15, 'coordinate': (1, 65), 'demand': 22},
{'customer_id': 16, 'coordinate': (51, 71), 'demand': 18},
{'customer_id': 17, 'coordinate': (75, 83), 'demand': 19},
{'customer_id': 18, 'coordinate': (29, 32), 'demand': 1},
{'customer_id': 19, 'coordinate': (83, 3), 'demand': 14},
{'customer_id': 20, 'coordinate': (50, 93), 'demand': 8},
{'customer_id': 21, 'coordinate': (80, 94), 'demand': 12},
{'customer_id': 22, 'coordinate': (5, 42), 'demand': 4},
{'customer_id': 23, 'coordinate': (62, 70), 'demand': 8},
{'customer_id': 24, 'coordinate': (31, 62), 'demand': 24},
{'customer_id': 25, 'coordinate': (19, 97), 'demand': 24},
{'customer_id': 26, 'coordinate': (91, 75), 'demand': 2},
{'customer_id': 27, 'coordinate': (27, 49), 'demand': 10},
{'customer_id': 28, 'coordinate': (23, 15), 'demand': 15},
{'customer_id': 29, 'coordinate': (20, 70), 'demand': 2},
{'customer_id': 30, 'coordinate': (85, 60), 'demand': 14},
{'customer_id': 31, 'coordinate': (98, 85), 'demand': 9}]
cvrp = CVRP(customer_list)
ga = GeneticAlgorithm(cvrp)
ga.run()
求解结果如下:
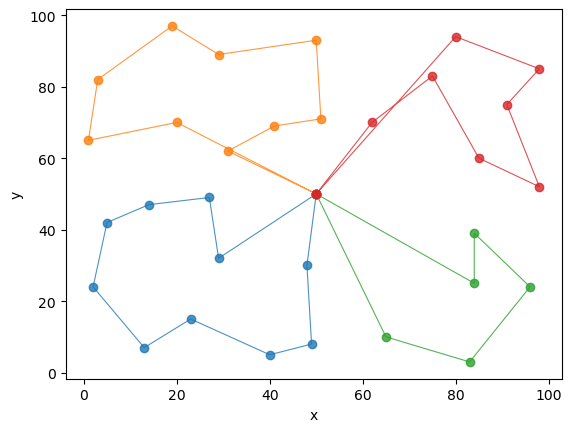
本文求解结果,图左veh used:4,obj=845.52,[[0, 27, 24, 8, 22, 9, 28, 4, 18, 6, 0], [0, 29, 15, 10, 25, 5, 20, 14, 0], [0, 2, 3, 11, 19, 1, 13, 7, 12, 30, 0], [0, 23, 26, 31, 21, 17, 16, 0]]
6中博客求解结果:图右,运算结果最优解为728.1, 路径为[0, 6, 19, 11, 3, 2, 28, 4, 9, 22, 8,
27, 18, 0], [0, 24, 29, 15, 10, 25, 5, 20, 16, 14, 0], [0, 23, 17, 21,
31, 26, 30, 12, 1, 13, 7, 0]

五、CVRP标准算例测试集
- https://blog.csdn.net/meiyoushui_/article/details/110367916
- http://iescm.com/vrp/instances/P1CVRP.asp
参考
版权声明:参考CSDN博主「_2312」原创文章进行复现,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/tangshishe/article/details/116197720
标签:
相关文章
最新发布
- 光流法结合深度学习神经网络的原理及应用(完整代码都有Python opencv)
- Python 图像处理进阶:特征提取与图像分类
- 大数据可视化分析-基于python的电影数据分析及可视化系统_9532dr50
- 【Python】入门(运算、输出、数据类型)
- 【Python】第一弹---解锁编程新世界:深入理解计算机基础与Python入门指南
- 华为OD机试E卷 --第k个排列 --24年OD统一考试(Java & JS & Python & C & C++)
- Python已安装包在import时报错未找到的解决方法
- 【Python】自动化神器PyAutoGUI —告别手动操作,一键模拟鼠标键盘,玩转微信及各种软件自动化
- Pycharm连接SQL Sever(详细教程)
- Python编程练习题及解析(49题)
点击排行
- 版本匹配指南:Numpy版本和Python版本的对应关系
- 版本匹配指南:PyTorch版本、torchvision 版本和Python版本的对应关系
- Anaconda版本和Python版本对应关系(持续更新...)
- Python 可视化 web 神器:streamlit、Gradio、dash、nicegui;低代码 Python Web 框架:PyWebIO
- 相关性分析——Pearson相关系数+热力图(附data和Python完整代码)
- Python与PyTorch的版本对应
- Windows上安装 Python 环境并配置环境变量 (超详细教程)
- Python pyinstaller打包exe最完整教程

