首页 > Python资料 博客日记
IDA Python 使用总结
2024-02-25 11:00:04Python资料围观387次
环境配置
切换 python 版本
运行 IDA 安装目录下的 idapyswitch.exe ,选择使用的 python 解释器。
在 PyCharm 中写 IDAPython 脚本
在 PyCharm 的设置→项目→Python解释器点击设置选择全部显示…
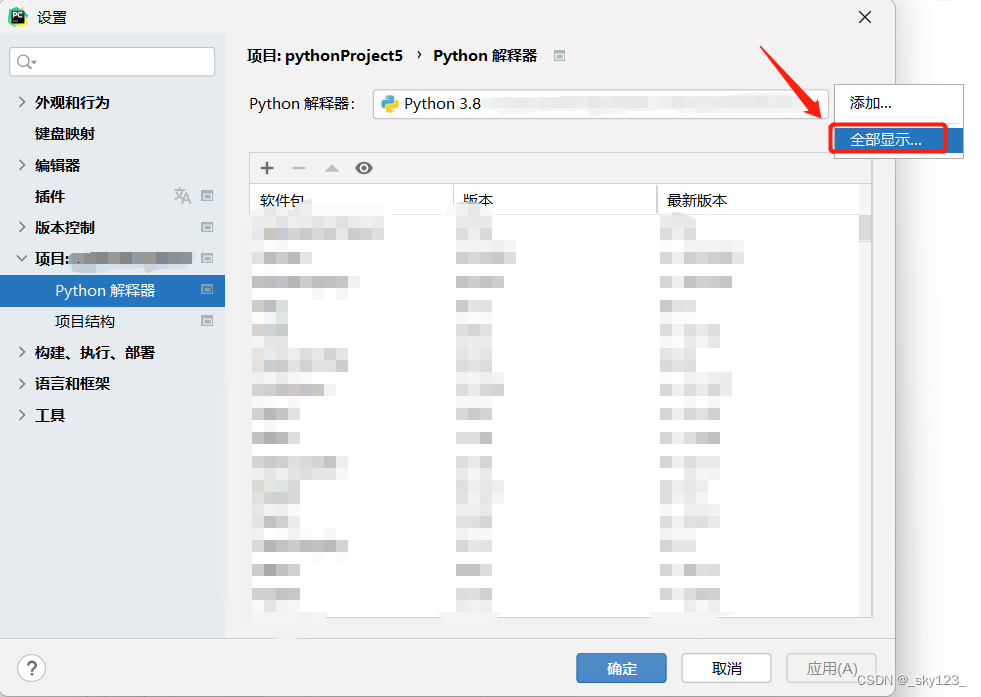
点击如下位置添加自定义路径

路径选择 IDA Pro 7.6\python\3 貌似 3 和 2 表示 Python3 和 Python2 。

之后就可以使用 PyCharm 的智能补全编写 IDAPython 程序了。
IDA Python 常用 API
常见模块
- IDC:封装IDA与IDC函数的兼容性模块
- idautils:高级实用的模块
- idaapi:允许访问更加底层的数据
获取地址
idc.here()或idc.get_screen_ea():取当前地址ida_ida.inf_get_min_ea():获取最小地址(可以使用的)ida_ida.inf_get_max_ea():获取最大地址(可以使用的)idc.read_selection_start():获取所选范围的起始地址idc.read_selection_end():获取所选范围的结束地址idc.get_name_ea_simple(name):获取名称对应的地址,如果获取不到则返回ida_idaapi.BADADDR。
获取地址处的值
idc.get_wide_byte(addr):以 1 字节为单位获取地址处的值idc.get_wide_word(addr):以 2 字节(字)的单位获取地址处的值idc.get_wide_dword(addr):以 4 字节的单位获取地址处的值idc.get_qword(addr):以 8 字节的单位获取地址处的值idc.get_bytes(addr, len):获取addr地址处len长度的数据idc.get_item_size(addr):获取addr地址处的数据大小,例如汇编指令长度。
修改地址处的值
ida_bytes.patch_byte(addr, value):修改addr地址的值为value,每次修改 1 个字节。ida_bytes.patch_word(addr, value):每次修改 2 个字节ida_bytes.patch_dword(addr, value):每次修改 4 个字节ida_bytes.patch_qword(addr, value):每次修改 8 个字节idc.patch_bytes(addr, data):在addr地址处写入data(bytes 类型数据)
修改地址处的类型
idc.del_items(addr):去除目标地址处数据的属性。idc.create_insn(addr):将目标地址处的数据设置为代码。有可能会失败,可以与ida_name.set_name(addr, '')配合来避免失败。
汇编指令操作
idc.GetDisasm(addr)或idc.generate_disasm_line(addr,flags):获取地址处的汇编语句,这里flags通常为 0 。idc.print_operand(addr,index):获取指定地址addr的汇编指令的第index个操作数(字符串形式),如果index索引超过操作数的个数则返回空字符串。下面简单举几个例子感受一下:汇编 inxex = 0 index = 1 pop raxrax‘’ mov [rsp+10h], rax[rsp+10h]raxcall $+5$+5‘’ add rax, 68FBhrax68FBhjz short loc_1400100CCloc_1400100CC‘’ popfq‘’ ‘’ retn‘’ ‘’ idc.get_operand_type(addr, index):获取操作数的类型。o_void (0):无效操作数,表示没有操作数。o_reg (1):寄存器操作数,表示一个寄存器。o_mem (2):内存操作数,表示一个内存地址。o_phrase (3):短语操作数,表示根据寄存器和偏移量计算的内存地址。o_displ (4):带偏移量的内存操作数,表示根据寄存器、偏移量和可选标志寄存器计算的内存地址。o_imm (5):立即数操作数,表示一个立即数值。o_far (6):远跳转操作数,表示一个远跳转地址。o_near (7):相对跳转操作数,表示一个相对于当前指令地址的跳转地址。
idc.get_operand_value(addr, index):获取指定索引操作数中的值。- 对于寄存器操作数 (
o_reg),返回寄存器的编号。 - 对于内存操作数 (
o_mem),返回内存地址的值。 - 对于立即数操作数 (
o_imm),返回立即数的值。 - 对于相对跳转操作数 (
o_near),返回跳转的地址。 - 对于其他特定于处理器的操作数类型,返回相应的值,具体含义需要参考相关文档。
- 对于寄存器操作数 (
idc.print_insn_mnem(addr):获取指定地址addr的汇编指令的操作指令(如 mov、add)。idc.next_head(addr):获取当前地址的汇编的下一条汇编的地址。idc.prev_head(addr):获取当前地址的汇编的上一条汇编的地址。
由于 IDA Python 没有有效的汇编功能且 idc.generate_disasm_line(addr,flags) 反汇编出的汇编代码与主流的反汇编器 keystone_engine 不通用,因此通常利用 keystone_engine 与 capstone 结合来实现汇编与反汇编功能。
from keystone import *
from capstone import *
asmer = Ks(KS_ARCH_X86, KS_MODE_64)
disasmer = Cs(CS_ARCH_X86, CS_MODE_64)
def disasm(machine_code, addr=0):
l = ""
for i in disasmer.disasm(machine_code, addr):
l += "{:8s} {};\n".format(i.mnemonic, i.op_str)
return l.strip('\n')
def asm(asm_code, addr=0):
l = b''
for i in asmer.asm(asm_code, addr)[0]:
l += bytes([i])
return l
段操作
idc.get_segm_name(addr):获取地址addr所在段的名字(参数为当前的地址)。idc.get_segm_start(addr):获取地址addr所在段的开始地址idc.get_segm_end(addr):获取地址addr所在段的结束地址idc.get_first_seg():获取第一个段的地址idc.get_next_seg(addr):获取地址大于addr的第一个段的起始地址idautil.Segments():返回一个列表记录所有段的地址
遍历所有的段
import idc
import idaapi
import idautils
for seg_addr in idautils.Segments():
segname = idc.get_segm_name(seg_addr)
segstart = idc.get_segm_start(seg_addr)
segend = idc.get_segm_end(seg_addr)
print("段名:" + segname + " 起始地址:" + hex(segstart) + " 结束地址:" + hex(segend));
函数操作
idautils.Functions(startaddr,endaddr):获取指定地址之间的所有函数idc.get_func_name(addr):获取指定地址所在函数的函数名get_func_cmt(addr, repeatable):获取函数的注释repeatable:0 是获取常规注释,1 是获取重复注释。
idc.set_func_cmt(ea, cmt, repeatable):设置函数注释idc.choose_func(title):弹出选择框要求用户进行选择函数,返回值为用户选择的函数的地址,若直接关闭选择框则返回值为 0xffffffffffffffff 。idc.get_func_off_str(addr):寻找函数结尾,如果函数存在则返回结尾地址,否则返回BADADDR。ida_funcs.set_func_end(addr, newend):设置函数结尾为newendida_funcs.set_func_start(addr, newstart):设置函数开头为newstartidc.set_name(addr, name):设置地址处的名字为nameidc.get_prev_func(addr):获取addr所在函数的前一个函数的地址idc.get_next_func(addr):获取addr所在函数的后一个函数的地址ida_funcs.add_func(addr):在addr地址创建函数
遍历 .text 段内的所有函数
import idc
import idaapi
import idautils
for seg in idautils.Segments():
segname = idc.get_segm_name(seg)
segstart = idc.get_segm_start(seg)
segend = idc.get_segm_end(seg)
if (segname == '.text'):
for funcaddr in Functions(segstart,segend):
funname = idc.get_func_name(funcaddr)
funend = idc.find_func_end(funcaddr)
funnext = idc.get_next_func(funcaddr)
funnextname = idc.get_func_name(funnext)
print("当前函数名: " + funname + "当前结束地址: " + hex(funend) +"下一个函数地址: " + hex(funnext) + "下一个函数名: " + funnextname)
数据查询
idc.find_binary(ea, flag, searchstr, radix=16):查找二进制找到返回地址没找到返回 -1 (BADADDR)flags:搜索标志。SEARCH_DOWN:向下搜索SEARCH_UP:向上搜索SEARCH_NEXT:获取下一个找到的对象。SEARCH_CASE:指定大小写敏感度SEARCH_UNICODE:搜索 Unicode 字符串。
searchstr:要搜索的二进制模式或指令序列,例如E8 00 00 00 00 58。radix:模式中数字的基数,默认为十六进制(16)。
ida_search.find_data(ea, sflag):从ea开始寻找下一个数据地址ida_search.find_code(ea, sflag):从ea开始寻找下一个代码地址ida_kernwin.jumpto(ea):跳转到ea位置
数据校验函数
ida_bytes.get_full_flags(ea):获取ea地址处的标志,其中包含了ea地址处的相关属性。ida_bytes.is_code(f):判断是否为代码,其中f为获取的标志位。ida_bytes.is_data(f):判断是否为数据,其中f为获取的标志位。ida_bytes.del_items(ea):删除ea地址处的类型。
交叉引用
idautils.CodeRefsTo(ea, flow):获取引用ea地址处的内容的地址。其中flow表示代码顺序执行的是否计算在内,比如如果flow = True那么认为当前指令的上一条指令引用了当前指令。idautils.CodeRefsFrom(ea, flow):ea地址处的代码引用了何处的代码。idautils.DataRefsTo(ea):获取引用ea地址处的内容的地址。idautils.DataRefsFrom(ea):ea地址处的代码引用了何处的数据。
去混淆
基础理论
程序的结构
我们可以认为一个程序的代码结构如下图所示:
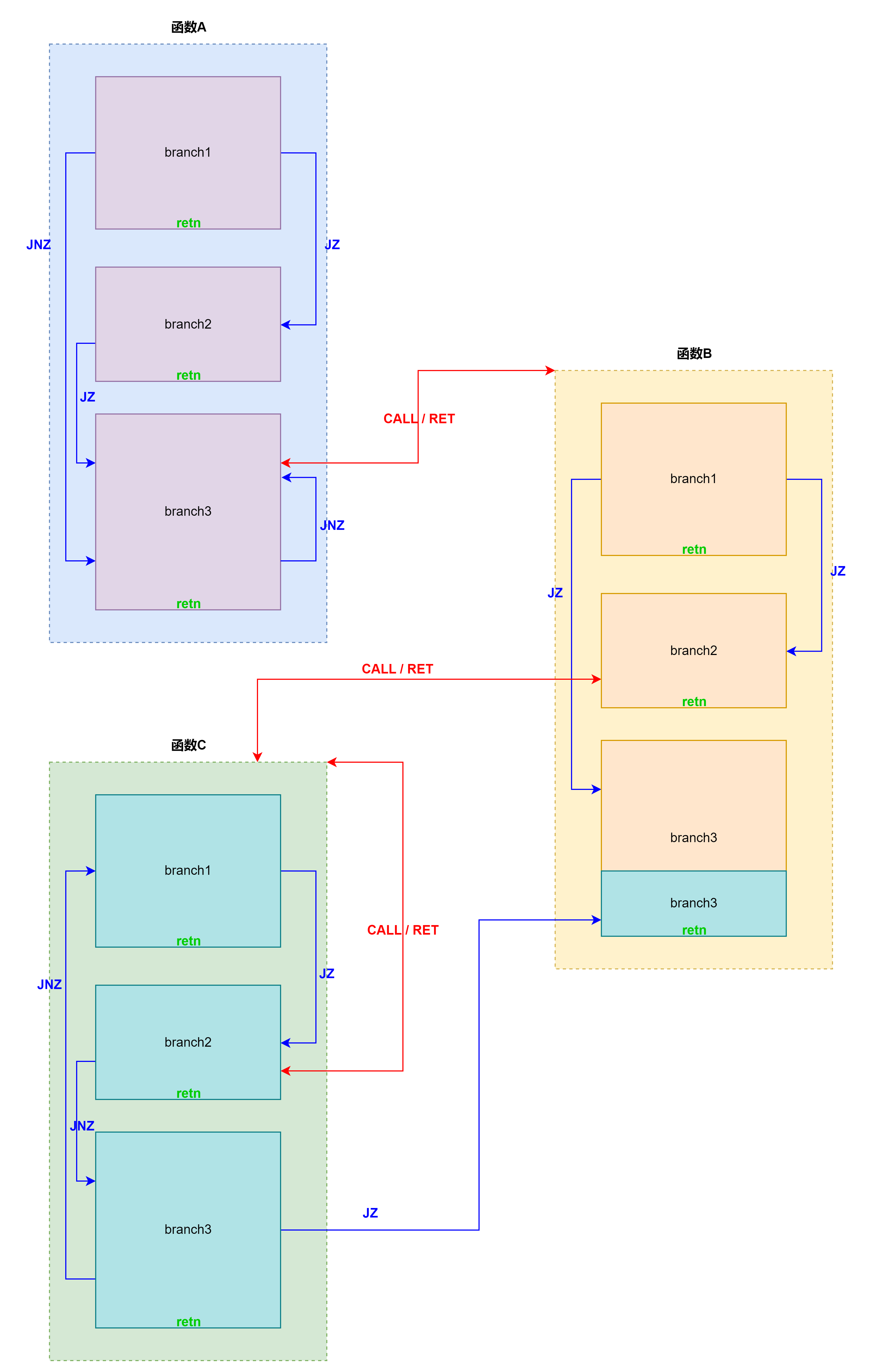
一个程序由多个函数(function)组成,而每个函数由多个分支(branch)组成,对于函数和分支我们做如下定义:
- 函数:从 CALL 指令跳转到的代码开始,在不通过 CALL 指令跳转的前提下能访问到的所有代码。
- 分支:通过 JCC 跳转到的代码开始,直到以 RET 结尾或者跳转到已分析过的分支的代码块。
因此去混淆的时候我们可以有如下代码框架,即先 bfs 函数,然后在每个函数内部再 bfs 所有分支。在 bfs 的过程中将已去混淆的代码拼接起来。这样做的好处是同一个函数的代码尽可能放在一起,ida 在反编译的时候容易识别。
func_queue = Queue()
func_queue.put(entry_point)
while not func_queue.empty():
func_address = func_queue.get()
branch_queue = Queue()
branch_queue.put(func_address)
while not branch_queue.empty():
branch_address = branch_queue.get()
... # 去混淆代码
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'call': # CALL function
func_queue.put(call_target)
elif idc.print_insn_mnem(ea)[0] == 'j' # JCC branch
branch_queue.put(jcc_target)
... # 重定位代码
代码重定位
代码的位置移动时,原本的 CALL 和 JCC 等跳转指令要想跳转到原来的地方需要进行指令修正,这个可以借助 keystone-engine 和 capstone 来完成。
def mov_code(ea, new_code_ea):
return asm(disasm(idc.get_bytes(ea, idc.get_item_size(ea)), ea), new_code_ea)
然而在完成去混淆后程序中的绝大多数代码都移动了位置,因此程序中所有的 CALL 和 JCC 等跳转指令跳转的地址需要进行修正,也就是重定位。
对于指令修正我们可以通过并查集来维护。
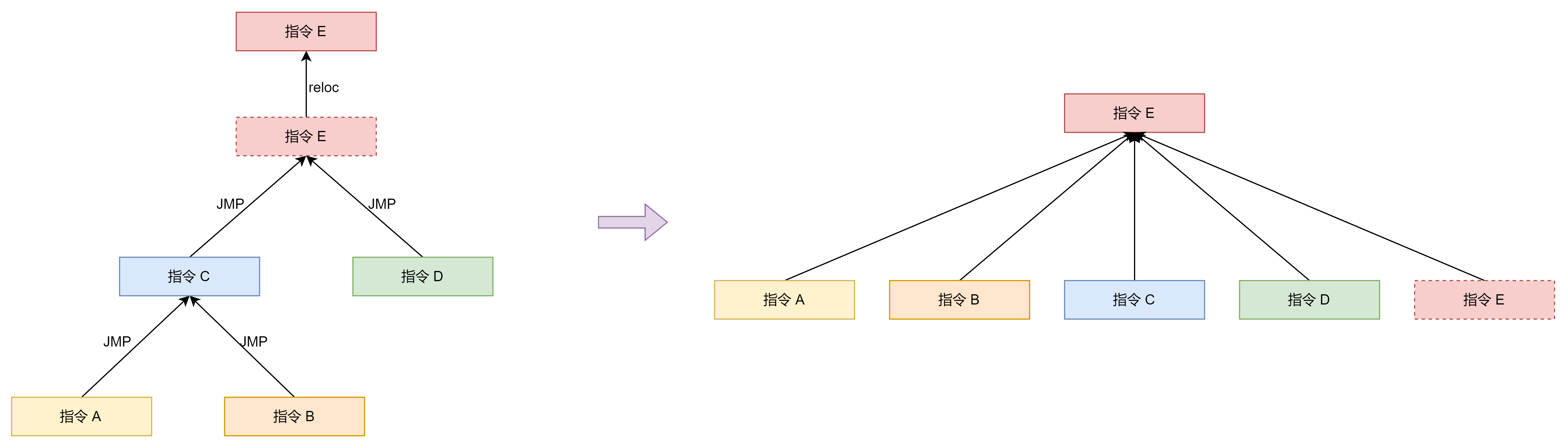
一个程序的跳转指令可以看做是上图左边的结构。即存在一个跳转指令跳转到另一个跳转指令的情况。通过并查集我们可以将指令 A,B,C,D,E 的真实地址都修正为指令 E 的真实地址。
在使用并查集维护重定位的时候需要注意以下几点:
- 上图中的指令 E 需要确保不存在指令复用的情况。因为有的代码混淆会将程序拆分成指令后放到一个巨大的 switch 中,然后通过在 switch 中查找依次执行指令。这种情况会造成一条指令在不同的分支中都会使用,如果此时我们用并查集维护就会把该指令重定位到其中一个使用该指令的地址,但实际上该指令还会在其他地址出现,这就造成了程序可能会跳转到错误的分支上。对于这种情况我们需要重定位查找 switch 的代码到去混淆的代码上,而不是重定位 switch 中的具体指令,这样就保证一一对应了。
- 在上图的结构中我们可以发现,只有连接根节点的边是重定位的边,其余的边都是跳转的边。因为在跳转的时候我们不需要关心中间的跳转指令在哪里,而是需要关心最终跳转到的位置的真实地址。因此在并查集合并的时候如果是一条 JMP 指令就需要将该指令的重定位后的实际地址合并到指令的原本地址,然后将指令的原本地址合并到指令的跳转地址,否则将该指令的原本地址合并到指令的重定位后的实际地址。这样在并查集路径压缩之后每一个跳转指令跳转地址都被重定位到非 JMP 指令的实际地址。
例题:强网杯2022 find_basic
观察发现程序由下面的代码块构成:
.text:000048F4 pushf
.text:000048F5 pusha
.text:000048F6 mov cl, 3Fh ; '?'
.text:000048F8 call sub_44FA
.text:000048F8
.text:000048FD pop eax
分析该代码块的执行过程,发现本质是在一个 switch 中查找实际指令。该代码块可由 lea ecx, [esp+4] 指令代替。

首先,我们需要将程序中的代码块提取出来,然后记录几个有用的信息:
start_ea:代码块的起始地址end_ea:代码块的结束地址imm:在 switch 中查找指令用的立即数reg:存放立即数用的寄存器call_target:调用的 switch 函数
在提取代码块的有效信息的同时也可以检测该代码块是否有效,因此分析发现程序中会在代码块直接插入一些有实际功能的代码。
class Block:
def __init__(self, start_ea, end_ea, imm, reg, call_target):
self.start_ea = start_ea
self.end_ea = end_ea
self.imm = imm
self.reg = reg
self.call_target = call_target
def get_block(start_ea):
global imm, reg, call_target
mnem_list = ['pushf', 'pusha', 'mov', 'call', 'pop']
ea = start_ea
for i in range(5):
mnem = idc.print_insn_mnem(ea)
assert mnem == mnem_list[i]
if mnem == 'mov':
imm = idc.get_operand_value(ea, 1)
reg = idc.print_operand(ea, 0)
elif mnem == 'call':
call_target = idc.get_operand_value(ea, 0)
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
return Block(start_ea, ea, imm, reg, call_target)
在提取出代码块之后利用提取到的有效信息可以在 call_target 中查找代码块对应的实际代码。这里有几个特殊情况:
- 一般情况在 cmp 判断找到对应位置后会依次执行 jnz,popa,popf 三条指令,然后后面紧跟着代码块对应的实际代码。然而想下面这种情况,在执行完 popf 后面紧跟着 pusha 而不是代码块对应的实际代码,简单分析一下发现这种情况代码块对应的实际代码为 retn 。这种情况需要返回 True 表示一个 branch 的结束。
.text:000045CC popa .text:000045CD popf .text:000045CE pushf .text:000045CF pusha .text:000045D0 call dec_index .text:000045D0 .text:000045D5 popa .text:000045D6 popf .text:000045D7 retn - 通常认为代码块对应的实际代码的结束标志为一个 jmp 指令,但是有的地方在 jmp 之后还会执行几条有效指令,因此判断实际代码的结束标志应当是 pushf 。
def get_real_code(block, new_code_ea):
ea = block.call_target
while True:
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'cmp':
reg = idc.print_operand(ea, 0)
imm = idc.get_operand_value(ea, 1)
if reg == block.reg and imm == block.imm:
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
break
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
# 在 cmp 判断找到对应位置后会依次执行 jnz,popa,popf 三条指令
assert idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'jnz'
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
assert idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'popa'
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
assert idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'popf'
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'pushf': # 第一种特殊情况,实际是 ret 指令。
return True, asm('ret')
new_code = b''
while True:
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'jmp': # 第二种特殊情况,跳转过去可能还会有几条实际功能指令。
jmp_ea = idc.get_operand_value(ea, 0)
if idc.print_insn_mnem(jmp_ea) == 'pushf':
break
ea = jmp_ea
else:
code = mov_code(ea, new_code_ea)
new_code += code
new_code_ea += len(code)
ea += get_item_size(ea)
return False, new_code
这里涉及到了维护重定位的并查集 RelocDSU ,对应代码如下。在 get 函数中如果遇到了 jmp 指令且操作数是立即数就路径压缩到跳转的地址,直到地址在 .got.plt 或者指令不是 jmp 指令。另外判断是否是已处理代码是根据地址对应的最终地址是否不在 .text 段。
class RelocDSU:
def __init__(self):
self.reloc = {}
def get(self, ea):
if ea not in self.reloc:
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'jmp' and idc.get_operand_type(ea, 0) != idc.o_reg:
jmp_ea = idc.get_operand_value(ea, 0)
if idc.get_segm_name(jmp_ea) == '.got.plt':
self.reloc[ea] = ea
return self.reloc[ea], False
self.reloc[ea], need_handle = self.get(idc.get_operand_value(ea, 0))
return self.reloc[ea], need_handle
else:
self.reloc[ea] = ea
if self.reloc[ea] != ea: self.reloc[ea] = self.get(self.reloc[ea])[0]
return self.reloc[ea], idc.get_segm_name(self.reloc[ea]) == '.text'
def merge(self, ea, reloc_ea):
self.reloc[self.get(ea)[0]] = self.get(reloc_ea)[0]
reloc = RelocDSU()
接下来就是考虑如何提取出一个 branch 的代码了。前面提到过程序中会在代码块直接插入一些有实际功能的代码,因此需要借助 try:...except:... 和 assert 来处理。除此之外这里还有几个特殊情况:
- 程序中的 0x900 和 0x435c 处分别有一个获取返回地址 eip 到 ebx 和 eax 的函数,程序借助这两个函数来访问全局变量实现地址无关代码,然而重定位后代码地址改变,因此这里需要将其修正为
mov reg, xxx。 - 需要根据程序中的 jmp 指令来决定下一步需要去混淆的代码位置,这里需要判断 jmp 后面跟的是否是立即数,另外需要判断 jmp 到的代码是否是已经处理过的代码。
- 并查集合并的时候如果是代码块,需要将代码块的地址合并到代码块对应指令的实际重定位后的地址;如果不是代码块如果是 jmp 指令且操作数是立即数,需要将 jmp 指令和该指令的重定位后的实际地址合并到指令的原本地址,然后将指令的原本地址合并到指令的跳转地址,否则将该指令的地址合并到重定位后的地址。
def handle_one_branch(branch_address, new_code_ea):
new_code = b''
ea = branch_address
while True:
try:
block = get_block(ea)
is_ret, real_code = get_real_code(block, new_code_ea)
reloc.merge(ea, new_code_ea)
ea = block.end_ea
new_code_ea += len(real_code)
new_code += real_code
if is_ret: break
except:
get_eip_func = {0x900: 'ebx', 0x435c: 'eax'}
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'call' and get_operand_value(ea, 0) in get_eip_func:
reloc.merge(ea, new_code_ea)
real_code = asm('mov %s, 0x%x' % (get_eip_func[get_operand_value(ea, 0)], ea + 5), new_code_ea)
else:
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'jmp' and idc.get_operand_type(ea, 0) != idc.o_reg:
reloc.merge(new_code_ea, ea)
else:
reloc.merge(ea, new_code_ea)
real_code = mov_code(ea, new_code_ea)
new_code += real_code
if real_code == asm('ret'): break
new_code_ea += len(real_code)
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'jmp' and idc.get_operand_type(ea, 0) != idc.o_reg: # jmp reg is a swtich
jmp_ea = idc.get_operand_value(ea, 0)
if reloc.get(jmp_ea)[1] == False: break # 跳回之前的代码说明是个循环
ea = reloc.get(jmp_ea)[0]
else:
ea += get_item_size(ea)
return new_code
能够处理 branch 后,我们就可以 bfs 依次处理所有的 function 和 branch 了,这里还有几个特殊情况:
- 0x4148 地址处的函数中有一个 switch ,由于是通过跳转表跳转,去混淆脚本分析不到跳转的分支,因此需要读取跳转表找到跳转的 branch 然后添加到
branch_queue中。 - 寻找新的 branch 时需要判断 jcc 的操作数类型是否是立即数。
func_queue = Queue()
func_queue.put(entry_point)
while not func_queue.empty():
func_address = func_queue.get()
if reloc.get(func_address)[1] == False: continue
reloc.merge(func_address, new_code_ea)
branch_queue = Queue()
branch_queue.put(func_address)
if func_address == 0x4148: # 特判 0x4148 地址处的函数,读取跳转表。
assert new_code_ea == 0x963d0
for eax in range(0x20):
jmp_target = (ida_bytes.get_dword(jmp_table[0] + eax * 4) + jmp_table[1]) & 0xFFFFFFFF
new_jmp_target, need_handle = reloc.get(jmp_target)
if need_handle: branch_queue.put(jmp_target)
while not branch_queue.empty():
branch_address = branch_queue.get()
new_code = handle_one_branch(branch_address, new_code_ea)
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(new_code_ea, new_code)
# 当前 branch 去完混淆之后需要遍历代码找到 call 和 jmp 指令从而找到其他的 function 和 branch 。
ea = new_code_ea
while ea < new_code_ea + len(new_code):
idc.create_insn(ea)
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'call':
call_target, need_handle = reloc.get(get_operand_value(ea, 0))
if need_handle: func_queue.put(call_target)
elif idc.print_insn_mnem(ea)[0] == 'j' and idc.get_operand_type(ea, 0) != idc.o_reg:
jcc_target, need_handle = reloc.get(get_operand_value(ea, 0))
if need_handle == True:
branch_queue.put(jcc_target)
ea += get_item_size(ea)
new_code_ea += len(new_code)
在完成代码去混淆之后需要对代码进行重定位,重定位的时候需要注意 jmp 指令长度的变化。
ea = new_code_start
while ea < new_code_ea:
idc.create_insn(ea)
mnem = idc.print_insn_mnem(ea)
if mnem == 'call':
call_target, need_handle = reloc.get(get_operand_value(ea, 0))
assert need_handle == False
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(ea, asm('call 0x%x' % (call_target), ea))
elif mnem[0] == 'j' and idc.get_operand_type(ea, 0) != idc.o_reg:
jcc_target, need_handle = reloc.get(get_operand_value(ea, 0))
assert need_handle == False
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(ea, asm('%s 0x%x' % (mnem, jcc_target), ea).ljust(idc.get_item_size(ea), b'\x90'))
elif mnem == 'pushf':
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(ea, b'\x90' * 9)
ea += 9
continue
ea += get_item_size(ea)
最后去混淆后的 switch 不能被 ida 正常识别出来,具体原因是前面获取返回地址 eip 的函数被 patch 成了 mov reg, xxx 指令,导致其与编译器默认编译出的汇编不同(程序开启了 PIE,直接访问跳转表的地址 ida 不能正确识别),因此需要将这里的代码重新 patch 回去。
同时为了不影响原本程序中的数据,这里我将修复的跳转表放到了其他位置。另外还有两个字符串全局变量也移动到了正确位置。
new_jmp_table = (0xA6000 - 0x2D54, 0xA6000)
# 移动并修复跳转表
for eax in range(0x20):
jmp_target = (ida_bytes.get_dword(jmp_table[0] + eax * 4) + jmp_table[1]) & 0xFFFFFFFF
new_jmp_target, need_handle = reloc.get(jmp_target)
assert need_handle == False
ida_bytes.patch_dword(new_jmp_table[0] + eax * 4, (new_jmp_target - new_jmp_table[1]) & 0xFFFFFFFF)
need_patch_addr = 0x963D7
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(need_patch_addr, asm('call 0x900;add ebx, 0x%x' % (new_jmp_table[1] - (need_patch_addr + 5)), need_patch_addr)) # 修复指令
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(new_jmp_table[1] - 0x2d7a, ida_bytes.get_bytes(jmp_table[1] - 0x2d7a, 0x26)) # 复制字符串到正确位置
最终去混淆脚本如下:
from queue import *
import ida_bytes
from idc import *
import idc
from keystone import *
from capstone import *
asmer = Ks(KS_ARCH_X86, KS_MODE_32)
disasmer = Cs(CS_ARCH_X86, CS_MODE_32)
def disasm(machine_code, addr=0):
l = ""
for i in disasmer.disasm(machine_code, addr):
l += "{:8s} {};\n".format(i.mnemonic, i.op_str)
return l.strip('\n')
def asm(asm_code, addr=0):
l = b''
for i in asmer.asm(asm_code, addr)[0]:
l += bytes([i])
return l
def print_asm(ea):
print(disasm(idc.get_bytes(ea, idc.get_item_size(ea)), ea))
class RelocDSU:
def __init__(self):
self.reloc = {}
def get(self, ea):
if ea not in self.reloc:
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'jmp' and idc.get_operand_type(ea, 0) != idc.o_reg:
jmp_ea = idc.get_operand_value(ea, 0)
if idc.get_segm_name(jmp_ea) == '.got.plt':
self.reloc[ea] = ea
return self.reloc[ea], False
self.reloc[ea], need_handle = self.get(idc.get_operand_value(ea, 0))
return self.reloc[ea], need_handle
else:
self.reloc[ea] = ea
if self.reloc[ea] != ea: self.reloc[ea] = self.get(self.reloc[ea])[0]
return self.reloc[ea], idc.get_segm_name(self.reloc[ea]) == '.text'
def merge(self, ea, reloc_ea):
self.reloc[self.get(ea)[0]] = self.get(reloc_ea)[0]
reloc = RelocDSU()
class Block:
def __init__(self, start_ea, end_ea, imm, reg, call_target):
self.start_ea = start_ea
self.end_ea = end_ea
self.imm = imm
self.reg = reg
self.call_target = call_target
def mov_code(ea, new_code_ea):
return asm(disasm(idc.get_bytes(ea, idc.get_item_size(ea)), ea), new_code_ea)
def get_real_code(block, new_code_ea):
ea = block.call_target
while True:
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'cmp':
reg = idc.print_operand(ea, 0)
imm = idc.get_operand_value(ea, 1)
if reg == block.reg and imm == block.imm:
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
break
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
# 在 cmp 判断找到对应位置后会依次执行 jnz,popa,popf 三条指令
assert idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'jnz'
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
assert idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'popa'
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
assert idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'popf'
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'pushf': # 第一种特殊情况,实际是 ret 指令。
return True, asm('ret')
new_code = b''
while True:
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'jmp': # 第二种特殊情况,跳转过去可能还会有几条实际功能指令。
jmp_ea = idc.get_operand_value(ea, 0)
if idc.print_insn_mnem(jmp_ea) == 'pushf':
break
ea = jmp_ea
else:
code = mov_code(ea, new_code_ea)
new_code += code
new_code_ea += len(code)
ea += get_item_size(ea)
return False, new_code
def get_block(start_ea):
global imm, reg, call_target
mnem_list = ['pushf', 'pusha', 'mov', 'call', 'pop']
ea = start_ea
for i in range(5):
mnem = idc.print_insn_mnem(ea)
assert mnem == mnem_list[i]
if mnem == 'mov':
imm = idc.get_operand_value(ea, 1)
reg = idc.print_operand(ea, 0)
elif mnem == 'call':
call_target = idc.get_operand_value(ea, 0)
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
return Block(start_ea, ea, imm, reg, call_target)
def handle_one_branch(branch_address, new_code_ea):
new_code = b''
ea = branch_address
while True:
try:
block = get_block(ea)
is_ret, real_code = get_real_code(block, new_code_ea)
reloc.merge(ea, new_code_ea)
ea = block.end_ea
new_code_ea += len(real_code)
new_code += real_code
if is_ret: break
except:
get_eip_func = {0x900: 'ebx', 0x435c: 'eax'}
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'call' and get_operand_value(ea, 0) in get_eip_func:
reloc.merge(ea, new_code_ea)
real_code = asm('mov %s, 0x%x' % (get_eip_func[get_operand_value(ea, 0)], ea + 5), new_code_ea)
else:
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'jmp' and idc.get_operand_type(ea, 0) != idc.o_reg:
reloc.merge(new_code_ea, ea)
else:
reloc.merge(ea, new_code_ea)
real_code = mov_code(ea, new_code_ea)
new_code += real_code
if real_code == asm('ret'): break
new_code_ea += len(real_code)
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'jmp' and idc.get_operand_type(ea, 0) != idc.o_reg: # jmp reg is a swtich
jmp_ea = idc.get_operand_value(ea, 0)
if reloc.get(jmp_ea)[1] == False: break # 跳回之前的代码说明是个循环
ea = reloc.get(jmp_ea)[0]
else:
ea += get_item_size(ea)
return new_code
def solve():
entry_point = 0x48F4
new_code_start = 0x96150
new_code_ea = new_code_start
jmp_table = (0x892ac, 0x8c000) # [0x8c000 + (eax>>2) - 0x2d54] + 0x8c000
for _ in range(0x10000): idc.del_items(new_code_ea + _)
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(new_code_ea, 0x10000 * b'\x90')
func_queue = Queue()
func_queue.put(entry_point)
while not func_queue.empty():
func_address = func_queue.get()
if reloc.get(func_address)[1] == False: continue
reloc.merge(func_address, new_code_ea)
branch_queue = Queue()
branch_queue.put(func_address)
if func_address == 0x4148: # 特判 0x4148 地址处的函数,读取跳转表。
assert new_code_ea == 0x963d0
for eax in range(0x20):
jmp_target = (ida_bytes.get_dword(jmp_table[0] + eax * 4) + jmp_table[1]) & 0xFFFFFFFF
new_jmp_target, need_handle = reloc.get(jmp_target)
if need_handle: branch_queue.put(jmp_target)
while not branch_queue.empty():
branch_address = branch_queue.get()
new_code = handle_one_branch(branch_address, new_code_ea)
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(new_code_ea, new_code)
# 当前 branch 去完混淆之后需要遍历代码找到 call 和 jmp 指令从而找到其他的 function 和 branch 。
ea = new_code_ea
while ea < new_code_ea + len(new_code):
idc.create_insn(ea)
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'call':
call_target, need_handle = reloc.get(get_operand_value(ea, 0))
if need_handle: func_queue.put(call_target)
elif idc.print_insn_mnem(ea)[0] == 'j' and idc.get_operand_type(ea, 0) != idc.o_reg:
jcc_target, need_handle = reloc.get(get_operand_value(ea, 0))
if need_handle == True:
branch_queue.put(jcc_target)
ea += get_item_size(ea)
new_code_ea += len(new_code)
ea = new_code_start
while ea < new_code_ea:
idc.create_insn(ea)
mnem = idc.print_insn_mnem(ea)
if mnem == 'call':
call_target, need_handle = reloc.get(get_operand_value(ea, 0))
assert need_handle == False
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(ea, asm('call 0x%x' % (call_target), ea))
elif mnem[0] == 'j' and idc.get_operand_type(ea, 0) != idc.o_reg:
jcc_target, need_handle = reloc.get(get_operand_value(ea, 0))
assert need_handle == False
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(ea, asm('%s 0x%x' % (mnem, jcc_target), ea).ljust(idc.get_item_size(ea), b'\x90'))
elif mnem == 'pushf':
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(ea, b'\x90' * 9)
ea += 9
continue
ea += get_item_size(ea)
new_jmp_table = (0xA6000 - 0x2D54, 0xA6000)
# 移动并修复跳转表
for eax in range(0x20):
jmp_target = (ida_bytes.get_dword(jmp_table[0] + eax * 4) + jmp_table[1]) & 0xFFFFFFFF
new_jmp_target, need_handle = reloc.get(jmp_target)
assert need_handle == False
ida_bytes.patch_dword(new_jmp_table[0] + eax * 4, (new_jmp_target - new_jmp_table[1]) & 0xFFFFFFFF)
need_patch_addr = 0x963D7
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(need_patch_addr, asm('call 0x900;add ebx, 0x%x' % (new_jmp_table[1] - (need_patch_addr + 5)), need_patch_addr)) # 修复指令
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(new_jmp_table[1] - 0x2d7a, ida_bytes.get_bytes(jmp_table[1] - 0x2d7a, 0x26)) # 复制字符串到正确位置
for _ in range(0x10000): idc.del_items(new_code_ea + _)
idc.jumpto(new_code_start)
ida_funcs.add_func(new_code_start)
print("finish")
solve()
例题:SUSCTF2022 tttree
首先将 0x140010074 ,0x140017EFA ,140018C67 起始处的数据转换为汇编。
观察汇编,发现很多代码块之间相互跳转,因此先按照 retn 划分代码块。通过对代码块的观察,发现这些代码块按照 call $+5;pop rax(即 E8 00 00 00 00 58 ) 的出现次数可以分为三种:
-
出现 0 次:

本质上是其它操作+retn。 -
出现 1 次:
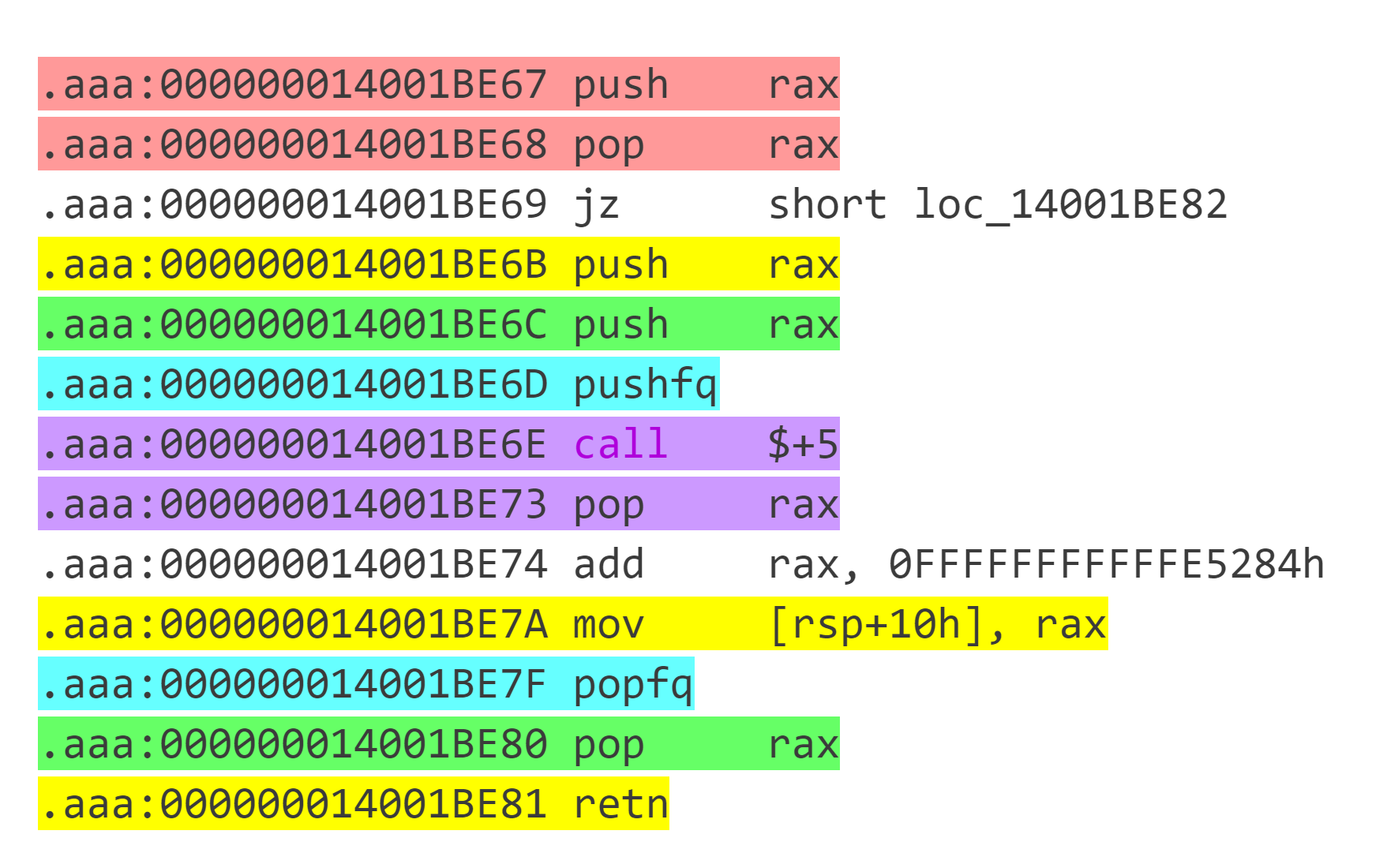
这种代码块本质为其它操作+jmp target,注意其它操作中可能包含 branch 。 -
出现 2 次:
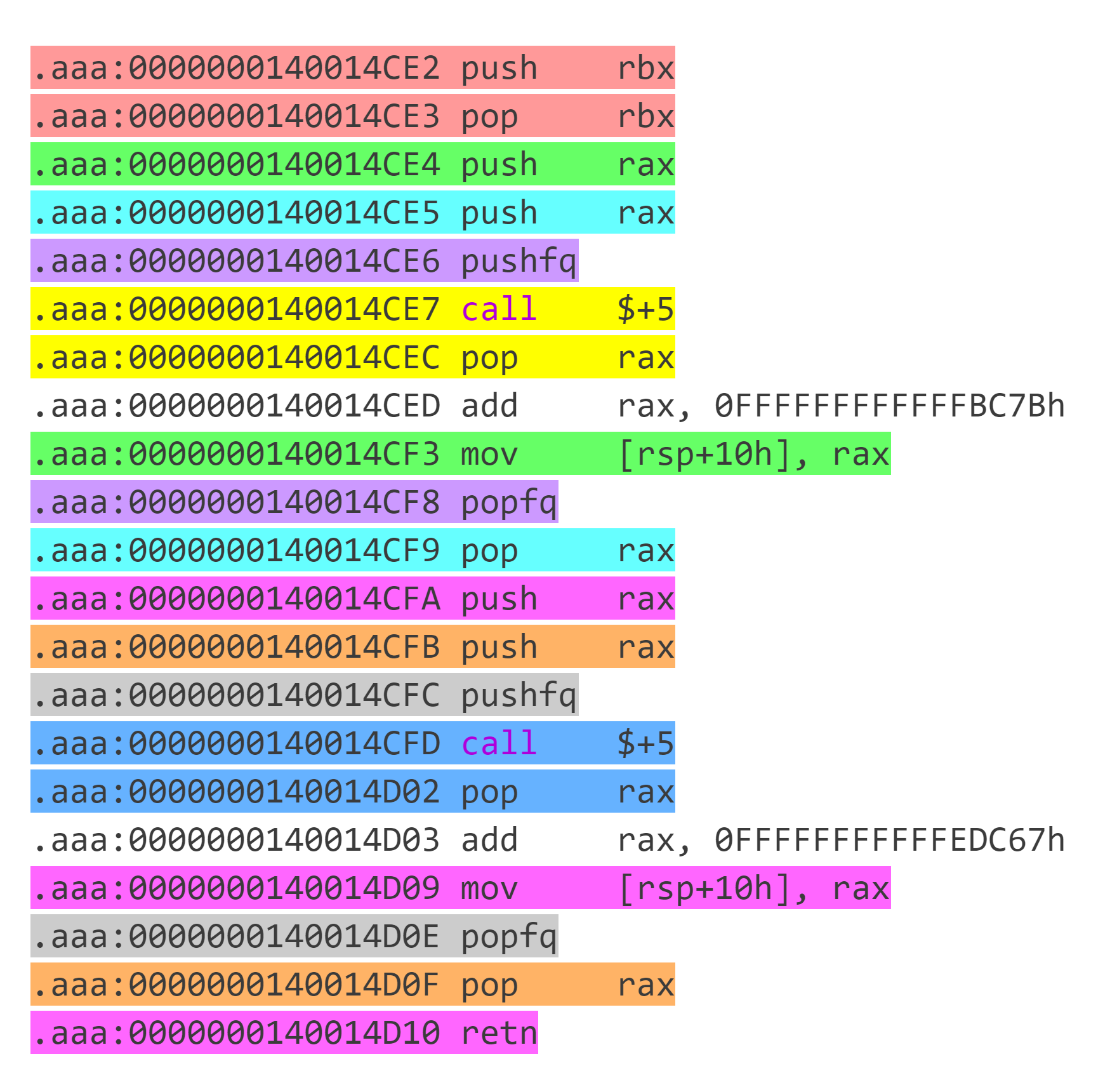
这个可以看做 2 个出现 1 次的代码块两个拼在一起,其中前面一个代码块去掉
retn。执行完前面一个代码块后由于没有retn,因此target1留在栈中。执行第 2 个代码块跳转到target2执行 ,在target2代码块返回时会返回到target1。因此这种代码块本质上相当于其它操作+call target2且下一个要执行的代码块为target1。
我们定义代码块 Block 几个关键信息:
start_addr:代码块的起始地址。asm_list:代码块的有效汇编,由于汇编指令可能包含[rip + xxx],因此需要记录汇编指令的地址以便后续修正。direct_next:执行完此代码块后接下来要执行的代码块地址。branch_list:代码块中的所有条件跳转语句跳到的地址。call_target:代码块调用函数地址。
class Block:
def __init__(self, start_ea, asm_list, direct_next, branch_list, call_target):
self.start_ea = start_ea
self.asm_list = asm_list
self.direct_next = direct_next
self.branch_list = branch_list
self.call_target = call_target
def __str__(self):
return 'start_ea: 0x%x\ndirect_next: 0x%x\ncall_target: 0x%x\nbranch_list: %s\nasm_list:\n%s\n' % (
0 if self.start_ea == None else self.start_ea,
0 if self.direct_next == None else self.direct_next,
0 if self.call_target == None else self.call_target,
str([hex(x) for x in self.branch_list]),
str('\n'.join([hex(addr) + ' ' + asm for addr, asm in self.asm_list]))
)
get_block 函数可以获取给定地址处的代码块并提取相关信息。代码块中可能有 push xxx;pop xxx; 这样的无意义指令,可以通过栈模拟来去除。
def get_block(start_ea):
ea = start_ea
stack = []
asm_list = []
branch_list = []
call_target = None
direct_next = None
while True:
idc.create_insn(ea)
mnem = idc.print_insn_mnem(ea)
# 处理混淆中跳转的情况
if mnem == 'pushfq':
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
assert idc.get_bytes(ea, idc.get_item_size(ea)) == b'\xE8\x00\x00\x00\x00'
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
jmp_base = ea
assert idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'pop' and idc.get_operand_type(ea, 0) == o_reg
reg = idc.print_operand(ea, 0)
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
assert idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'add' and idc.print_operand(ea, 0) == reg
assert idc.get_operand_type(ea, 1) == o_imm
jmp_target = (jmp_base + idc.get_operand_value(ea, 1)) & 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
assert idc.get_bytes(ea, idc.get_item_size(ea)) == asm('mov [rsp + 0x10], %s' % reg, ea)
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
assert idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'popfq'
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
assert idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'pop' and idc.print_operand(ea, 0) == reg
assert len(stack) != 0 and stack[-1][0] == 'push' and stack[-1][1] == reg
stack.pop()
asm_list.pop()
assert len(stack) != 0 and stack[-1][0] == 'push' and stack[-1][1] == reg
stack.pop()
asm_list.pop()
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'retn':
if direct_next == None:
direct_next = jmp_target
elif call_target == None:
call_target = jmp_target
asm_list.append((0, 'call 0x%x' % (call_target)))
else:
print("🤔🤔🤔🤔🤔🤔")
assert False
break
else:
assert call_target == None and direct_next == None
direct_next = jmp_target
continue
if mnem == 'push':
stack.append((mnem, idc.print_operand(ea, 0)))
elif mnem == 'pop':
if len(stack) != 0 and stack[-1][0] == 'push' and stack[-1][1] == idc.print_operand(ea, 0):
stack.pop()
asm_list.pop()
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
continue
else:
stack.clear()
else:
stack.clear()
asm_list.append((ea, disasm(idc.get_bytes(ea, idc.get_item_size(ea)), ea)))
if mnem == 'retn': break
if mnem[0] == 'j' and mnem != 'jmp' and idc.get_operand_type(ea, 0) != o_reg:
branch_list.append(idc.get_operand_value(ea, 0))
if mnem == 'jmp':
if idc.get_segm_name(idc.get_operand_value(ea, 0)) not in ['.text', '.aaa']:
break
else:
ea = idc.get_operand_value(ea, 0)
else:
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
return Block(start_ea, asm_list, direct_next, branch_list, call_target)
能够获取代码块信息之后就可以 bfs 函数以及函数中的所有分支,提取出汇编代码并写入 newcode 段。这里需要注意以下几点:
- 涉及 rip 的汇编指令不能只是简单把指令中的
rip替换为对应的具体数值,因为有的指令立即数的长度被限制在 4 字节,直接替换成数值会溢出。一个比较好的解决方法是将rip替换为rip + (指令原本地址 - 指令当前地址)。这样借助 rip 寄存器扩大访问范围并且代码移动的距离不会超过 0x100000000 因此可以保证正确性。 - 如果
block.direct_next对应的代码已经被去混淆了需要加上一条 jmp 指令跳转到已经去混淆的代码。 - 有的汇编指令 keystone 不支持汇编,比如
bnd ret,需要特判。
while not func_queue.empty():
func_address = func_queue.get()
if reloc.get(func_address)[1] == False: continue
branch_queue = Queue()
branch_queue.put(func_address)
while not branch_queue.empty():
branch_address = branch_queue.get()
ea = branch_address
while True:
block = get_block(ea)
reloc.merge(ea, new_code_ea)
for addr, insn in block.asm_list:
insn = insn.replace('rip', 'rip - 0x%x' % (new_code_ea - addr))
if insn == 'bnd ret ;':
code = b'\xF2\xC3'
else:
code = asm(insn, new_code_ea)
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(new_code_ea, code)
if addr != 0: reloc.merge(addr, new_code_ea)
new_code_ea += len(code)
if block.call_target != None:
call_target, need_handle = reloc.get(block.call_target)
if need_handle: func_queue.put(call_target)
for branch_address in block.branch_list:
jcc_target, need_handle = reloc.get(branch_address)
if need_handle: branch_queue.put(jcc_target)
if block.direct_next == None: break
next_target, need_handle = reloc.get(block.direct_next)
if need_handle == False:
code = asm('jmp 0x%x' % (next_target), new_code_ea)
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(new_code_ea, code)
new_code_ea += len(code)
break
else:
ea = block.direct_next
最后对代码进行重定位,需要注意的是代码块中的有效指令中也可能有 call 指令,这里 call 调用的是一个类似 plt 表的结构,会直接跳转到导入表中的函数地址表指向的函数,需要特判这种情况。
ea = new_code_start
while ea < new_code_ea:
assert idc.create_insn(ea) != 0
mnem = idc.print_insn_mnem(ea)
if mnem == 'call':
call_target, need_handle = reloc.get(get_operand_value(ea, 0))
if need_handle == True:
if idc.print_insn_mnem(call_target) == 'jmp' and idc.get_segm_name(idc.get_operand_value(call_target, 0)) == '.idata':
ea += get_item_size(ea)
continue
else:
assert False
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(ea, asm('call 0x%x' % (call_target), ea).ljust(idc.get_item_size(ea), b'\x90'))
elif mnem[0] == 'j' and idc.get_operand_type(ea, 0) != idc.o_reg:
jcc_target, need_handle = reloc.get(get_operand_value(ea, 0))
assert need_handle == False
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(ea, asm('%s 0x%x' % (mnem, jcc_target), ea).ljust(idc.get_item_size(ea), b'\x90'))
ea += get_item_size(ea)
最后完整代码:
from queue import *
from idc import *
import idc
from keystone import *
from capstone import *
asmer = Ks(KS_ARCH_X86, KS_MODE_64)
disasmer = Cs(CS_ARCH_X86, CS_MODE_64)
def disasm(machine_code, addr=0):
l = ""
for i in disasmer.disasm(machine_code, addr):
l += "{:8s} {};\n".format(i.mnemonic, i.op_str)
return l.strip('\n')
def asm(asm_code, addr=0):
l = b''
for i in asmer.asm(asm_code, addr)[0]:
l += bytes([i])
return l
class RelocDSU:
def __init__(self):
self.reloc = {}
def get(self, ea):
if ea not in self.reloc:
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'jmp' and idc.get_operand_type(ea, 0) != idc.o_reg:
jmp_ea = idc.get_operand_value(ea, 0)
if idc.get_segm_name(jmp_ea) == '.idata':
self.reloc[ea] = ea
return self.reloc[ea], False
self.reloc[ea], need_handle = self.get(idc.get_operand_value(ea, 0))
return self.reloc[ea], need_handle
else:
self.reloc[ea] = ea
if self.reloc[ea] != ea: self.reloc[ea] = self.get(self.reloc[ea])[0]
return self.reloc[ea], idc.get_segm_name(self.reloc[ea]) in ['.text', '.aaa']
def merge(self, ea, reloc_ea):
# print((hex(ea), hex(reloc_ea)))
self.reloc[self.get(ea)[0]] = self.get(reloc_ea)[0]
reloc = RelocDSU()
class Block:
def __init__(self, start_ea, asm_list, direct_next, branch_list, call_target):
self.start_ea = start_ea
self.asm_list = asm_list
self.direct_next = direct_next
self.branch_list = branch_list
self.call_target = call_target
def __str__(self):
return 'start_ea: 0x%x\ndirect_next: 0x%x\ncall_target: 0x%x\nbranch_list: %s\nasm_list:\n%s\n' % (
0 if self.start_ea == None else self.start_ea,
0 if self.direct_next == None else self.direct_next,
0 if self.call_target == None else self.call_target,
str([hex(x) for x in self.branch_list]),
str('\n'.join([hex(addr) + ' ' + asm for addr, asm in self.asm_list]))
)
def get_block(start_ea):
ea = start_ea
stack = []
asm_list = []
branch_list = []
call_target = None
direct_next = None
while True:
idc.create_insn(ea)
mnem = idc.print_insn_mnem(ea)
# 处理混淆中跳转的情况
if mnem == 'pushfq':
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
assert idc.get_bytes(ea, idc.get_item_size(ea)) == b'\xE8\x00\x00\x00\x00'
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
jmp_base = ea
assert idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'pop' and idc.get_operand_type(ea, 0) == o_reg
reg = idc.print_operand(ea, 0)
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
assert idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'add' and idc.print_operand(ea, 0) == reg
assert idc.get_operand_type(ea, 1) == o_imm
jmp_target = (jmp_base + idc.get_operand_value(ea, 1)) & 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
assert idc.get_bytes(ea, idc.get_item_size(ea)) == asm('mov [rsp + 0x10], %s' % reg, ea)
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
assert idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'popfq'
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
assert idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'pop' and idc.print_operand(ea, 0) == reg
assert len(stack) != 0 and stack[-1][0] == 'push' and stack[-1][1] == reg
stack.pop()
asm_list.pop()
assert len(stack) != 0 and stack[-1][0] == 'push' and stack[-1][1] == reg
stack.pop()
asm_list.pop()
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea) == 'retn':
if direct_next == None:
direct_next = jmp_target
elif call_target == None:
call_target = jmp_target
asm_list.append((0, 'call 0x%x' % (call_target)))
else:
print("🤔🤔🤔🤔🤔🤔")
assert False
break
else:
assert call_target == None and direct_next == None
direct_next = jmp_target
continue
if mnem == 'push':
stack.append((mnem, idc.print_operand(ea, 0)))
elif mnem == 'pop':
if len(stack) != 0 and stack[-1][0] == 'push' and stack[-1][1] == idc.print_operand(ea, 0):
stack.pop()
asm_list.pop()
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
continue
else:
stack.clear()
else:
stack.clear()
asm_list.append((ea, disasm(idc.get_bytes(ea, idc.get_item_size(ea)), ea)))
if mnem == 'retn': break
if mnem[0] == 'j' and mnem != 'jmp' and idc.get_operand_type(ea, 0) != o_reg:
branch_list.append(idc.get_operand_value(ea, 0))
if mnem == 'jmp':
if idc.get_segm_name(idc.get_operand_value(ea, 0)) not in ['.text', '.aaa']:
break
else:
ea = idc.get_operand_value(ea, 0)
else:
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
return Block(start_ea, asm_list, direct_next, branch_list, call_target)
entry_point = 0x1400133B7
new_code_start = 0x14001D000
def solve():
for i in range(0x10000):
idc.set_name(new_code_start + i, '')
idc.del_items(new_code_start + i)
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(new_code_start, b'\x90' * 0x10000)
func_queue = Queue()
func_queue.put(entry_point)
new_code_ea = new_code_start
while not func_queue.empty():
func_address = func_queue.get()
if reloc.get(func_address)[1] == False: continue
branch_queue = Queue()
branch_queue.put(func_address)
while not branch_queue.empty():
branch_address = branch_queue.get()
ea = branch_address
while True:
block = get_block(ea)
reloc.merge(ea, new_code_ea)
for addr, insn in block.asm_list:
insn = insn.replace('rip', 'rip - 0x%x' % (new_code_ea - addr))
if insn == 'bnd ret ;':
code = b'\xF2\xC3'
else:
code = asm(insn, new_code_ea)
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(new_code_ea, code)
if addr != 0: reloc.merge(addr, new_code_ea)
new_code_ea += len(code)
if block.call_target != None:
call_target, need_handle = reloc.get(block.call_target)
if need_handle: func_queue.put(call_target)
for branch_address in block.branch_list:
jcc_target, need_handle = reloc.get(branch_address)
if need_handle: branch_queue.put(jcc_target)
if block.direct_next == None: break
next_target, need_handle = reloc.get(block.direct_next)
if need_handle == False:
code = asm('jmp 0x%x' % (next_target), new_code_ea)
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(new_code_ea, code)
new_code_ea += len(code)
break
else:
ea = block.direct_next
ea = new_code_start
while ea < new_code_ea:
assert idc.create_insn(ea) != 0
mnem = idc.print_insn_mnem(ea)
if mnem == 'call':
call_target, need_handle = reloc.get(get_operand_value(ea, 0))
if need_handle == True:
if idc.print_insn_mnem(call_target) == 'jmp' and idc.get_segm_name(idc.get_operand_value(call_target, 0)) == '.idata':
ea += get_item_size(ea)
continue
else:
assert False
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(ea, asm('call 0x%x' % (call_target), ea).ljust(idc.get_item_size(ea), b'\x90'))
elif mnem[0] == 'j' and idc.get_operand_type(ea, 0) != idc.o_reg:
jcc_target, need_handle = reloc.get(get_operand_value(ea, 0))
assert need_handle == False
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(ea, asm('%s 0x%x' % (mnem, jcc_target), ea).ljust(idc.get_item_size(ea), b'\x90'))
ea += get_item_size(ea)
for i in range(0x10000): idc.del_items(new_code_start + i)
idc.jumpto(new_code_start)
idc.add_func(new_code_start)
print("finish")
solve()
去花指令
花指令目前没有太好的去除办法,但是同一题目中花指令种类和变化都是有限的,也就是说我们可以将题目中所有花指令的类型总结出来,然后分别编写相应的查找和处理规则。
例题:看雪CTF2019 圆圈舞DancingCircle
用IDA打开DancingCircle,按G输入 0x401f58 跳转至核心函数,发现有大量花指令。因此需要借助 ida python 脚本正则表达式匹配去除。
分析汇编代码,发现花指令有如下几类:
call 花指令
-
call + pop
例如 0x00401F9B 处的花指令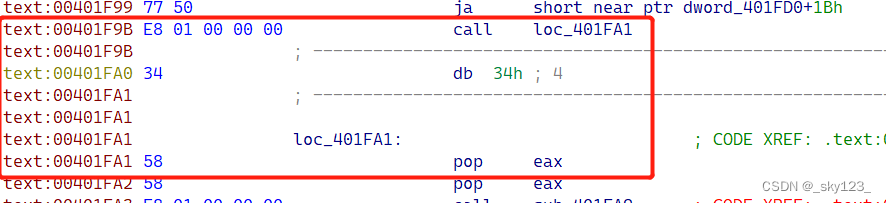
另外还有 push eax + call + pop eax + pop eax 类型的。 -
call + add esp, 4
例如 0x00401F62 处的花指令

-
call + add [esp], 6 + retn
例如 0x00401FA3 处的花指令

jx + jnx 花指令
例如 0x00402D67 处的花指令

这类花指令可以做如下检测:
- 两个跳转指令的第一个字节相差 1 且较小的那个是偶数。
- 前一个跳转的立即数比后一个多 2 。
fake jmp 花指令
例如 0x00401FB2 这处花指令:

这里有很多跳转,但分析后发现这些跳转都可以忽略。由于这一类花指令比较单一,因此直接匹配特征即可。
stx + jx 花指令
例如 0x0040261F 和 0x004026D7 两处花指令:

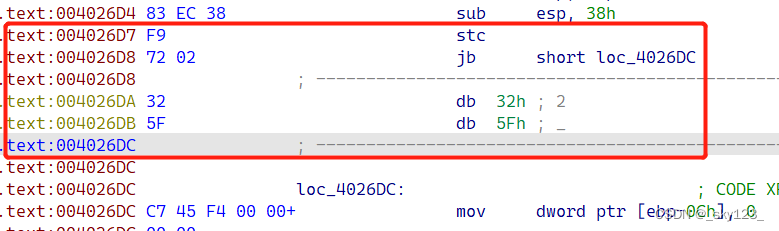
此类花指令本质是通过设置标志寄存器的值使得满足后面的条件跳转。由于此类指令较少,直接匹配特征即可。
import regex as re
from idc import *
import idc
from keystone import *
from capstone import *
asmer = Ks(KS_ARCH_X86, KS_MODE_32)
disasmer = Cs(CS_ARCH_X86, CS_MODE_32)
def disasm(machine_code, addr=0):
l = ""
for i in disasmer.disasm(machine_code, addr):
l += "{:8s} {};\n".format(i.mnemonic, i.op_str)
return l.strip('\n')
def asm(asm_code, addr=0):
l = b''
for i in asmer.asm(asm_code, addr)[0]:
l += bytes([i])
return l
def check_call_to_jmp(call_insn_addr):
call_target = idc.get_operand_value(call_insn_addr, 0)
if call_target not in range(start_ea, end_ea): return None
idc.create_insn(call_target)
if ida_bytes.get_bytes(call_target, idc.get_item_size(call_target)) == asm('add esp, 4', call_target):
return call_target + idc.get_item_size(call_target)
if idc.print_insn_mnem(call_target) == 'pop':
return call_target + idc.get_item_size(call_target)
insn = disasm(ida_bytes.get_bytes(call_target, idc.get_item_size(call_target)), call_target)
if '[esp],' in insn and ('add' in insn or 'sub' in insn) and idc.get_operand_type(call_target, 1) == o_imm:
idc.create_insn(call_target + idc.get_item_size(call_target))
if idc.print_insn_mnem(call_target + idc.get_item_size(call_target)) == 'retn':
return (call_insn_addr + 5 + (1 if idc.print_insn_mnem(call_target) == 'add' else -1) * idc.get_operand_value(call_target, 1)) & 0xFFFFFFFF
return None
def check_jcc_to_jmp(jcc_insn_addr):
code1 = ida_bytes.get_bytes(jcc_insn_addr, idc.get_item_size(jcc_insn_addr))
next_insn_addr = jcc_insn_addr + idc.get_item_size(jcc_insn_addr)
idc.create_insn(next_insn_addr)
code2 = ida_bytes.get_bytes(next_insn_addr, idc.get_item_size(next_insn_addr))
if abs(code1[0] - code2[0]) == 1 and min(code1[0], code2[0]) % 2 == 0 and idc.get_operand_value(jcc_insn_addr, 0) == idc.get_operand_value(next_insn_addr, 0):
return idc.get_operand_value(jcc_insn_addr, 0)
code = ida_bytes.get_bytes(jcc_insn_addr, 12)
print("bbbbb")
pattern_list = [
re.compile(rb"(?s)\x7C\x03\xEB\x03.\x74\xFB"),
re.compile(rb"(?s)\xEB\x07.\xEB\x01.\xEB\x04.\xEB\xF8."),
re.compile(rb"(?s)\xEB\x01.")
]
for pattern in pattern_list:
match = re.match(pattern, code)
if match != None and match.span()[1] != 0:
return jcc_insn_addr + match.span()[1]
return None
st_mnem_map = {'clc': ['jnb'], 'stc': ['jb']}
def check_st_to_jmp(st_insn_addr):
st_mnem = idc.print_insn_mnem(st_insn_addr)
next_insn_addr = st_insn_addr + idc.get_item_size(st_insn_addr)
idc.create_insn(next_insn_addr)
if idc.print_insn_mnem(next_insn_addr) in st_mnem_map[st_mnem]:
return idc.get_operand_value(next_insn_addr, 0)
return None
start_ea = 0x401000
end_ea = 0x4B9CD0
ea = start_ea
while ea < end_ea:
print("aaa: " + hex(ea))
for i in range(ea, ea + 0x10): idc.del_items(i)
if idc.create_insn(ea) == 0:
# idc.patch_byte(ea, 0x90)
ea += 1
continue
mnem = idc.print_insn_mnem(ea)
if mnem == 'call':
jmp_target = check_call_to_jmp(ea)
if jmp_target != None:
assert jmp_target > ea
print("call: " + hex(ea))
print("jmp target: " + hex(jmp_target))
if jmp_target > ea and abs(jmp_target - ea) <= 0x80:
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(ea, b"\x90" * (jmp_target - ea))
ea = jmp_target
else:
code = asm('jmp 0x%x' % (jmp_target), ea)
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(ea, code)
ea += len(code)
continue
elif mnem[0] == 'j':
jmp_target = check_jcc_to_jmp(ea)
if jmp_target != None:
print("jcc: " + hex(ea))
assert jmp_target > ea
if jmp_target > ea and abs(jmp_target - ea) <= 0x80:
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(ea, b"\x90" * (jmp_target - ea))
ea = jmp_target
else:
code = asm('jmp 0x%x' % (jmp_target), ea)
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(ea, code)
ea += len(code)
continue
elif mnem in st_mnem_map:
jmp_target = check_st_to_jmp(ea)
if jmp_target != None:
print("st: " + hex(ea))
assert jmp_target > ea
if jmp_target > ea and abs(jmp_target - ea) <= 0x80:
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(ea, b"\x90" * (jmp_target - ea))
ea = jmp_target
else:
code = asm('jmp 0x%x' % (jmp_target), ea)
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(ea, code)
ea += len(code)
continue
ea += idc.get_item_size(ea)
for _ in range(start_ea, end_ea):
idc.del_items(_)
idc.jumpto(0x004B8DE4)
print("finish")
标签:
相关文章
最新发布
- 光流法结合深度学习神经网络的原理及应用(完整代码都有Python opencv)
- Python 图像处理进阶:特征提取与图像分类
- 大数据可视化分析-基于python的电影数据分析及可视化系统_9532dr50
- 【Python】入门(运算、输出、数据类型)
- 【Python】第一弹---解锁编程新世界:深入理解计算机基础与Python入门指南
- 华为OD机试E卷 --第k个排列 --24年OD统一考试(Java & JS & Python & C & C++)
- Python已安装包在import时报错未找到的解决方法
- 【Python】自动化神器PyAutoGUI —告别手动操作,一键模拟鼠标键盘,玩转微信及各种软件自动化
- Pycharm连接SQL Sever(详细教程)
- Python编程练习题及解析(49题)
点击排行
- 版本匹配指南:Numpy版本和Python版本的对应关系
- 版本匹配指南:PyTorch版本、torchvision 版本和Python版本的对应关系
- Python 可视化 web 神器:streamlit、Gradio、dash、nicegui;低代码 Python Web 框架:PyWebIO
- Anaconda版本和Python版本对应关系(持续更新...)
- 相关性分析——Pearson相关系数+热力图(附data和Python完整代码)
- Python与PyTorch的版本对应
- Windows上安装 Python 环境并配置环境变量 (超详细教程)
- Python pyinstaller打包exe最完整教程

