首页 > Python资料 博客日记
Python数据分析案例23——电商评论文本分析(LDA,共现网络)
2024-05-10 01:00:05Python资料围观342次
本次案例适合物流,电商,大数据等专业的同学。
案例背景:
对于现在的某宝某东上面电商平台的商品,我们可以去找一家店铺,选着某个商品,爬取文本,然后进行如下的文本分析。
本次选择了某东上面的一个是手抓饼商品的评论,我爬取了2千多条,数据长这个样子:
需要这代码演示数据的同学可以参考:数据
数据预处理
读取数据,导入包,由于是文本数据,中文文本要分词处理,读取停用词
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import networkx as nx
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['KaiTi'] #指定默认字体 SimHei黑体
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False #解决保存图像是负号'
import jieba
stop_list = pd.read_csv("停用词.txt",index_col=False,quoting=3,sep="\t",names=['stopword'], encoding='utf-8')定义分词函数,新增一列分词后的列:cutword:
#Jieba分词函数
def txt_cut(juzi):
lis=[w for w in jieba.lcut(juzi) if w not in stop_list.values]
return (" ").join(lis)
df=pd.read_excel('result.xlsx')
df['cutword']=df['评论'].astype('str').apply(txt_cut)
df=df[['id','评价时间','商品种类','评论','cutword']]然后去重,填充缺失值:
df=df.drop_duplicates(subset=['评论'])
df=df.fillna(method='backfill')清洗后储存一下:
df.to_excel('分词后的评论.xlsx',index=False)重置索引,查看前五行:
df=df.reset_index(drop=True)
df.head()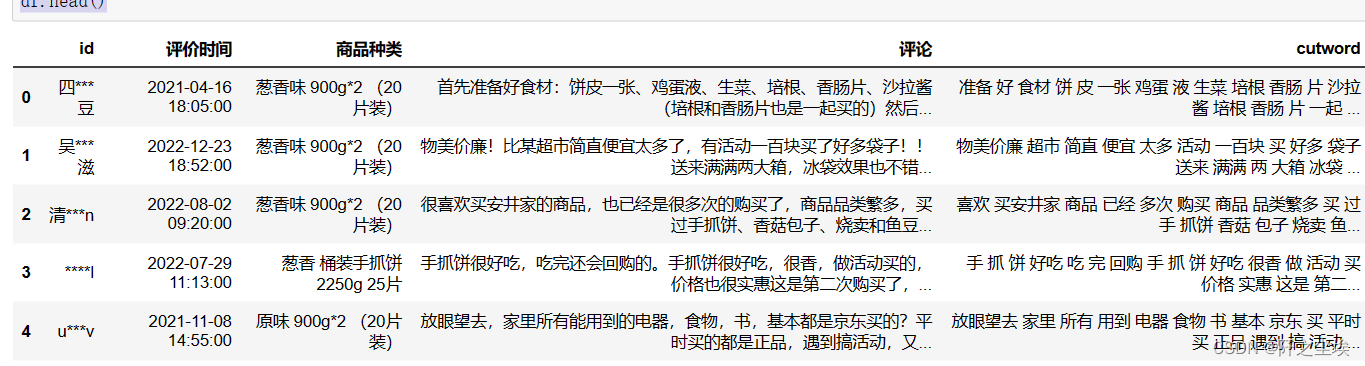
商品种类分析
计算每一类的数量
df['商品种类'].value_counts()
画饼图
import random #定义随机生成颜色函数
def randomcolor():
colorArr = ['1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','A','B','C','D','E','F']
color ="#"+''.join([random.choice(colorArr) for i in range(6)])
return color
[randomcolor() for i in range(3)]plt.figure(figsize=(5,5),dpi=180)
p1=df['商品种类'].value_counts()
plt.pie(p1,labels=p1.index,autopct="%1.3f%%",shadow=True,explode=(0.2,0,0,0,0),colors=[randomcolor() for i in range(5)]) #带阴影,某一块里中心的距离
plt.title("安井手抓饼销售类别占比")
plt.show()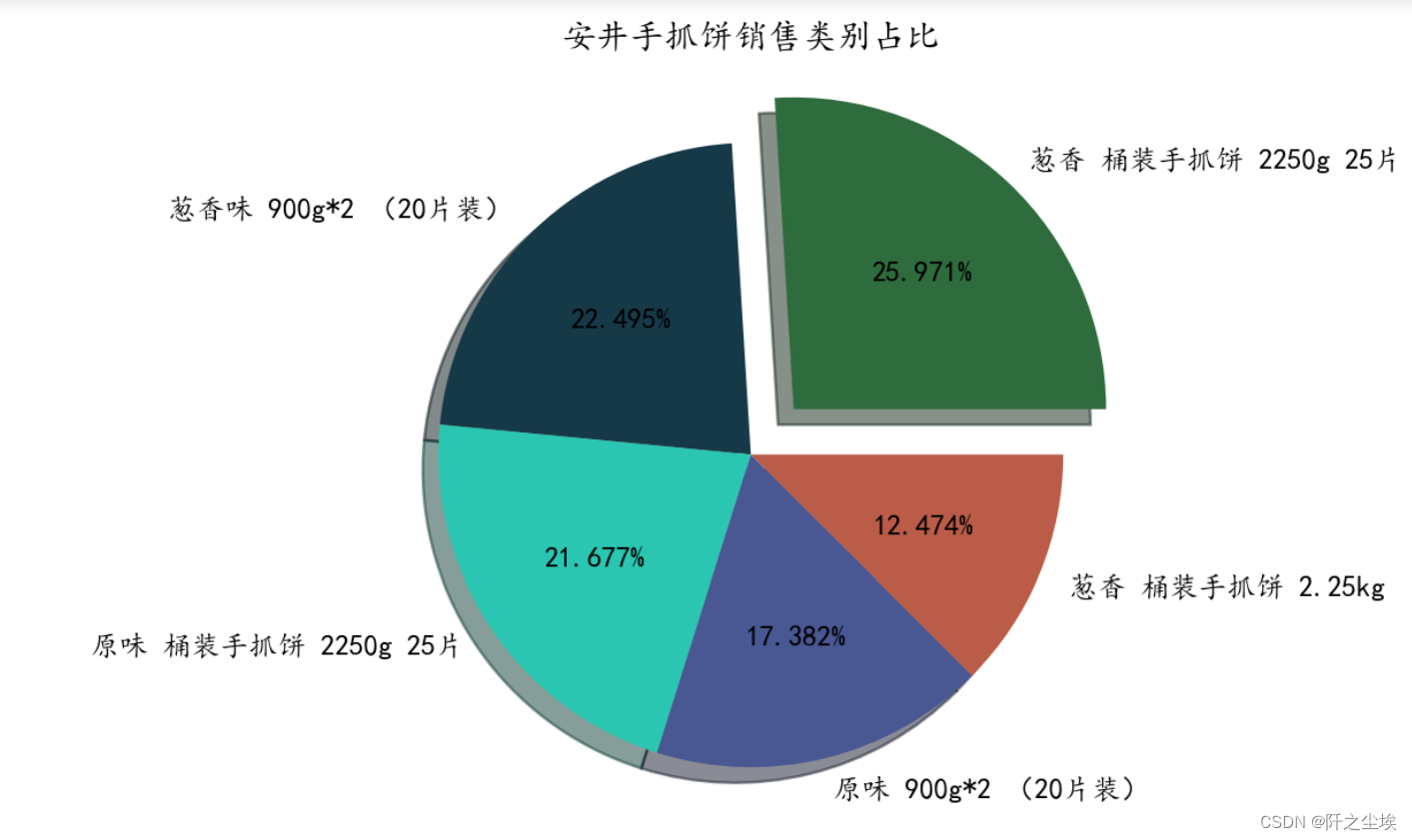
可以看到哪一类产品卖的多....
评论时间分析
#对收集到的评论的时间进行分析
year=pd.to_datetime(df['评价时间']).dt.year.value_counts()
month=pd.to_datetime(df['评价时间']).dt.month.value_counts()
year
画图:
plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=(10,5),dpi=128)
plt.subplot(121)
plt.pie(year,labels=year.index,autopct="%1.3f%%",shadow=True,explode=(0.2,0,0,0,0),colors=[randomcolor() for i in range(len(year))])
plt.title("安井手抓饼评论不同年份对比")
plt.subplot(122)
sns.barplot(y=month.index,x=month,orient="h")
plt.ylabel('月份')
plt.xlabel('评论数量',fontsize=14)
plt.title("安井手抓饼评论不同月份分布")
#plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
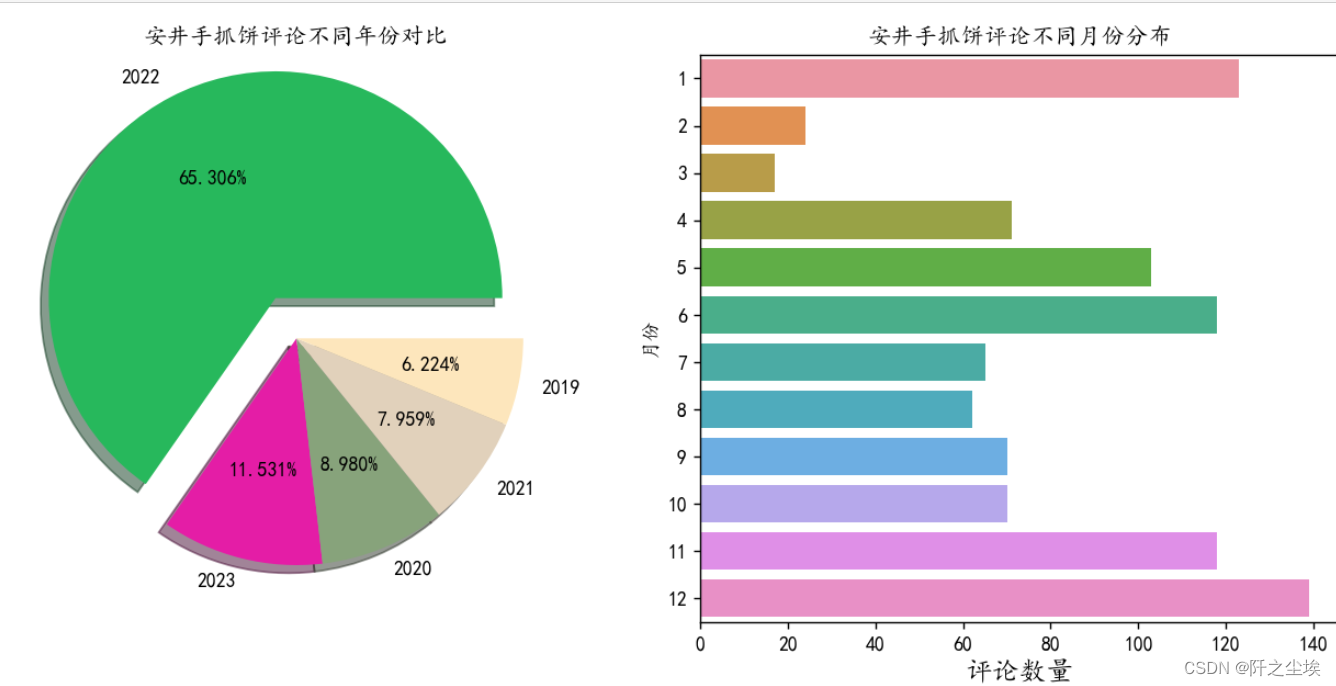
由于23年才过一个月,但是他的评论数量已经比2019到2021三年每一年的评论数量都多。 评论数量最多的是2022年,说明安井手抓饼在2022年的销售量得到了质的变化,其销售量对比三年前有了很高的增长率。
对于月份我们发现11月,12月,1月份安井手抓饼的评论最多,这也对应着这三个月份购买手抓饼的人最多,这可能和天气寒冷,而手抓饼方便做早餐有关。
文本分析
出现频率最高的词汇
import jieba.analyse
jieba.analyse.set_stop_words('停用词.txt')
#合并一起
text = ''
for i in range(len(df['cutword'])):
text += df['cutword'][i]+'\n'
j_r=jieba.analyse.extract_tags(text,topK=20,withWeight=True)
df1 = pd.DataFrame()
df1['word']= [word[0] for word in j_r] ;df1['frequency']=[word[1] for word in j_r]
df1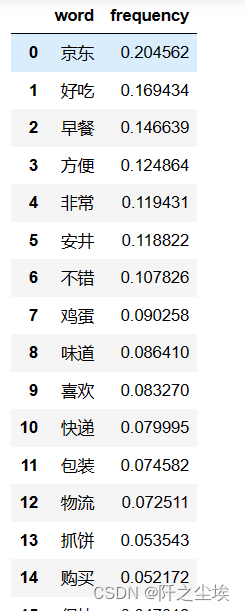
对应的词云图
from wordcloud import WordCloud
import random
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib
# Custom colour map based on Netflix palette
mask = np.array(Image.open('四叶草.png'))
cmap = matplotlib.colors.LinearSegmentedColormap.from_list("", [randomcolor() for i in range(10)])
text = text.replace(',', '').replace('[', '').replace("'", '').replace(']', '').replace('.', '')
wordcloud = WordCloud(font_path="r'C:\Windows\Fonts\simfang.ttf",background_color = 'white', width = 500, height = 200,colormap=cmap, max_words = 100, mask = mask).generate(text)
plt.figure( figsize=(10,6),dpi=512)
plt.imshow(wordcloud, interpolation = 'bilinear')
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout(pad=0)
plt.show()
共现语义网络
from tkinter import _flatten
cut_word_list = list(map(lambda x: ''.join(x), df['cutword'].tolist()))
content_str = ' '.join(cut_word_list).split()
word_fre = pd.Series(_flatten(content_str)).value_counts() # 统计词频
word_fre[:50]
keywords = word_fre[:50].index
keywords
计算矩阵
matrix = np.zeros((len(keywords)+1)*(len(keywords)+1)).reshape(len(keywords)+1, len(keywords)+1).astype(str)
matrix[0][0] = np.NaN
matrix[1:, 0] = matrix[0, 1:] = keywords
matrix 
cont_list = [cont.split() for cont in cut_word_list]
for i, w1 in enumerate(word_fre[:50].index):
for j, w2 in enumerate(word_fre[:50].index):
count = 0
for cont in cont_list:
if w1 in cont and w2 in cont:
if abs(cont.index(w1)-cont.index(w2)) == 0 or abs(cont.index(w1)-cont.index(w2)) == 1:
count += 1
matrix[i+1][j+1] = count储存
kwdata = pd.DataFrame(data=matrix)
kwdata.to_csv('关键词共现矩阵.csv', index=False, header=None, encoding='utf-8-sig')查看:
kwdata= pd.read_csv('关键词共现矩阵.csv')
kwdata .index = kwdata .iloc[:, 0].tolist()
kwdata_ = kwdata .iloc[:20, 1:21]
kwdata_.astype(int)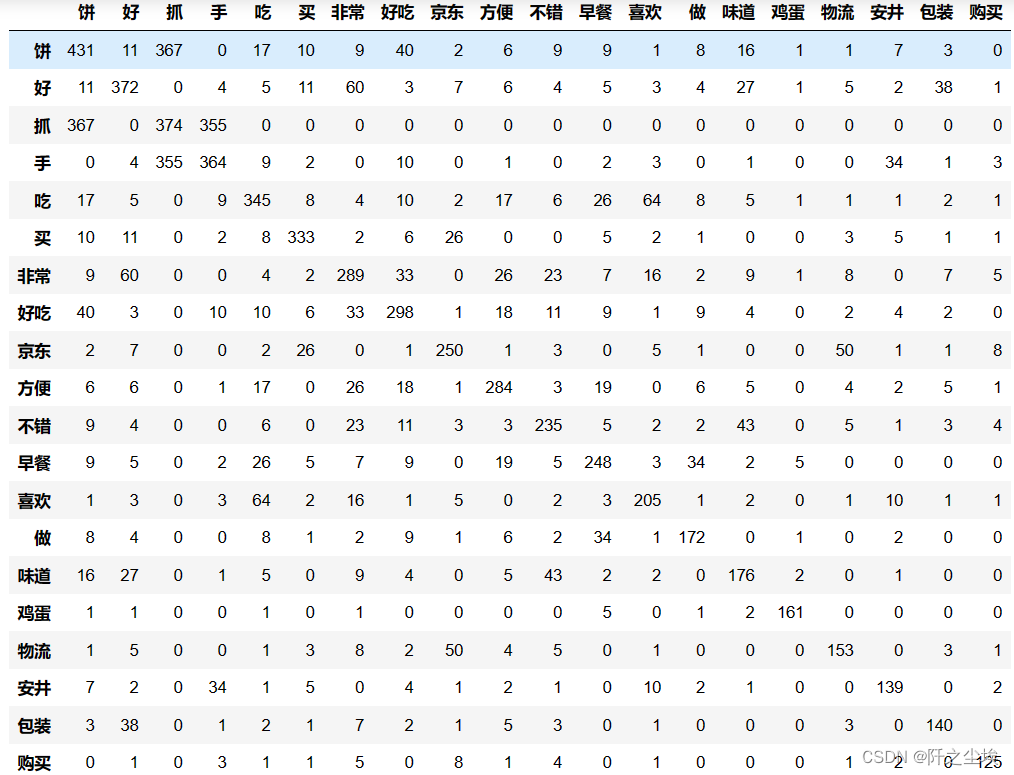
画图:
plt.figure(figsize=(7, 7),dpi=512)
graph1 = nx.from_pandas_adjacency(kwdata_)
nx.draw(graph1, with_labels=True, node_color='blue', font_size=25, edge_color='tomato')
#plt.savefig('共现网络图.jpg') 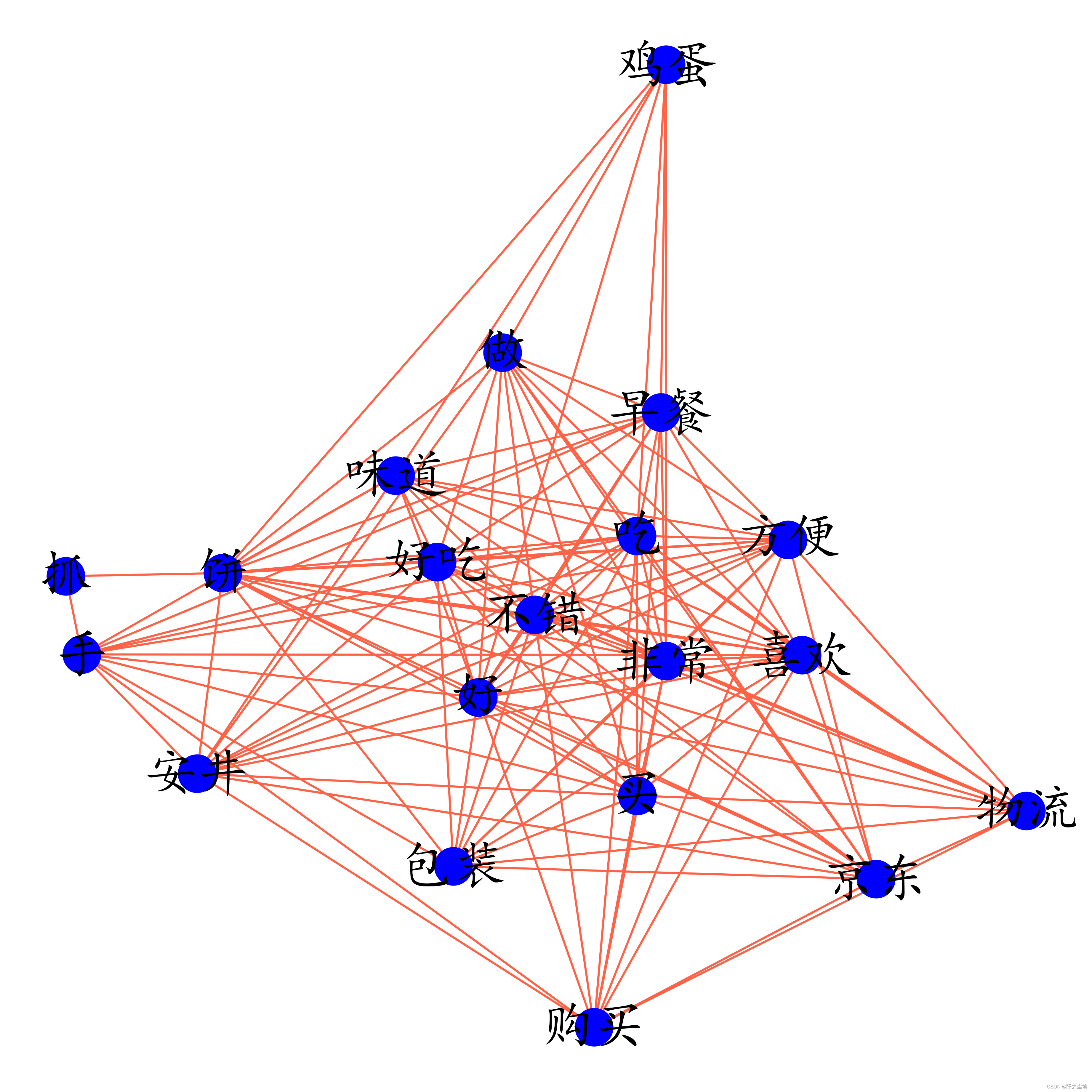
Tf-idf分析,词频逆文档频率
导入包
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer,TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.decomposition import LatentDirichletAllocation将文本转化为词向量
tf_vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer()
#tf_vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(ngram_range=(2,2)) #2元词袋
X = tf_vectorizer.fit_transform(df.cutword)
#print(tf_vectorizer.get_feature_names_out())
print(X.shape)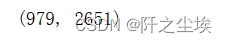
查看高频词
data1 = {'word': tf_vectorizer.get_feature_names_out(),
'tfidf': X.toarray().sum(axis=0).tolist()}
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data1).sort_values(by="tfidf" ,ascending=False,ignore_index=True)
df2.head(20) 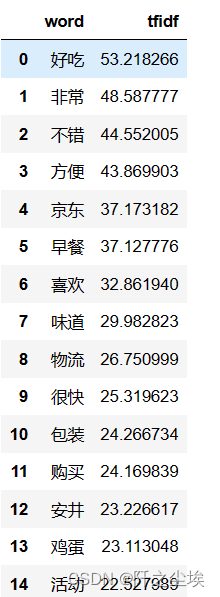
LDA建模
构建模型,拟合
n_topics = 4 #分为4类
lda = LatentDirichletAllocation(n_components=n_topics, max_iter=100,
learning_method='batch',
learning_offset=100,
# doc_topic_prior=0.1,
# topic_word_prior=0.01,
random_state=0)
lda.fit(X)定义一个能查看结果的函数:
def print_top_words(model, feature_names, n_top_words):
tword = []
tword2 = []
tword3=[]
for topic_idx, topic in enumerate(model.components_):
print("Topic #%d:" % topic_idx)
topic_w = [feature_names[i] for i in topic.argsort()[:-n_top_words - 1:-1]]
topic_pro=[str(round(topic[i],3)) for i in topic.argsort()[:-n_top_words - 1:-1]] #(round(topic[i],3))
tword.append(topic_w)
tword2.append(topic_pro)
print(" ".join(topic_w))
print(" ".join(topic_pro))
print(' ')
word_pro=dict(zip(topic_w,topic_pro))
tword3.append(word_pro)
return tword3##输出每个主题对应词语和概率
n_top_words = 10
feature_names = tf_vectorizer.get_feature_names_out()
word_pro = print_top_words(lda, feature_names, n_top_words)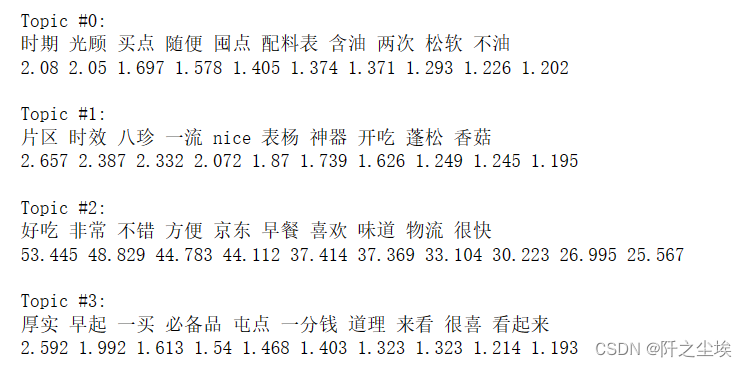
可以看到分为四类话题,每类话题前10 的词汇。
#输出每篇文章对应主题
topics=lda.transform(X)
topic=np.argmax(topics,axis=1)
df['topic']=topic
#df.to_excel("data_topic.xlsx",index=False)
print(topics.shape)
print(topics[0])
topic[0]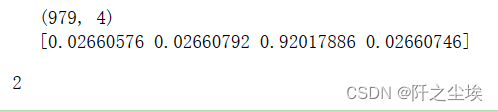
可以看到每段文本被分类到第几类话题里面去了。
词云图
from collections import Counter
from wordcloud import WordCloud
from matplotlib import colors
#from imageio import imread #形状设置
#mask = imread('爱心.png')
def generate_wordcloud(tup):
color_list=[randomcolor() for i in range(10)] #随机生成10个颜色
wordcloud = WordCloud(background_color='white',font_path='simhei.ttf',#mask = mask, #形状设置
max_words=10, max_font_size=50,random_state=42,
colormap=colors.ListedColormap(color_list) #颜色
).generate(str(tup))
return wordcloud画图:
dis_cols = 4 #一行几个
dis_rows = 3
dis_wordnum=10
plt.figure(figsize=(5 * dis_cols, 5 * dis_rows),dpi=128)
kind=len(df['topic'].unique())
for i in range(kind):
ax=plt.subplot(dis_rows,dis_cols,i+1)
most10 = [ (k,float(v)) for k,v in word_pro[i].items()][:dis_wordnum] #高频词
ax.imshow(generate_wordcloud(most10), interpolation="bilinear")
ax.axis('off')
ax.set_title("第{}类话题 前{}词汇".format(i,dis_wordnum), fontsize=30)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
结论
第零类话题,包含随时,光顾,买点,囤点这种词汇,主要可能描述着顾客做出购买这个商品的决策时的想法。然后还包括松软,不油,配料表等等,包含着顾客对安井手抓饼的做法的一些想法。
第一类话题包含着蓬松,神器,香菇等词汇,也是对安井手抓饼的描述,同时也包含开吃,nice,表扬等词,说明顾客对于手抓饼较为满意。
第二类话题包含的是京东,物流,早餐,好吃,味道,不错,很快等这些词汇说明顾客主要描述的是对于京东的物流服务很满意,然后以及买来安井手抓饼可以用来当早餐,味道很好,而且做法方便等想法。
第三类话题,包含厚实,必备器,一分钱,看起来,很喜欢等词汇说明,顾客对于安井手抓饼觉得产品质量不错,一分钱一分货,都喜欢买等想法。
由于评论都是好评,所以说这四类话题的主题和词汇可能稍微有点相似也是很正常的。
创作不易,看官觉得写得还不错的话点个关注和赞吧,本人会持续更新python数据分析领域的代码文章~(需要定制代码可私信)
标签:
相关文章
最新发布
- 光流法结合深度学习神经网络的原理及应用(完整代码都有Python opencv)
- Python 图像处理进阶:特征提取与图像分类
- 大数据可视化分析-基于python的电影数据分析及可视化系统_9532dr50
- 【Python】入门(运算、输出、数据类型)
- 【Python】第一弹---解锁编程新世界:深入理解计算机基础与Python入门指南
- 华为OD机试E卷 --第k个排列 --24年OD统一考试(Java & JS & Python & C & C++)
- Python已安装包在import时报错未找到的解决方法
- 【Python】自动化神器PyAutoGUI —告别手动操作,一键模拟鼠标键盘,玩转微信及各种软件自动化
- Pycharm连接SQL Sever(详细教程)
- Python编程练习题及解析(49题)
点击排行
- 版本匹配指南:Numpy版本和Python版本的对应关系
- 版本匹配指南:PyTorch版本、torchvision 版本和Python版本的对应关系
- Anaconda版本和Python版本对应关系(持续更新...)
- Python 可视化 web 神器:streamlit、Gradio、dash、nicegui;低代码 Python Web 框架:PyWebIO
- 相关性分析——Pearson相关系数+热力图(附data和Python完整代码)
- Python与PyTorch的版本对应
- Windows上安装 Python 环境并配置环境变量 (超详细教程)
- Python pyinstaller打包exe最完整教程

