首页 > Python资料 博客日记
双目相机测距原理
2024-03-14 09:00:04Python资料围观820次
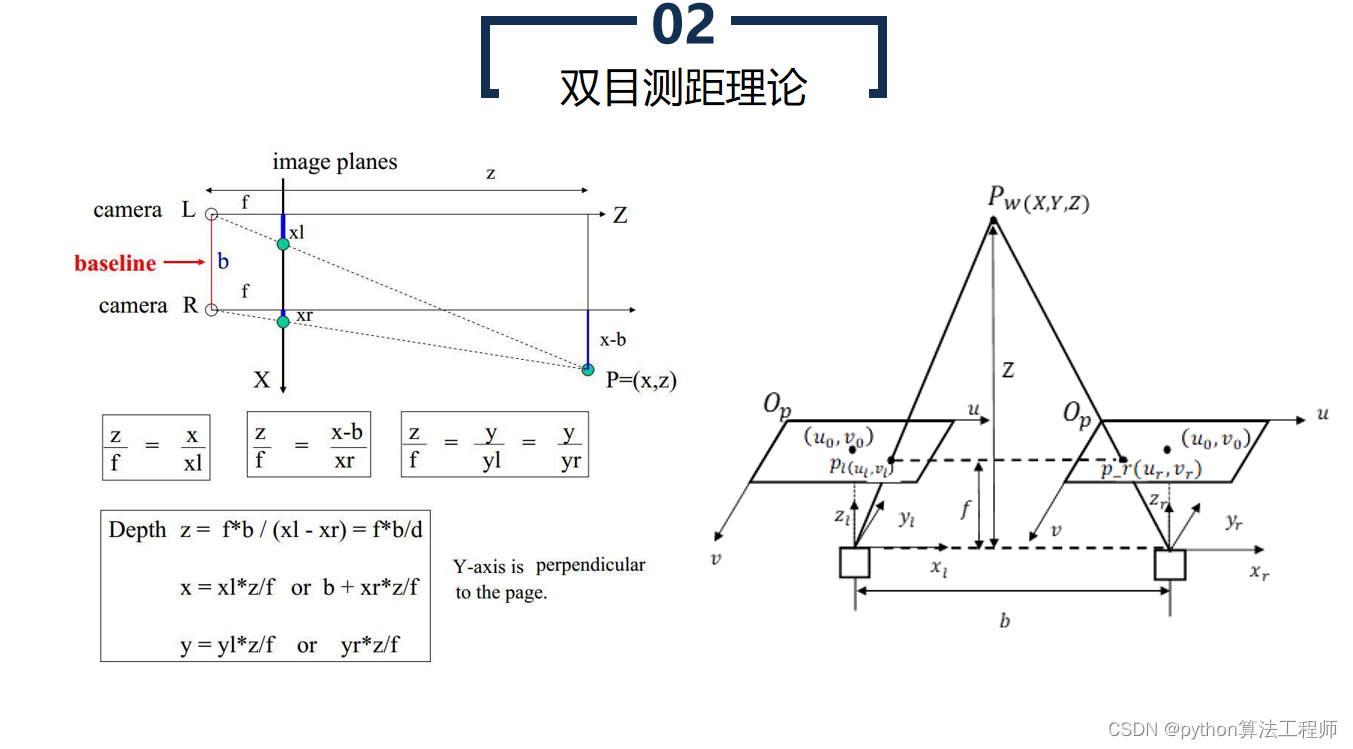
双目相机测距是一种常用的计算机视觉技术,它利用两个摄像头同时拍摄同一场景,通过测量两个摄像头视野中同一物体在图像上的像素差异,从而计算出物体距离的方法。
具体原理如下:
- 双目相机的构成
双目相机由两个摄像头组成,通常摆放在一定距离内,这个距离称为基线距离。两个摄像头同时拍摄同一场景,形成两张 2D 图像。
- 视差测量
当同一个物体同时出现在左右两张图像中时,由于摄像头之间的基线距离,它在两个图像中的位置会有所偏移,这种偏移量称为视差。视差可以通过计算两张图像中对应像素点的距离差来得到。
- 立体重建
通过视差,可以得到同一物体在两张图像中对应像素点的距离差,同时已知两个摄像头的基线距离和视角等参数,可以通过三角测量原理计算出该物体的三维坐标。
- 距离计算
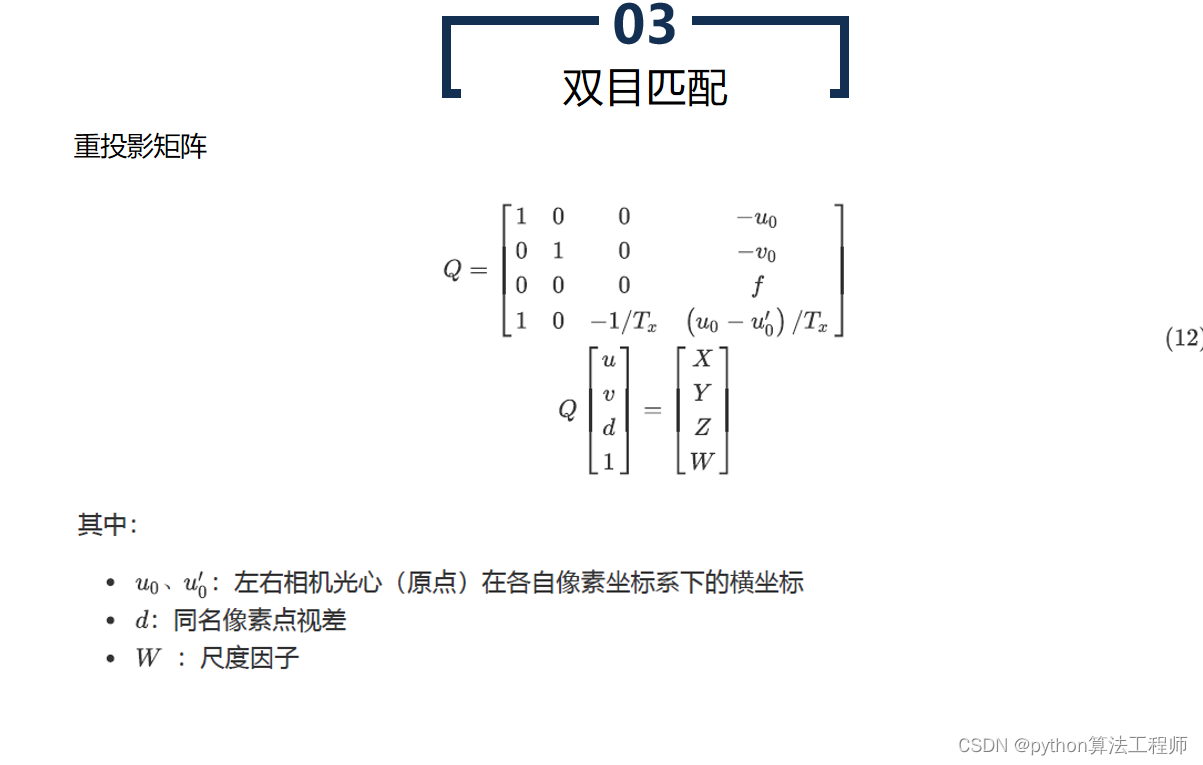
在已知三维坐标后,可以计算出物体距离的大小。通常使用以下公式进行计算:
距离 = (基线距离 × 焦距) / 视差
其中,基线距离和焦距是相机固定参数,视差是由图像像素计算得到的。
- 精度提高
为提高测距精度,需要考虑以下因素:
- 基线距离:基线距离越大,物体视差越大,测距精度越高。
- 焦距:焦距越大,视差越小,测距精度越高。
- 视角:视角越大,物体在图像中的像素差异越明显,测距精度越高。
- 物体表面纹理:表面纹理越丰富,视差越明显,测距精度越高。
以上是双目相机测距的基本原理,实际应用中还需要考虑相机标定、图像处理、噪声削弱等问题,以提高测距精度和稳定性。
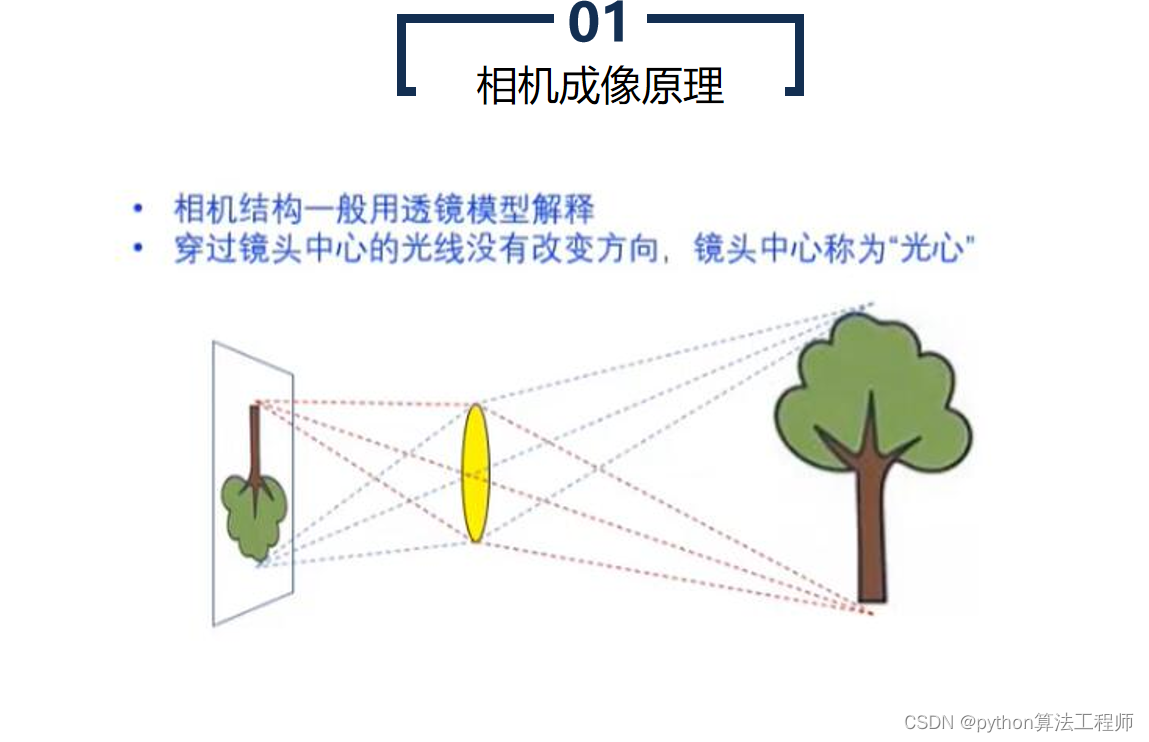
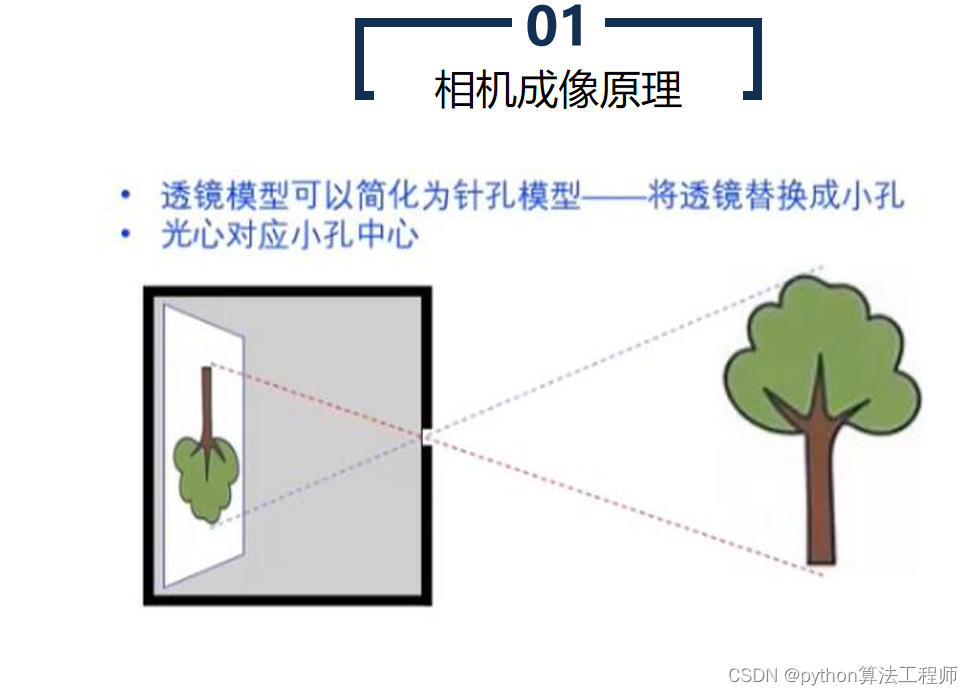
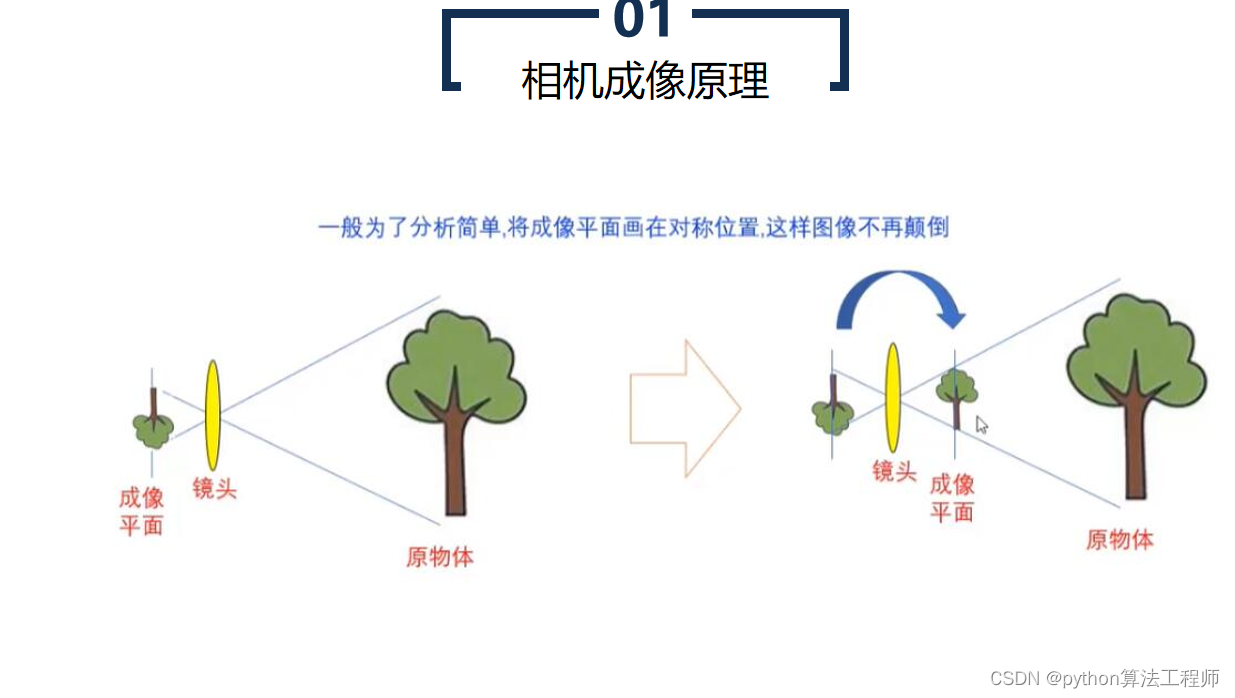
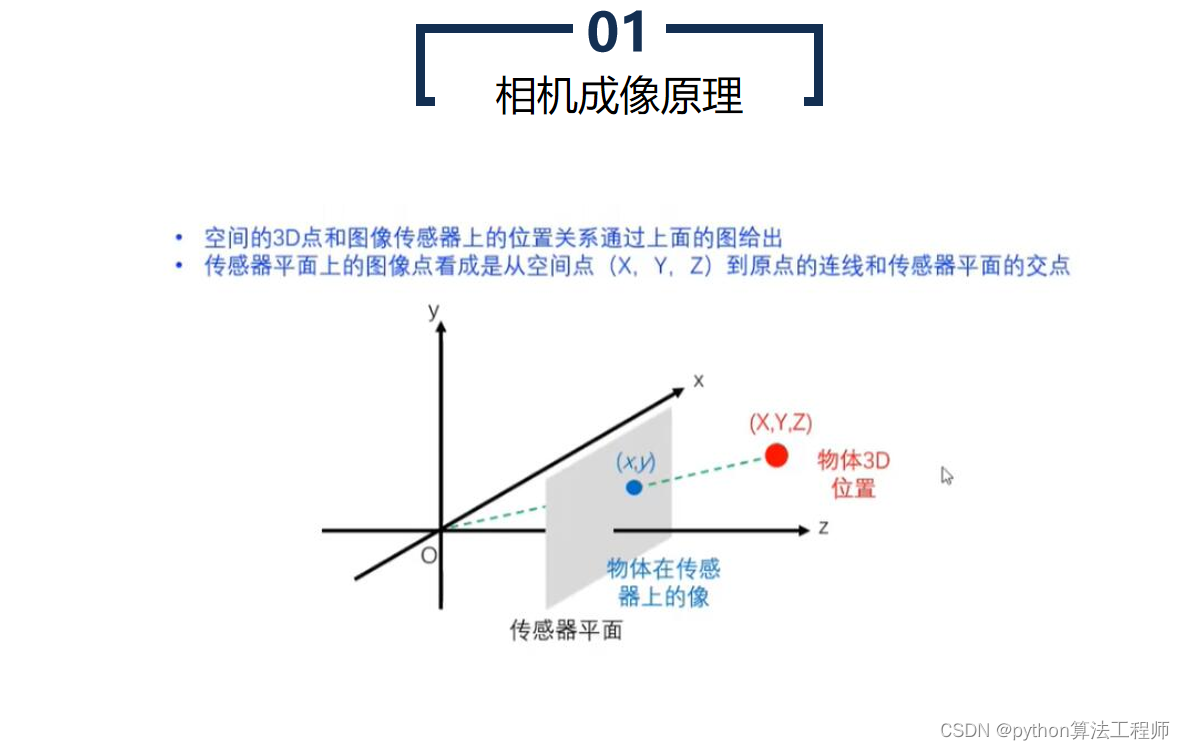

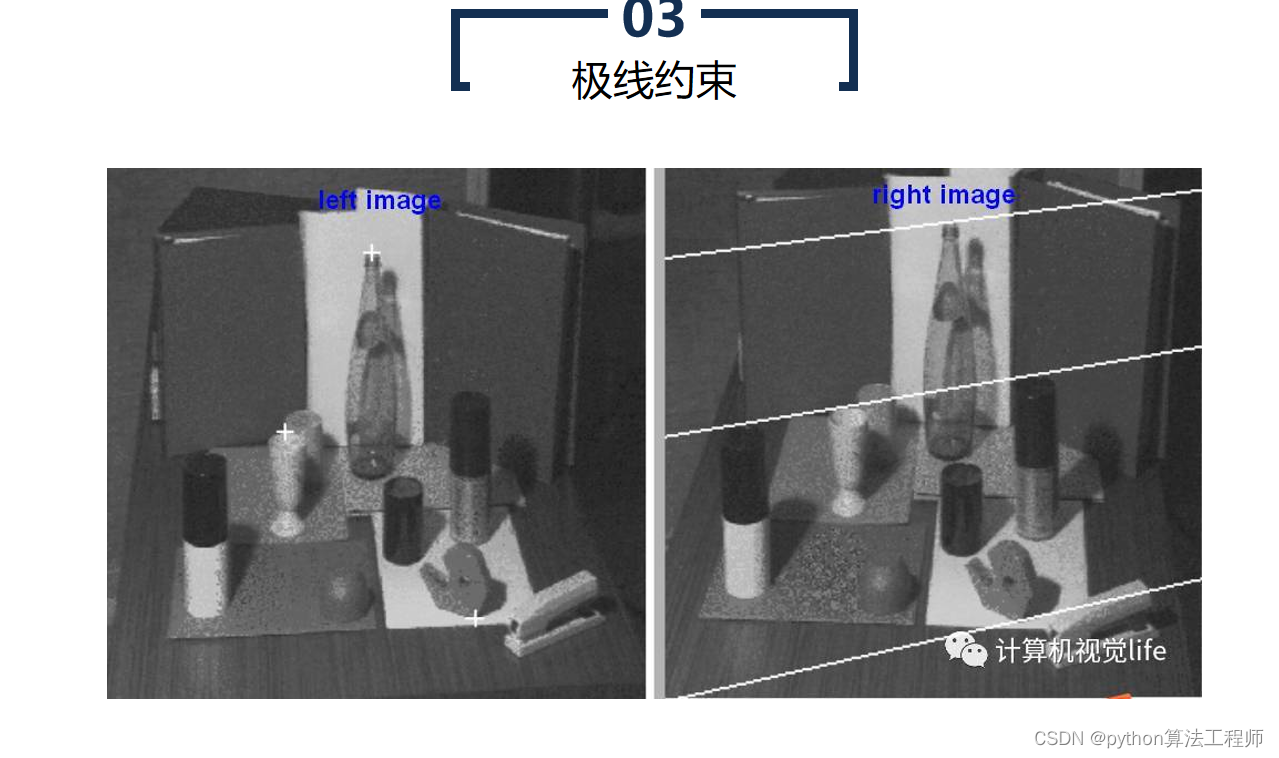
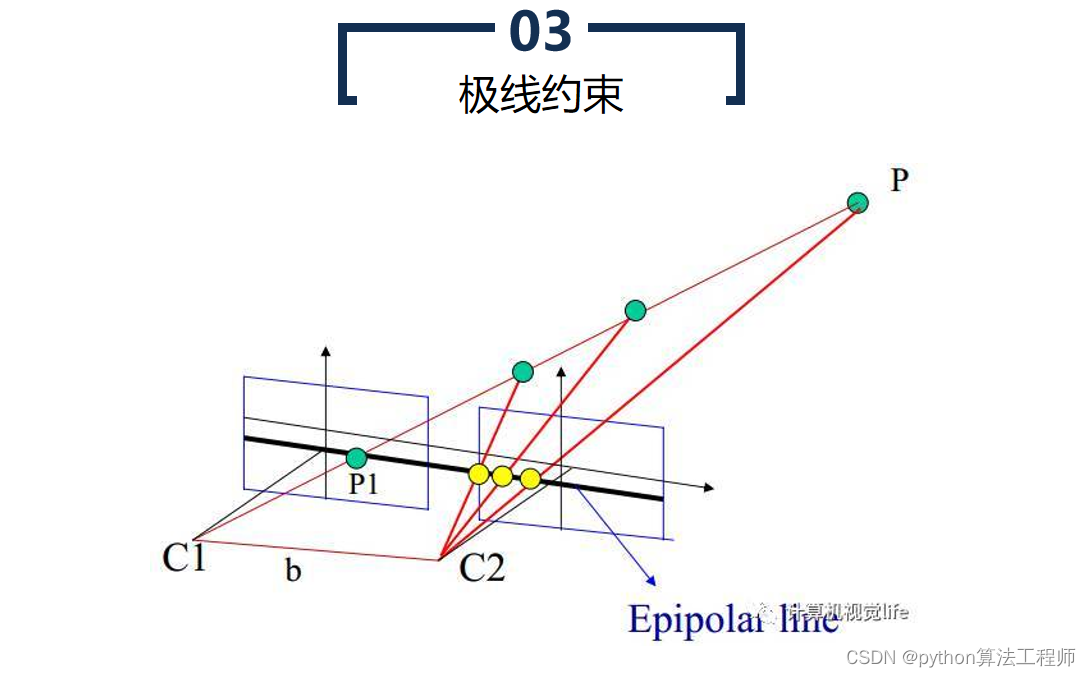
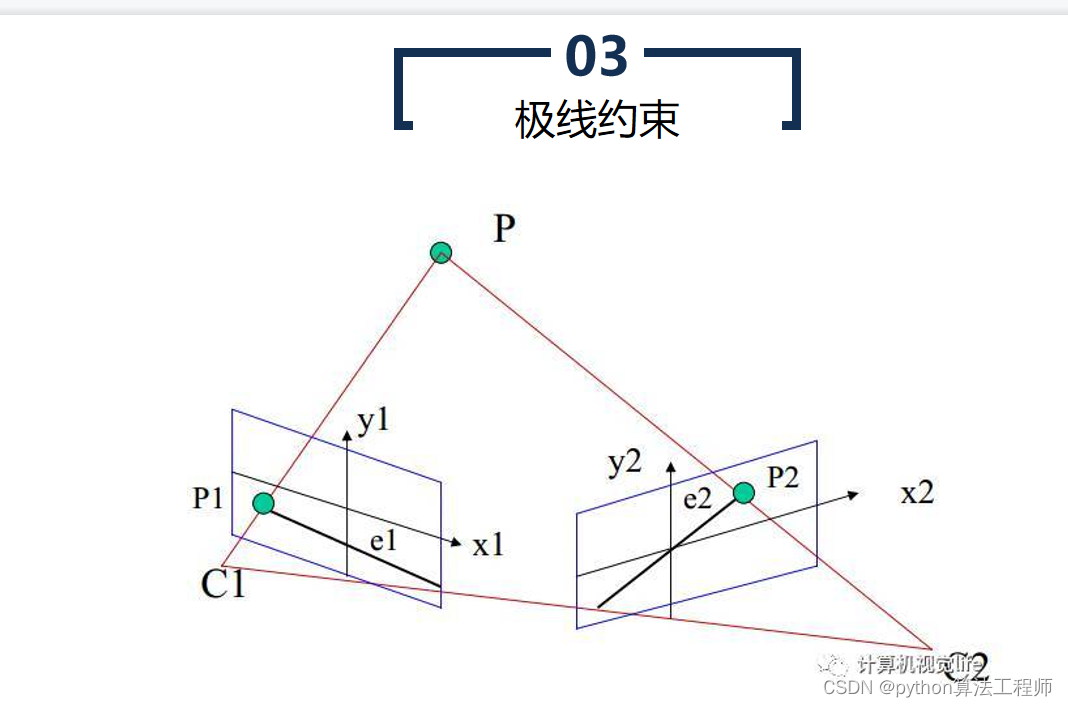
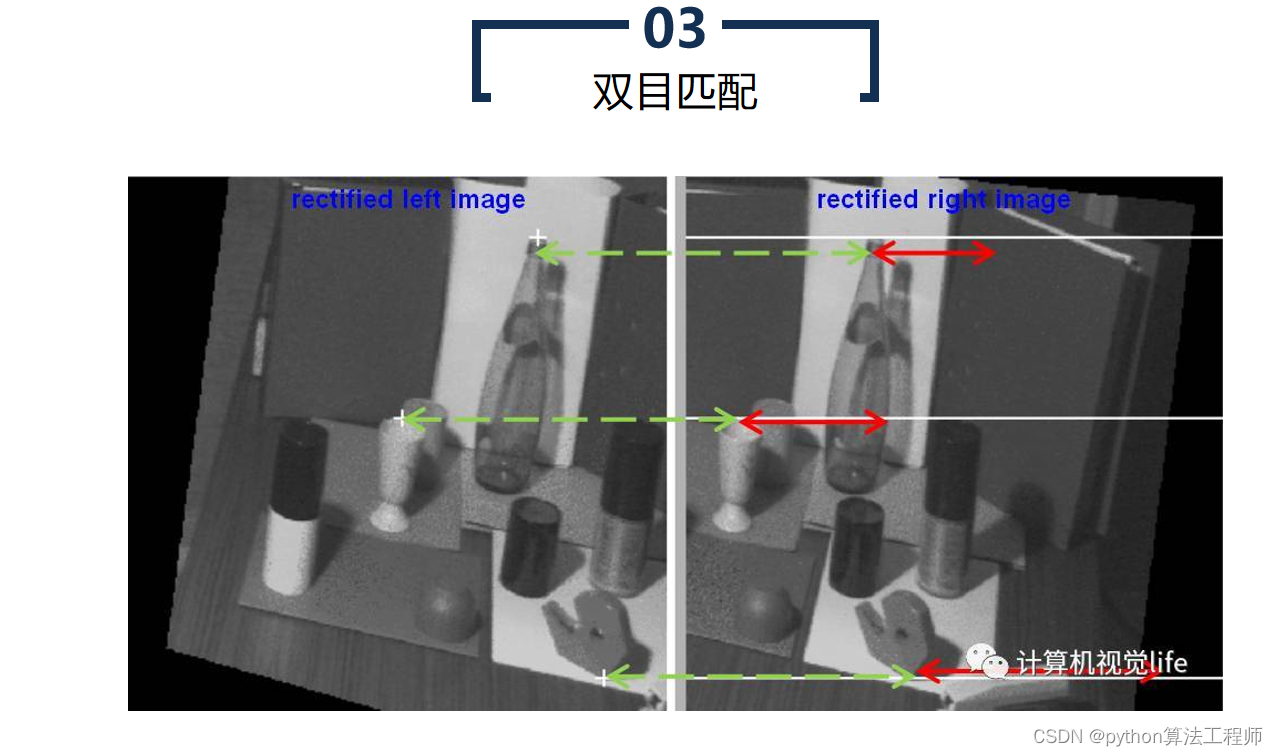
 极线约束是一种用于计算机视觉中的图像匹配的基础约束条件。在两张图像中匹配对应点时,极线约束可以帮助确定一个点在另一张图像中的搜索区域,从而提高匹配的准确性和效率。
极线约束是一种用于计算机视觉中的图像匹配的基础约束条件。在两张图像中匹配对应点时,极线约束可以帮助确定一个点在另一张图像中的搜索区域,从而提高匹配的准确性和效率。
具体来说,极线约束是指同一物体在两张图像中的投影点连线所在的直线。在极线几何中,两张图像之间的相机投影关系可以用本质矩阵表示,本质矩阵包含了相机的内部参数和相对姿态等信息。对于一对匹配的像素点,可以通过本质矩阵计算出它们在另一张图像上的匹配点所在的极线,从而缩小搜索空间,提高匹配效率,避免错误匹配。
极线约束的具体应用包括:
- 特征点匹配
对于两张图像中的特征点,可以利用极线约束来确定它们在另一张图像中的搜索区域。首先,对于第一张图像中的每个特征点,可以计算出它在另一张图像中的极线。然后,在极线上搜索与该特征点最相似的点,即可得到它在第二张图像中的匹配点。
- 立体匹配
对于双目相机拍摄的两张图像,可以利用极线约束来确定物体在另一张图像中的搜索区域,从而实现立体匹配。首先,对于第一张图像中的每个像素点,可以通过本质矩阵计算出它在另一张图像中的极线。然后,在极线上搜索与该像素点最匹配的像素点,即可得到它在第二张图像中的匹配点。
总的来说,极线约束是计算机视觉中一个重要的约束条件,可以帮助提高图像匹配的准确性和效率,广泛应用于特征点匹配、立体匹配等领域。

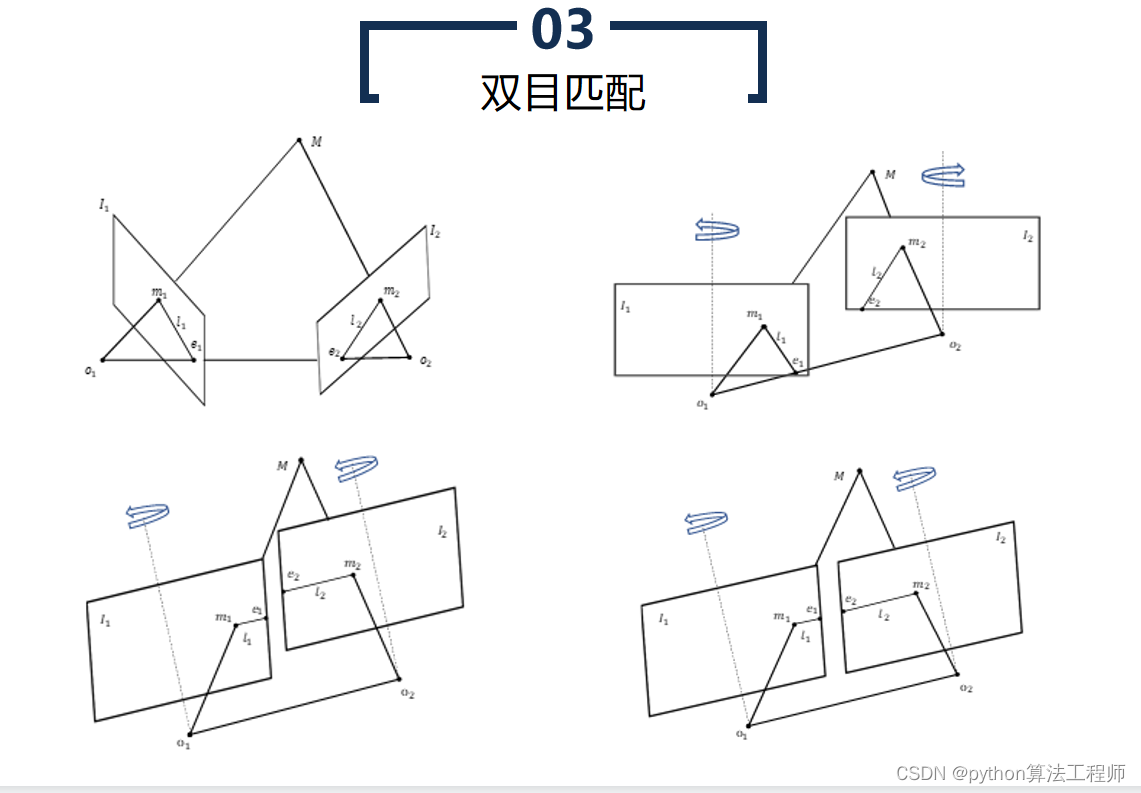
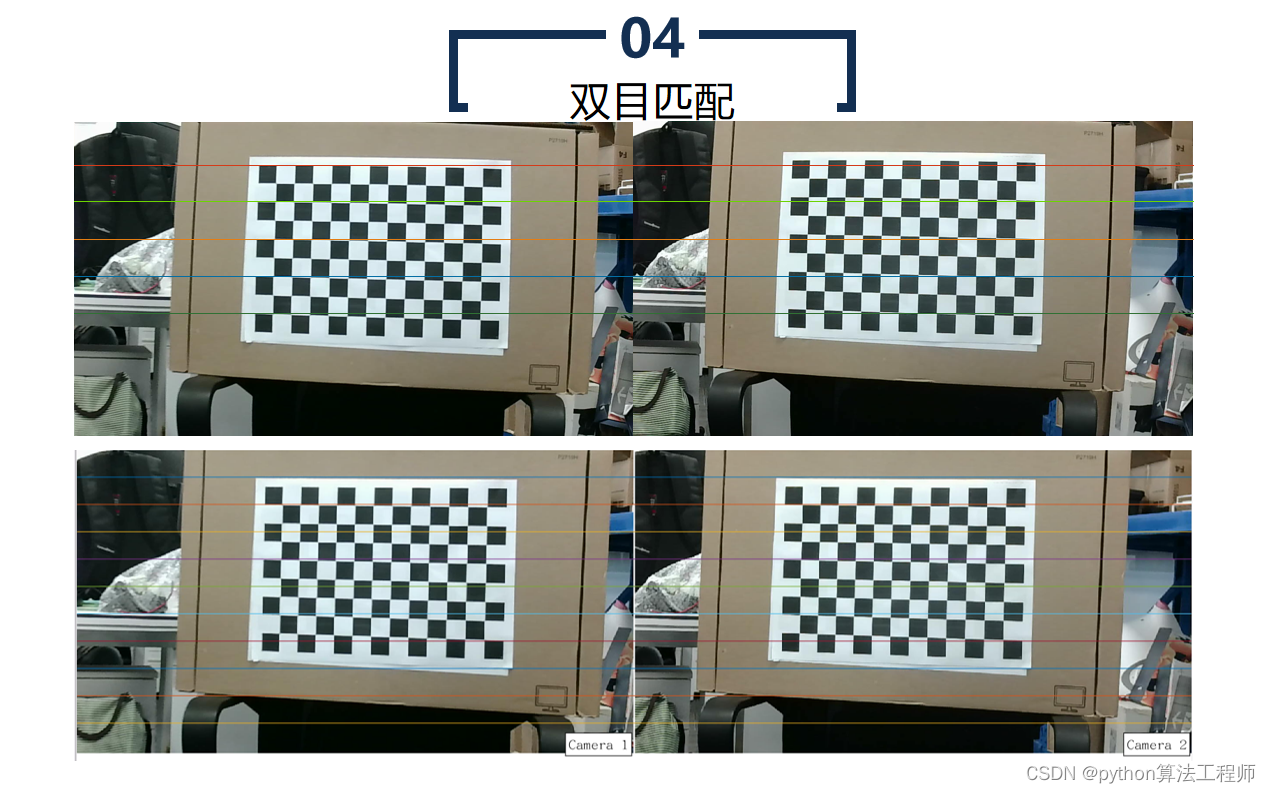
双目匹配是指在双目相机中利用两张图像中的像素点进行匹配,从而计算出像素点在物体上的三维坐标。双目匹配技术是计算机视觉中的一项重要技术,广泛应用于三维重建、机器人视觉、自动驾驶等领域。
双目匹配的基本流程如下:
- 图像预处理
首先需要进行图像预处理,包括图像去噪、颜色校正、去畸变等操作。这些操作可以提高图像质量,减少误匹配。
- 特征提取
然后从两张图像中提取特征点,通常使用的特征点包括角点、边缘点、斑点等。特征提取的目的是为了减少匹配的计算量,提高匹配效率。
- 特征匹配
利用特征点在两张图像中的位置和特征值进行匹配,找到两张图像中相同的特征点。常用的匹配算法包括基于描述子的匹配算法,如SIFT、SURF,以及基于光流的匹配算法等。
- 匹配代价计算
对于每个特征点,需要计算它在另一张图像中的匹配点的代价,代价通常使用像素之间的灰度差异或相关性等指标来计算。代价计算的目的是为了评估两个像素点之间的相似程度,从而确定它们是否匹配。
- 匹配代价聚合
将匹配代价进行聚合,得到每个像素点在另一张图像中的匹配代价,通常使用代价聚合算法,如动态规划算法、块匹配算法等。
- 匹配代价最小化
最后,通过匹配代价最小化算法,如动态规划算法、基于能量函数的优化算法等,找到每个像素点在另一张图像中的最佳匹配点,从而计算出像素点在物体上的三维坐标。
总的来说,双目匹配技术是计算机视觉中的一个重要技术,可以实现三维重建、机器人视觉、自动驾驶等应用,具有广泛的应用前景。
畸变
畸变是指在摄影或成像过程中,由于光学元件的形状、位置或材料等因素的影响,导致图像中的像素点不符合理想的规律分布,造成图像失真的现象。畸变分为径向畸变和切向畸变两种。
- 径向畸变:
径向畸变是由于光学元件的形状不规则或位置偏移等因素引起的,会使得图像中的像素点在径向方向上失真。常见的径向畸变有桶形畸变和枕形畸变。桶形畸变是指图像中的像素点向图像中心凹陷,而枕形畸变则是指图像中的像素点向图像边缘突出。径向畸变的校正方法通常包括基于多项式的校正方法和基于校正图像的校正方法等。
- 切向畸变:
切向畸变是由于光学元件的位置和角度不同引起的,会使得图像中的像素点在切向方向上失真。常见的切向畸变有横向畸变和纵向畸变。横向畸变是指图像中的像素点在水平方向上失真,而纵向畸变则是指图像中的像素点在竖直方向上失真。切向畸变的校正方法通常包括基于旋转和平移的校正方法和基于校正图像的校正方法等。
畸变在数字图像处理、计算机视觉和机器人视觉等领域中非常常见,需要通过适当的校正方法进行消除,以提高图像处理和视觉算法的精度和稳定性。
极线效应
极线效应是指在双目视觉系统中,由于两个相机的视野存在重叠区域,同一物体在两个相机中的投影点连线所在的直线称为极线。极线效应会导致双目匹配的错误和不稳定性。
在双目视觉系统中,由于两个相机的视野存在重叠区域,同一物体在两个相机中的投影点连线所在的直线称为极线。当双目视觉系统中的像素点在两个相机中的位置差异较大时,其在另一个相机中的投影点可能在极线的两端,这种情况下匹配过程会变得困难,导致双目匹配的错误和不稳定性。
极线效应的解决方法有很多,常用的方法包括极线校正、多视角几何、深度学习等。其中,极线校正是一种常用的方法,它可以通过旋转和平移两种变换来消除极线效应。
总的来说,极线效应是双目视觉系统中常见的问题,会导致双目匹配的错误和不稳定性,需要采用适当的方法来消除
Bouguet极线校
Bouguet极线校正是一种常用的立体视觉校正方法,用于消除双目相机拍摄图像中的畸变和极线效应,从而提高双目视觉系统的精度和稳定性。
在双目视觉系统中,由于两个相机的位置和角度不同,图像中的同一物体在两个相机中的投影位置也不同。这种差异会导致图像中的像素点之间存在畸变,从而影响双目视觉系统的精度和稳定性。另外,在双目视觉系统中,由于两个相机的视野存在重叠区域,同一物体在两个相机中的投影点连线所在的直线称为极线,极线效应会导致双目匹配的错误和不稳定性。
Bouguet极线校正方法可以通过旋转和平移两种变换来消除畸变和极线效应。具体来说,Bouguet极线校正方法的步骤如下:
- 计算本质矩阵
首先,需要利用标定板或物体进行相机标定,得到两个相机的内参矩阵和外参矩阵。然后,利用内参矩阵和相机位姿矩阵计算本质矩阵。
- 计算极线
利用本质矩阵计算出两个相机中所有像素点在另一个相机中的极线。
- 计算校正变换
利用极线计算出校正变换矩阵,包括旋转矩阵和平移向量。校正变换的目的是将每个像素点在另一个相机中的极线旋转到水平方向,从而消除极线效应。


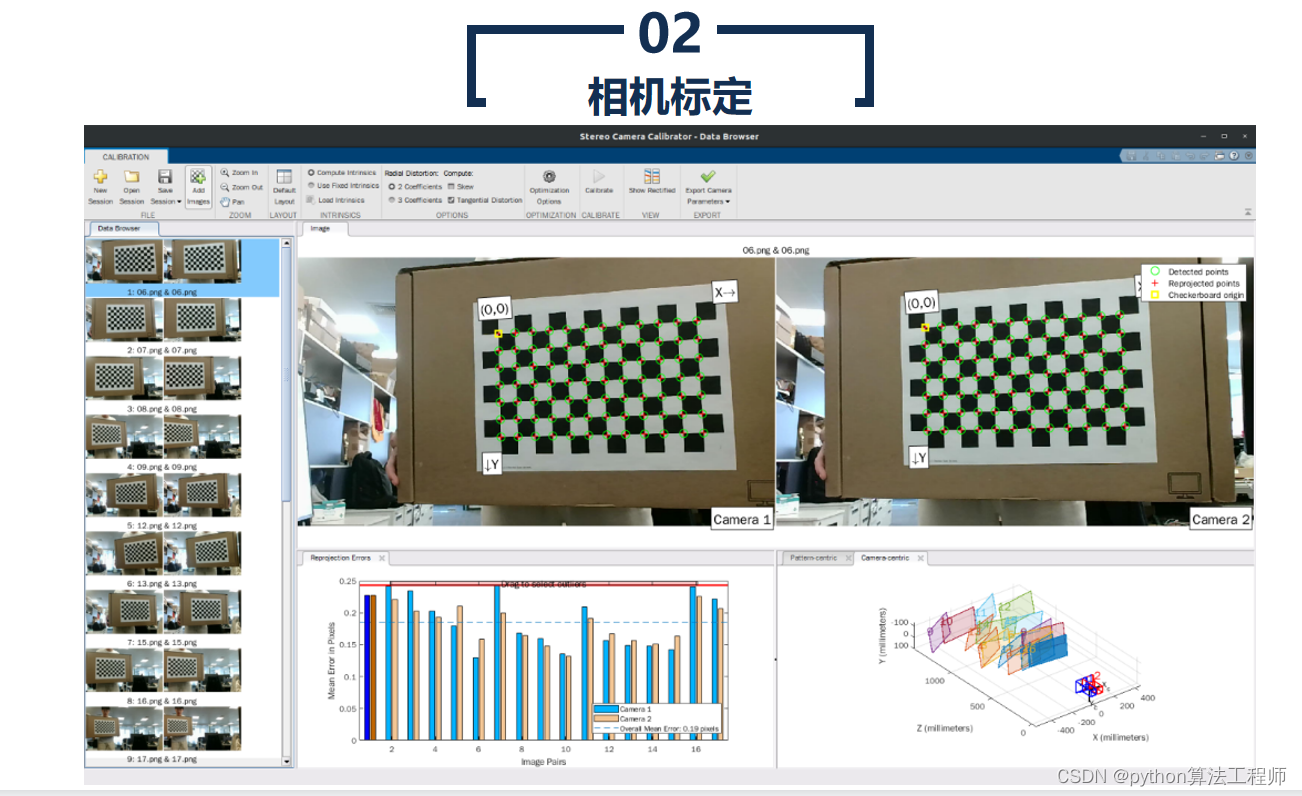
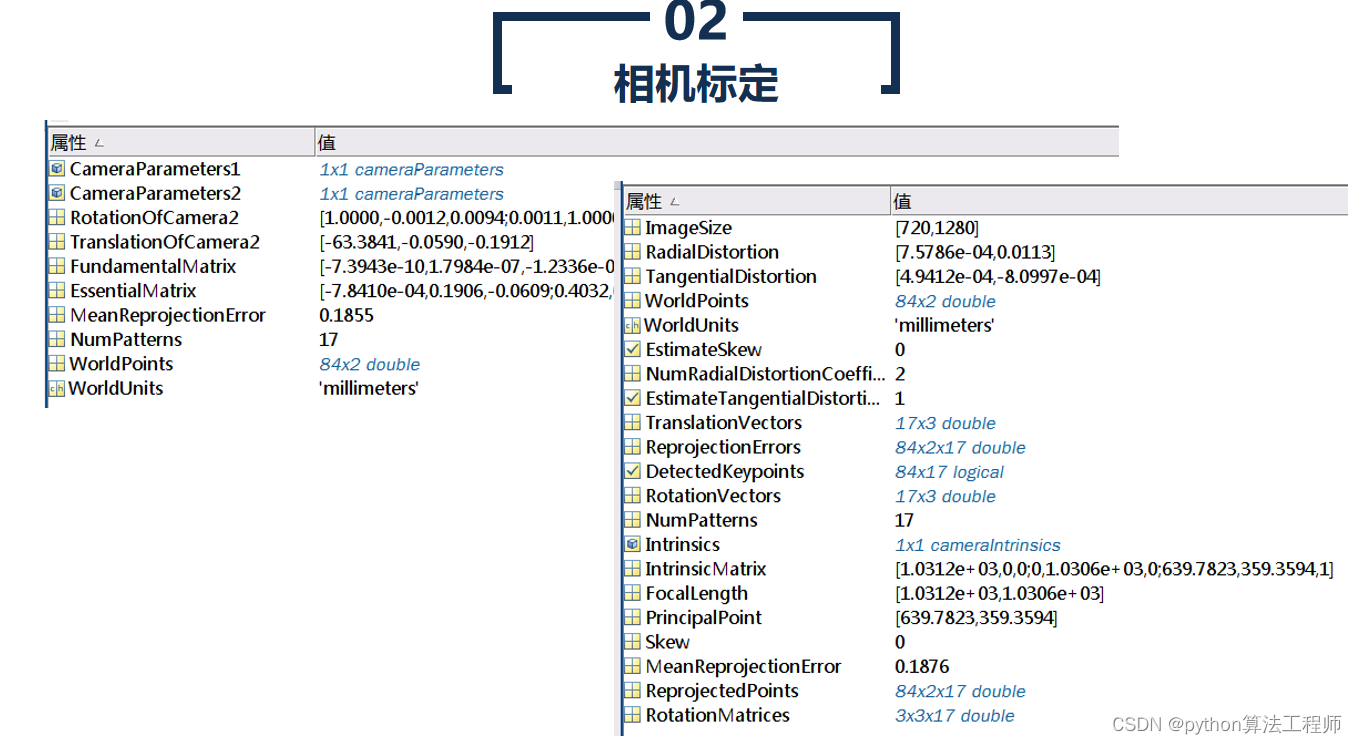
 相机标定是指通过对相机内部和外部参数进行测量和计算,建立相机的几何模型,以获得相机在成像过程中的几何变换关系和畸变参数等信息的过程。相机标定的目的是确定相机内部和外部参数,以便在计算机视觉、机器人视觉、虚拟现实等领域中应用相机成像数据。
相机标定是指通过对相机内部和外部参数进行测量和计算,建立相机的几何模型,以获得相机在成像过程中的几何变换关系和畸变参数等信息的过程。相机标定的目的是确定相机内部和外部参数,以便在计算机视觉、机器人视觉、虚拟现实等领域中应用相机成像数据。
相机标定通常需要使用一些标定物体,如标定板、标定棋盘等。标定物体需要具有一定的特征点,以便在相机成像过程中能够准确地检测和测量这些特征点的位置。
相机标定的具体步骤如下:
- 准备标定物体
选择合适的标定物体,如标定板、标定棋盘等,并在标定物体上标记出一些特征点。
- 拍摄标定图像
使用相机拍摄多张标定图像,保证标定物体在图像中有不同的位姿和角度,并且尽可能地覆盖整个图像空间。
- 检测特征点
使用图像处理算法检测标定物体上的特征点,并记录这些特征点在像素坐标系中的位置。
- 计算相机内部参数
使用标定图像中的特征点,计算相机内部参数,包括相机的主点、像元大小、畸变参数等。
- 计算相机外部参数
使用标定图像中的特征点,计算相机外部参数,包括相机的旋转矩阵和平移向量。
- 验证标定结果
使用标定结果来纠正图像中的畸变,并在测试数据上验证标定结果的准确性和稳定性。
相机标定是计算机视觉、机器人视觉和虚拟现实等领域中非常重要的工具和技术,可以为这些领域中的算法和应用提供准确的相机参数和畸变校正信息。
 校正图像是指通过对畸变图像进行处理,消除图像中的畸变效应,得到更为准确、稳定和可靠的图像。校正图像通常用于计算机视觉、机器人视觉、虚拟现实等领域中,以提高算法和应用的精度和稳定性。
校正图像是指通过对畸变图像进行处理,消除图像中的畸变效应,得到更为准确、稳定和可靠的图像。校正图像通常用于计算机视觉、机器人视觉、虚拟现实等领域中,以提高算法和应用的精度和稳定性。
校正图像的生成通常需要进行以下步骤:
- 相机标定
对相机进行标定,计算出相机的内部参数和畸变参数。这些参数可以用于对畸变图像进行校正。
- 畸变校正
使用相机的内部参数和畸变参数,对畸变图像进行校正。常用的畸变校正方法包括基于多项式的校正方法、基于校正图像的校正方法等。校正过程中,可以使用插值方法对校正后的像素进行补偿,以获得更为平滑和准确的校正图像。
- 透视校正
如果相机成像过程中存在透视畸变,需要进行透视校正。透视校正是指对图像进行逆透视变换,将图像中的斜线、梯形等形状变换为正方形或矩形,以消除透视畸变。
- 验证校正结果
使用校正图像进行算法和应用的测试和验证,以确保校正结果的准确性和稳定性。
校正图像在计算机视觉、机器人视觉、虚拟现实等领域中非常重要,可以提高图像处理和视觉算法的精度和稳定性。

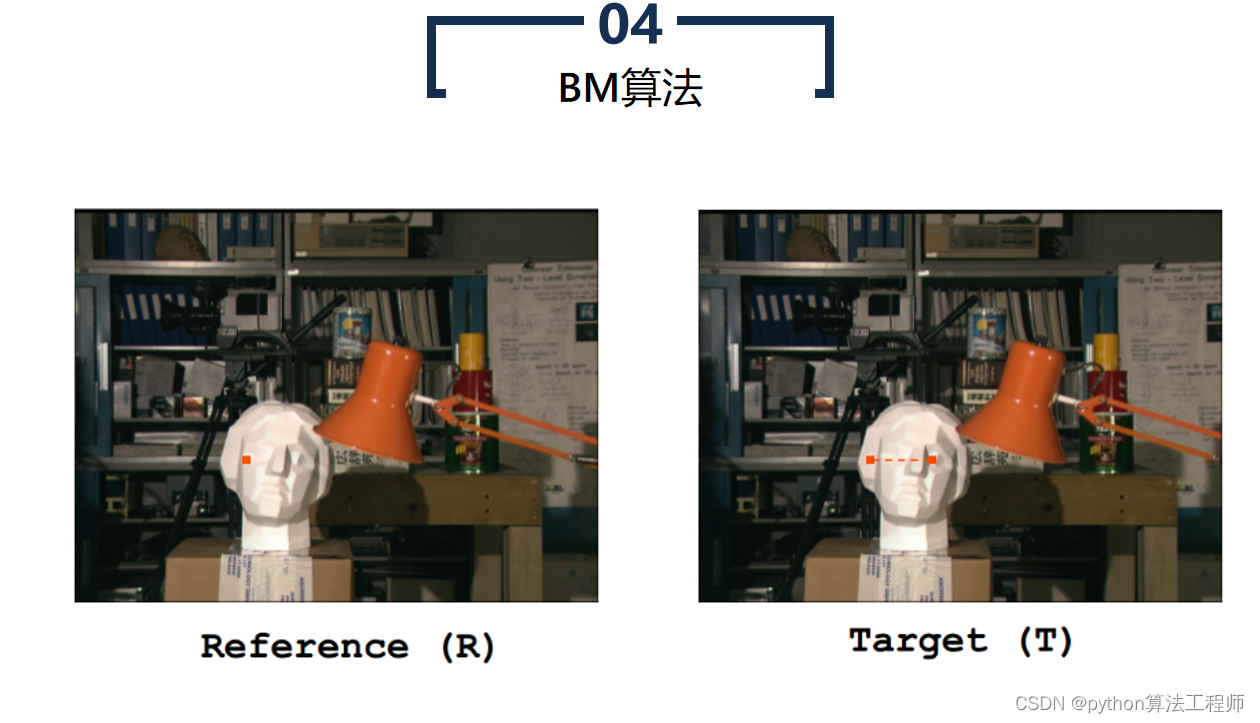
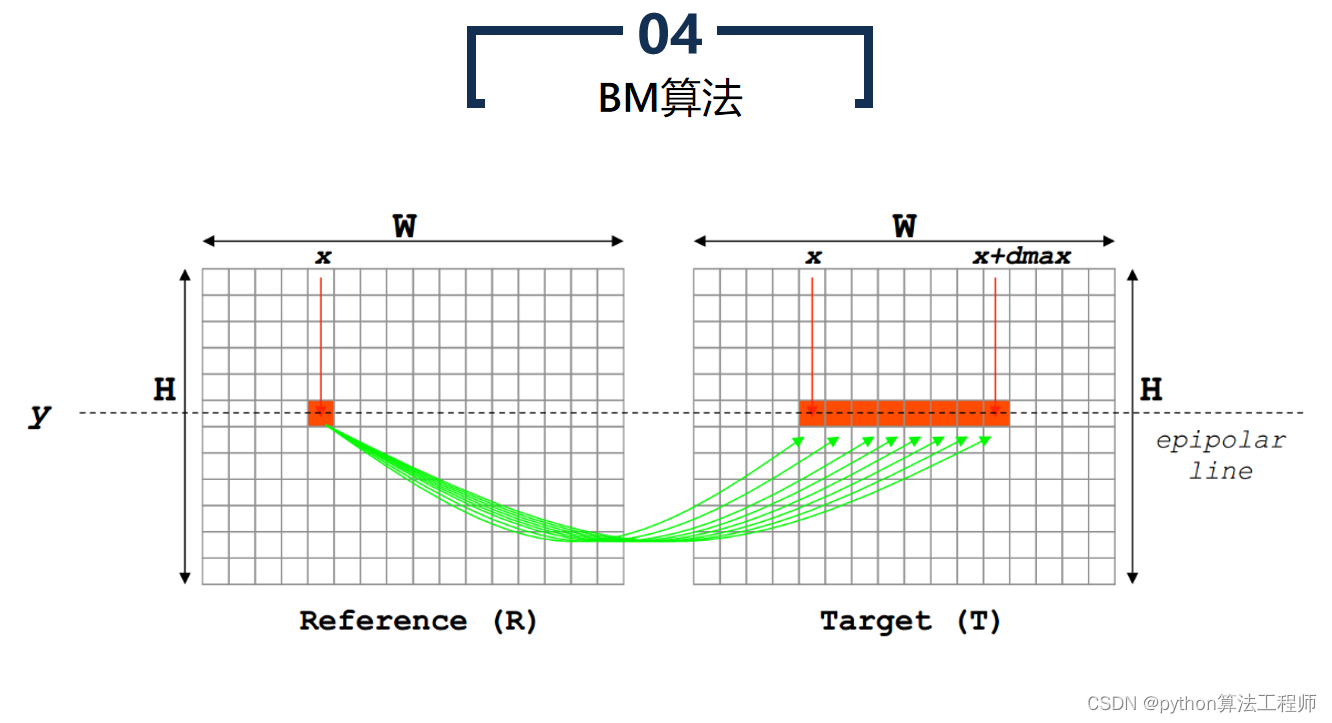
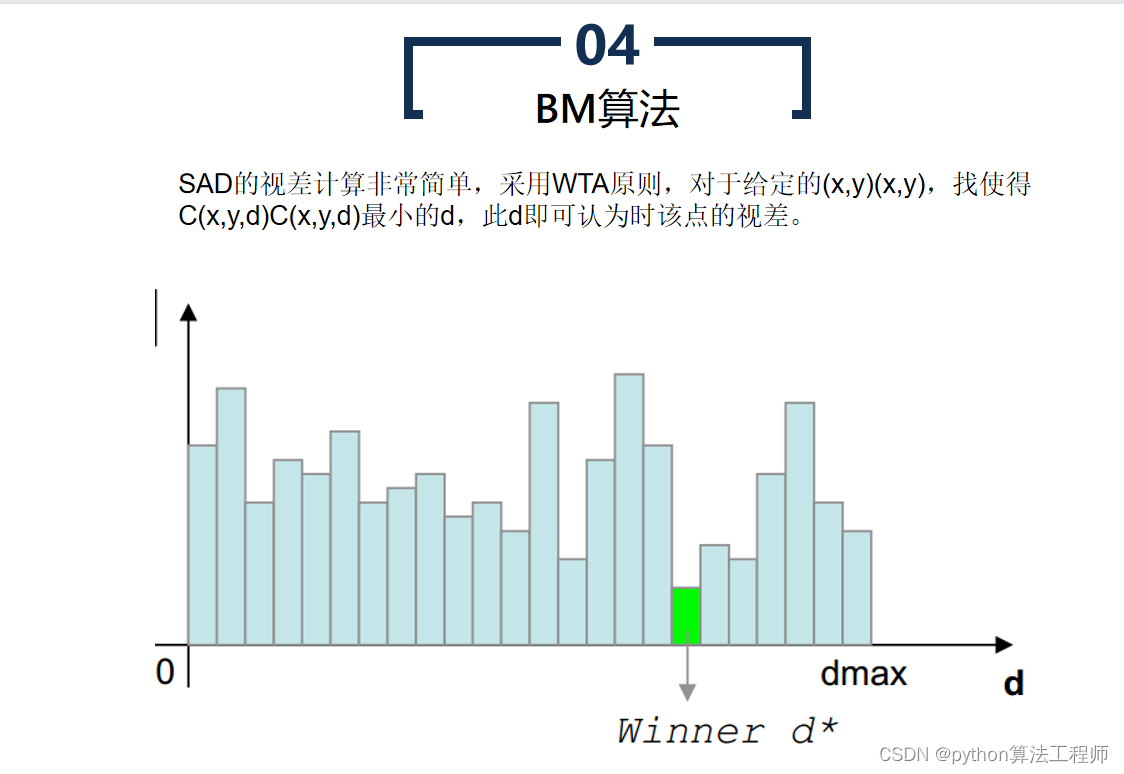
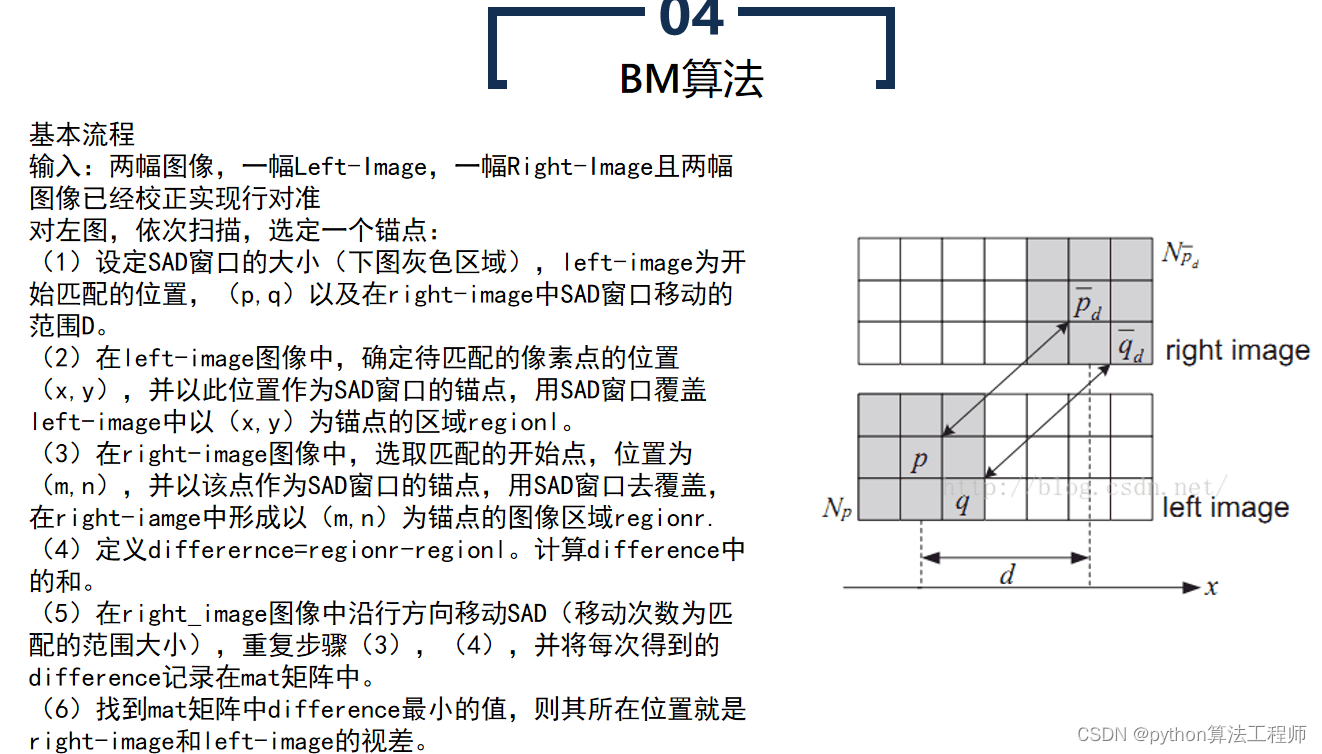
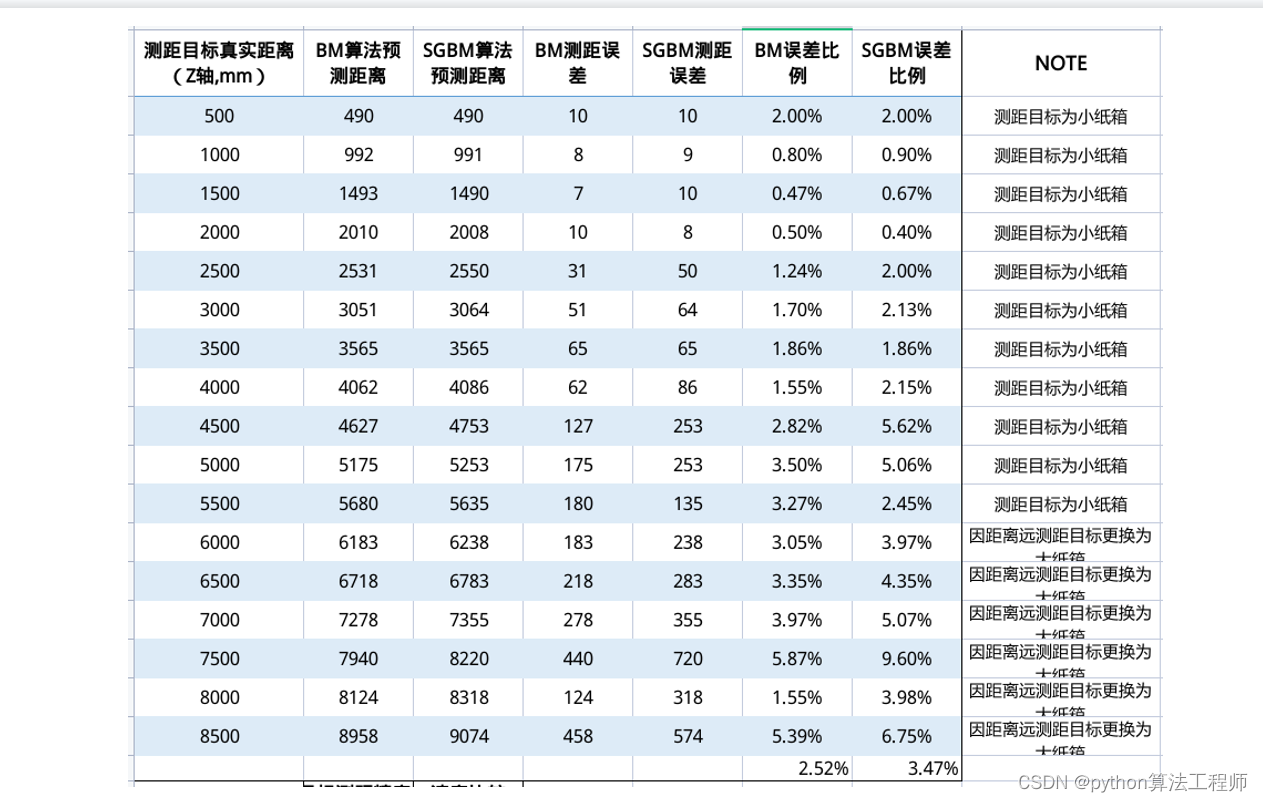
BM算法(Block Matching算法)是一种基于区块匹配的运动估计算法,常被用于视频压缩和视频编码中。BM算法认为当前帧与前一帧之间的像素运动是局部的,因此将图像分成若干个小区块,对每个区块进行运动估计,从而得到整个图像的运动场。
BM算法的具体步骤如下:
选择搜索窗口和匹配窗口
选择搜索窗口和匹配窗口的大小,搜索窗口用于在前一帧中搜索与当前区块相似的区块,匹配窗口用于计算两个区块之间的相似度。
- 计算相似度
将当前区块在搜索窗口中进行搜索,计算当前区块与搜索到的所有区块之间的相似度,找到相似度最高的区块作为匹配块。
- 估计运动向量
根据匹配块的位置和当前区块的位置,得到两个区块之间的运动向量,即当前区块的运动向量。
- 重复上述步骤
对图像中的每个区块都进行上述步骤,得到整个图像的运动场。
BM算法虽然简单,但其计算量较大,且对噪声和复杂运动的鲁棒性较差。因此,BM算法常常与其他运动估计算法结合使用,如Lucas-Kanade算法、Horn-Schunck算法等,以提高算法的精度和鲁棒性。


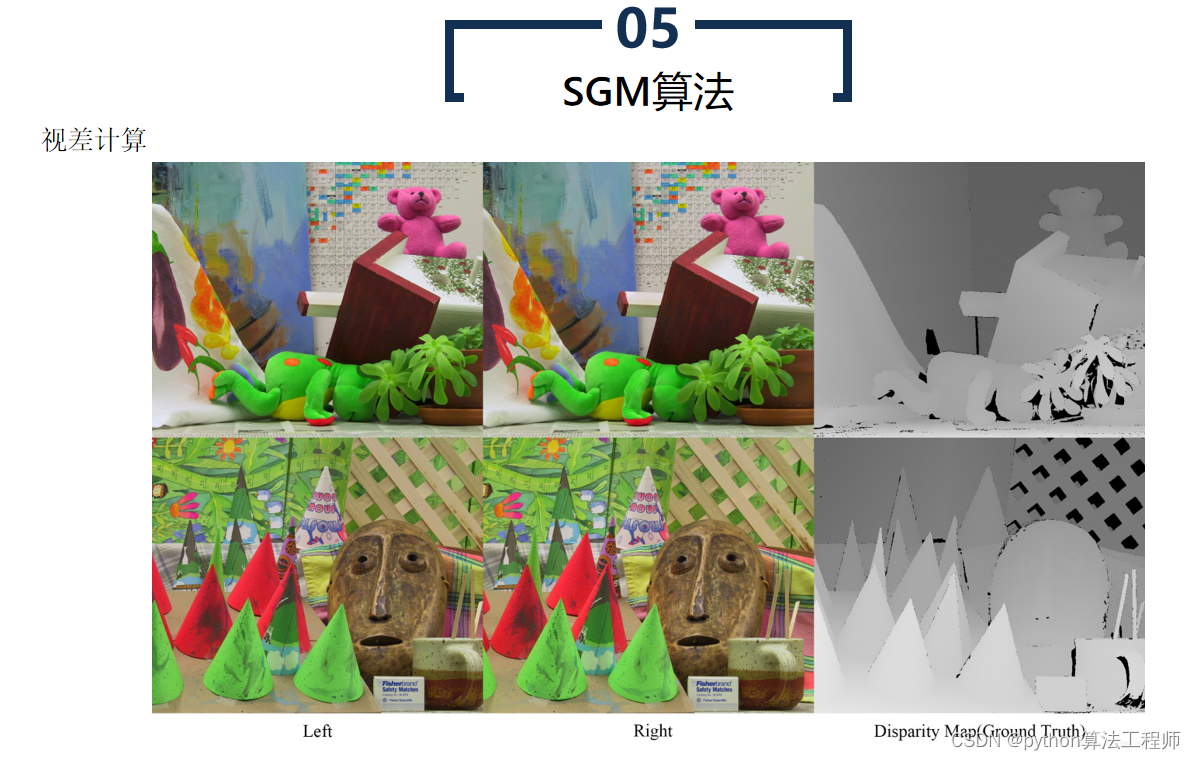
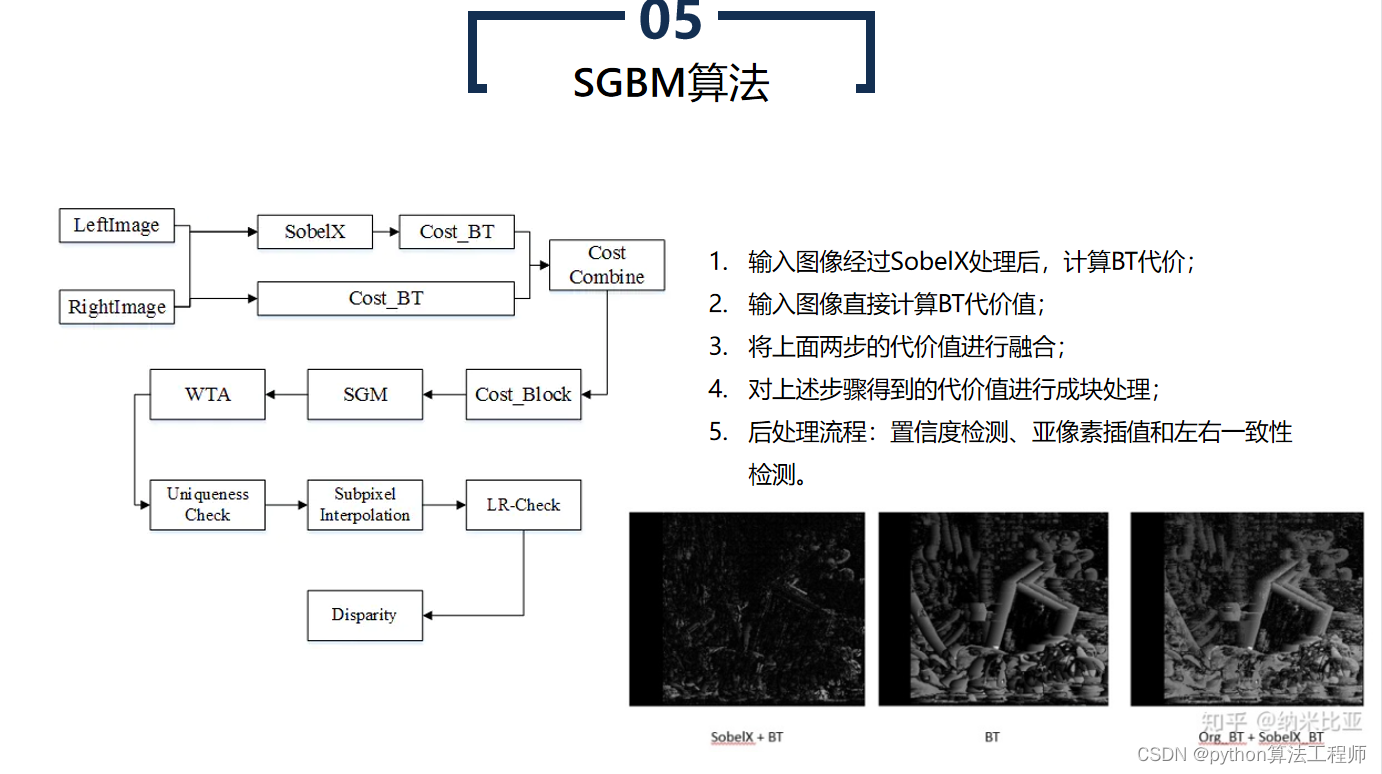
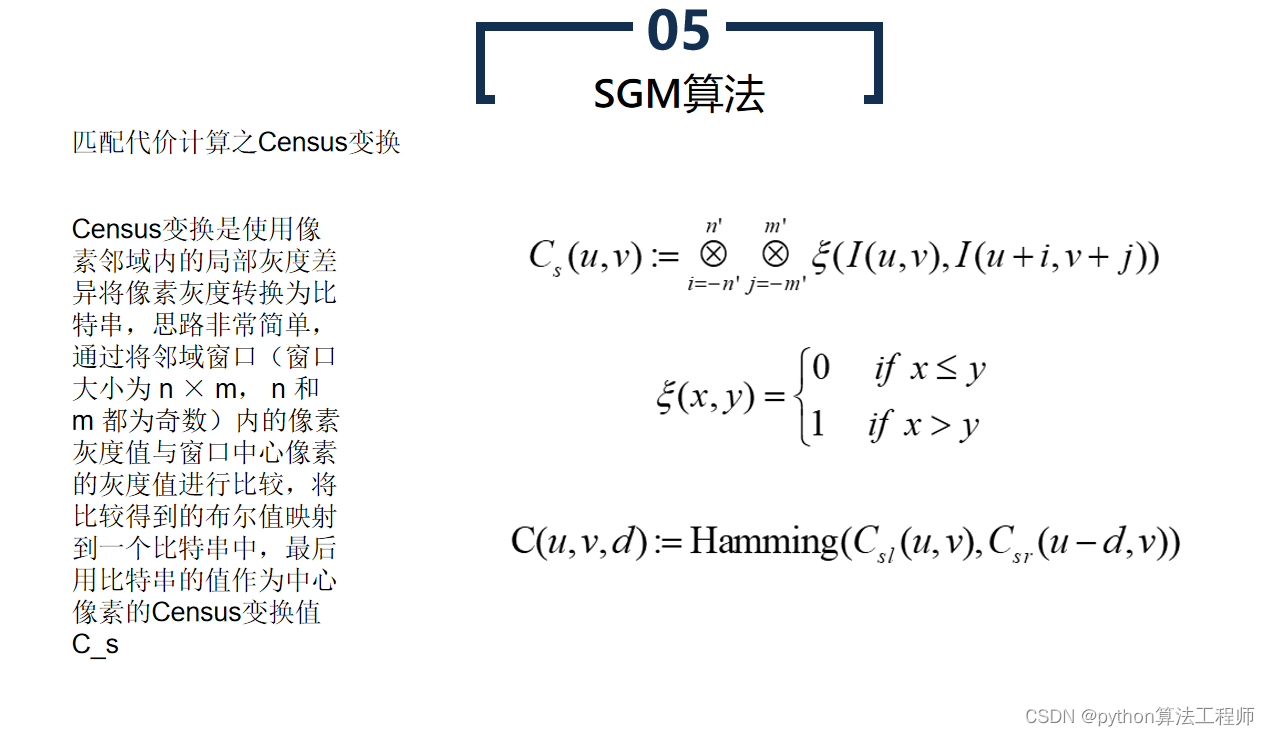
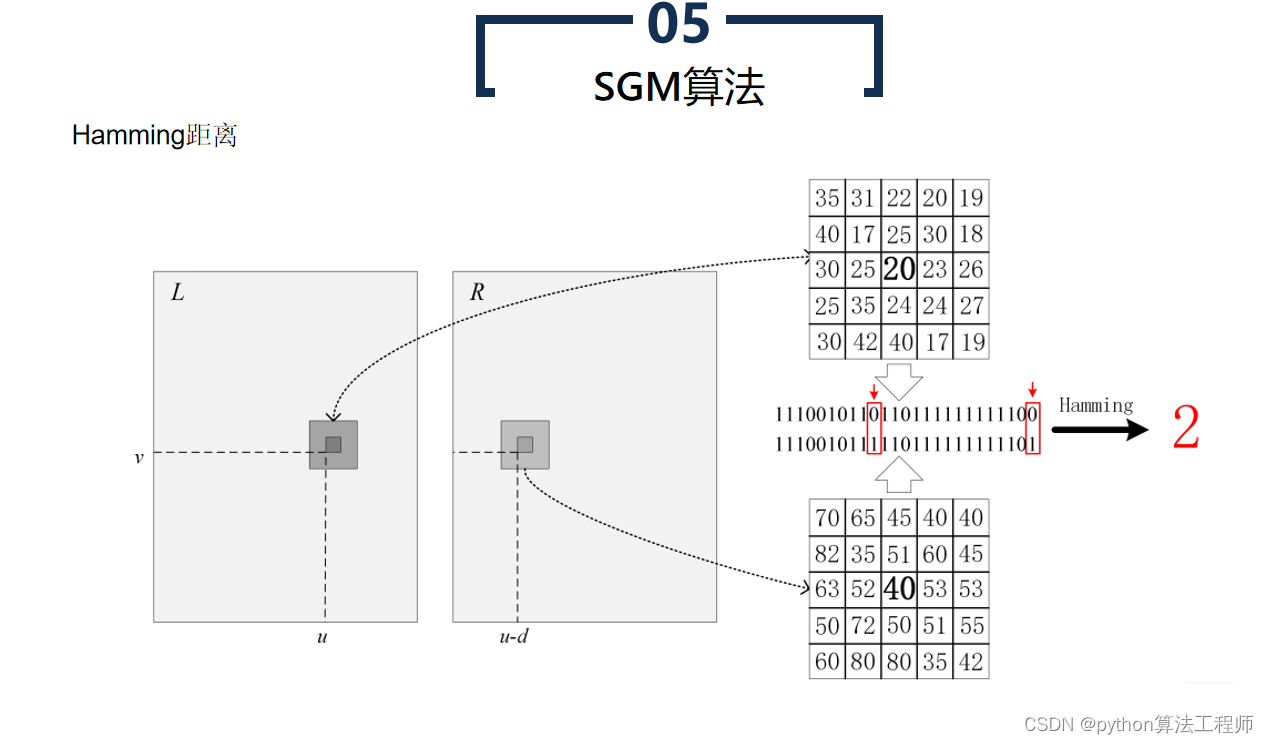
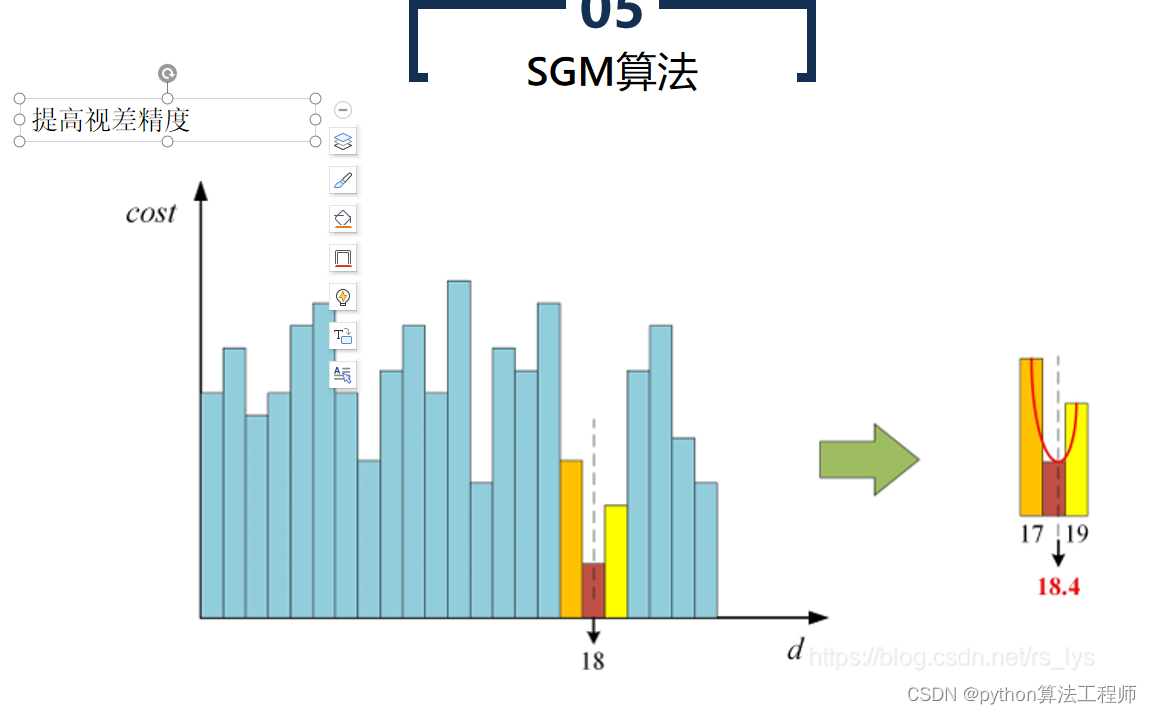
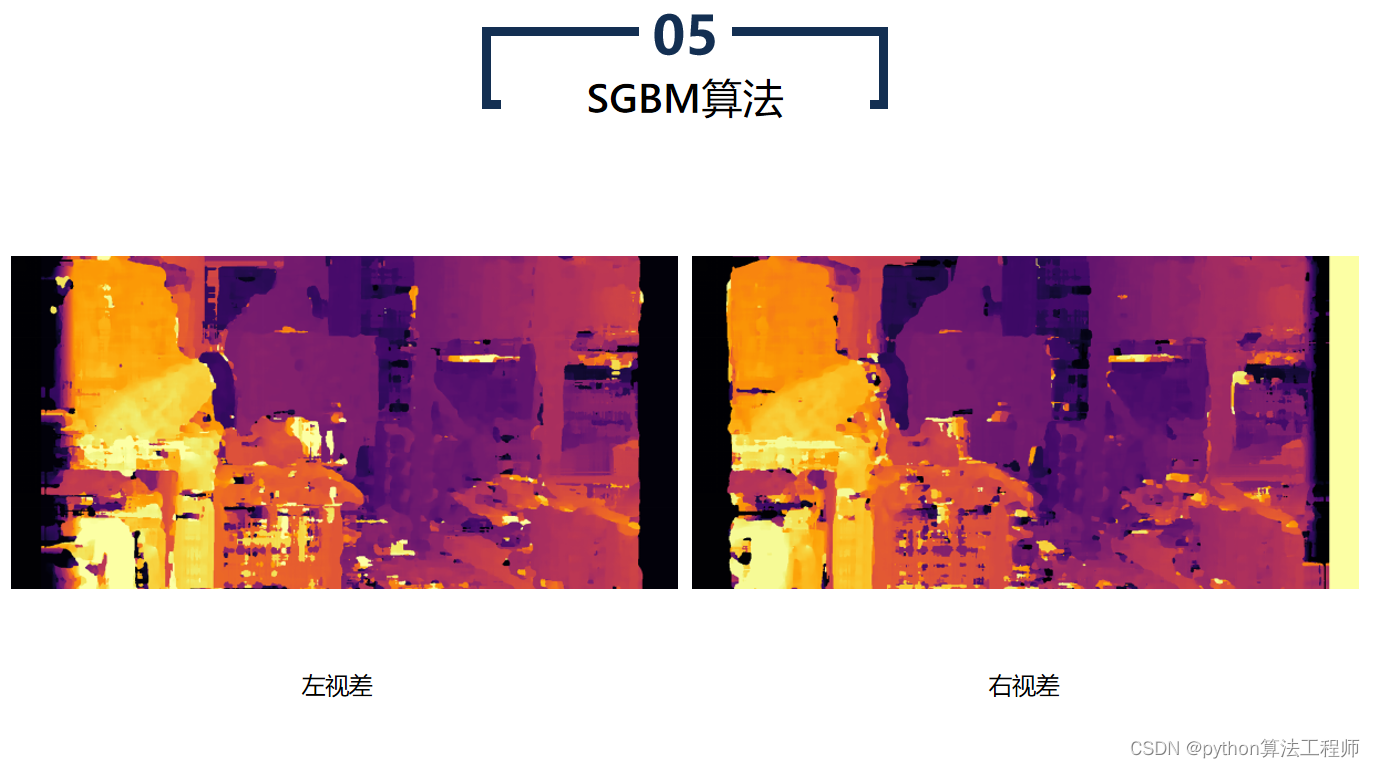
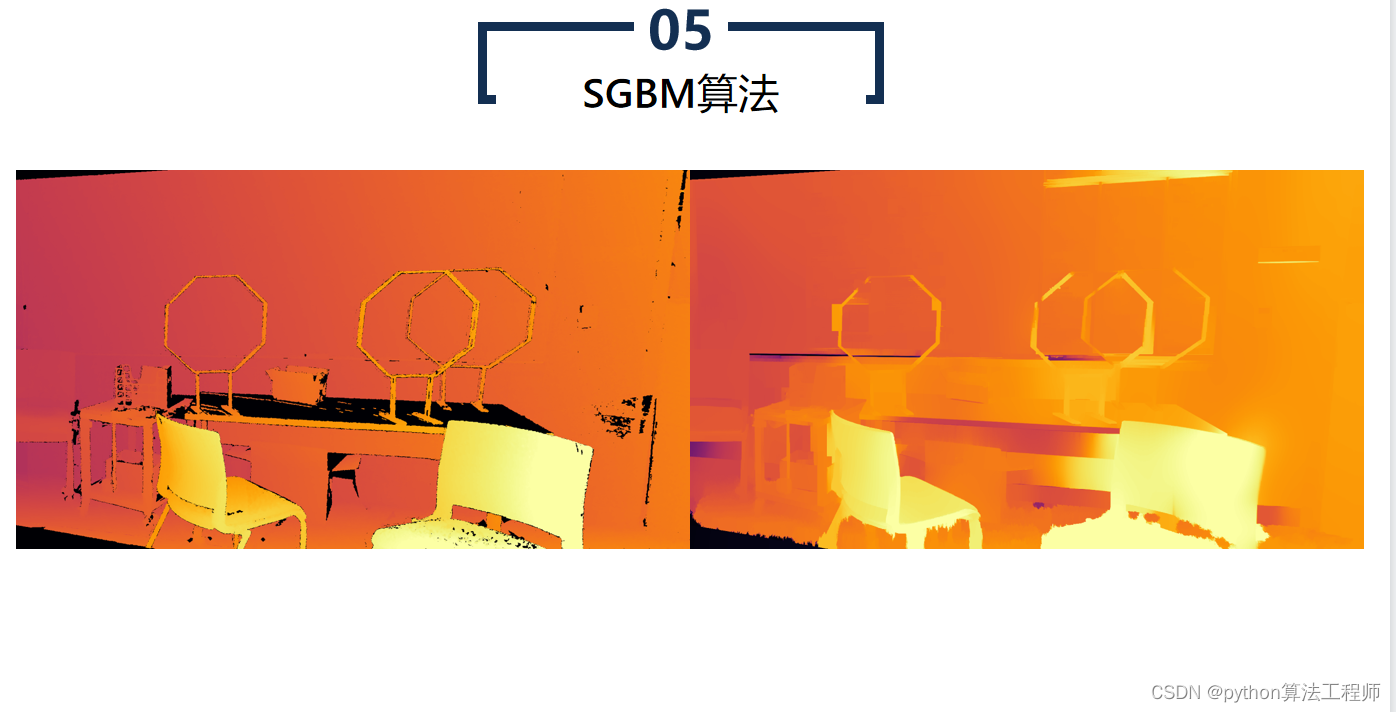
SGBM算法(Semi-Global Matching算法)是一种基于区块匹配的立体匹配算法,常用于计算立体图像中的视差图。SGBM算法是BM算法的改进版本,通过引入代价聚合和路径搜索等步骤,提高了算法的鲁棒性和精度。
SGBM算法的具体步骤如下:
- 预处理
对左右两个图像进行预处理,如去噪、灰度化、边缘检测等操作,以提高算法的精度和鲁棒性。
- 匹配代价计算
对每个像素,在预定义的搜索范围内,计算与其对应像素之间的匹配代价。常用的匹配代价包括灰度差异、SAD(Sum of Absolute Differences)代价、SSD(Sum of Squared Differences)代价等。
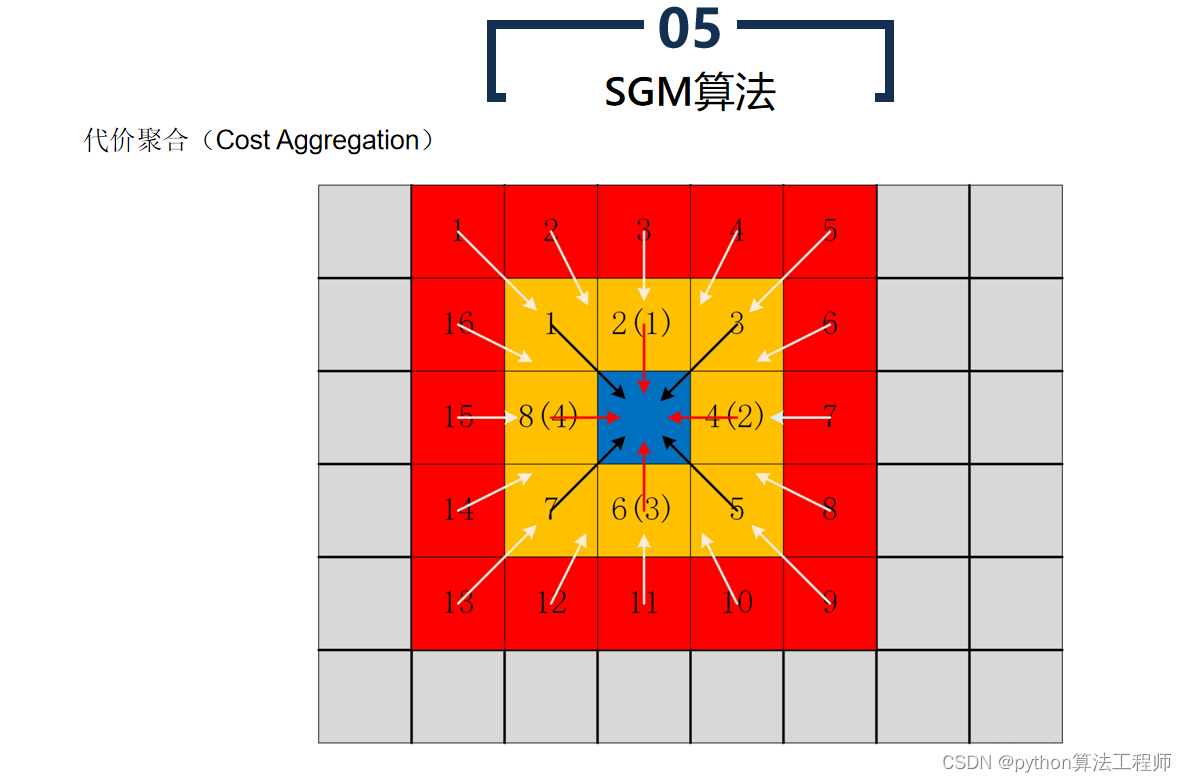
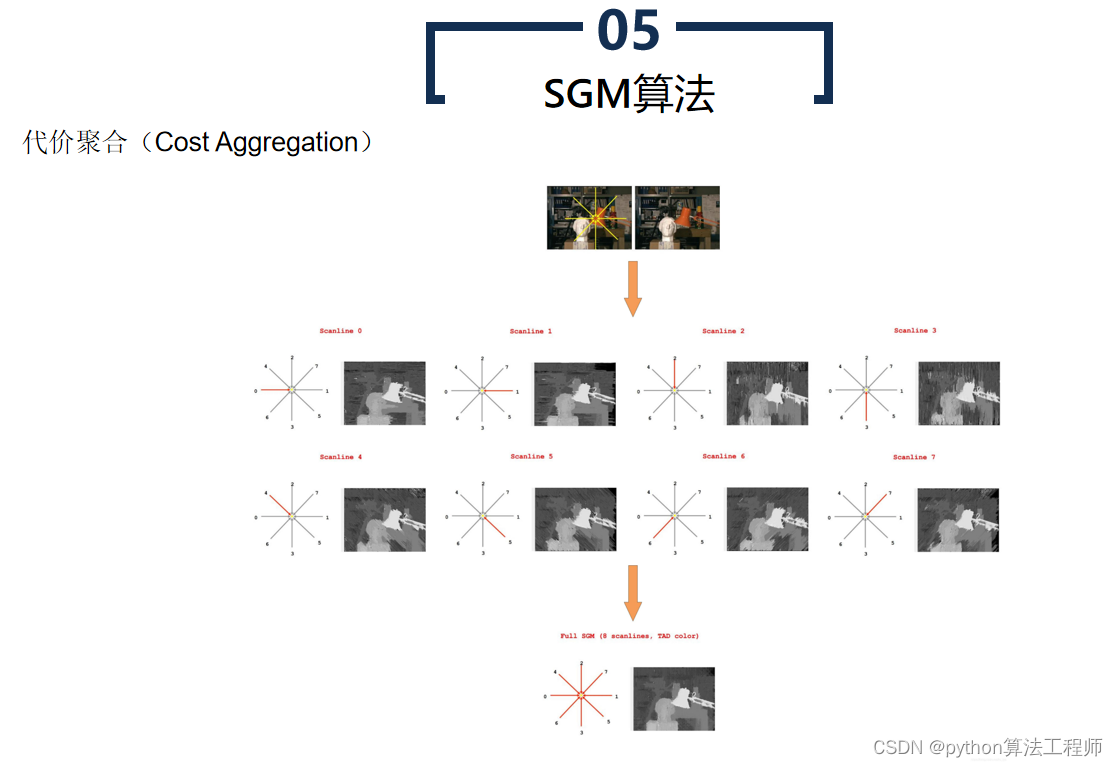
- 代价聚合
对每个像素,在预定义的搜索范围内,对其对应像素的匹配代价进行聚合,以获得代价的全局最小值。常用的代价聚合方法包括哈密尔顿路径(Hamiltonian path)搜索、动态规划(Dynamic Programming)等。
- 视差计算
根据代价聚合结果,计算每个像素的视差值。常用的视差计算方法包括平滑(Smoothing)和插值(Interpolation)等。
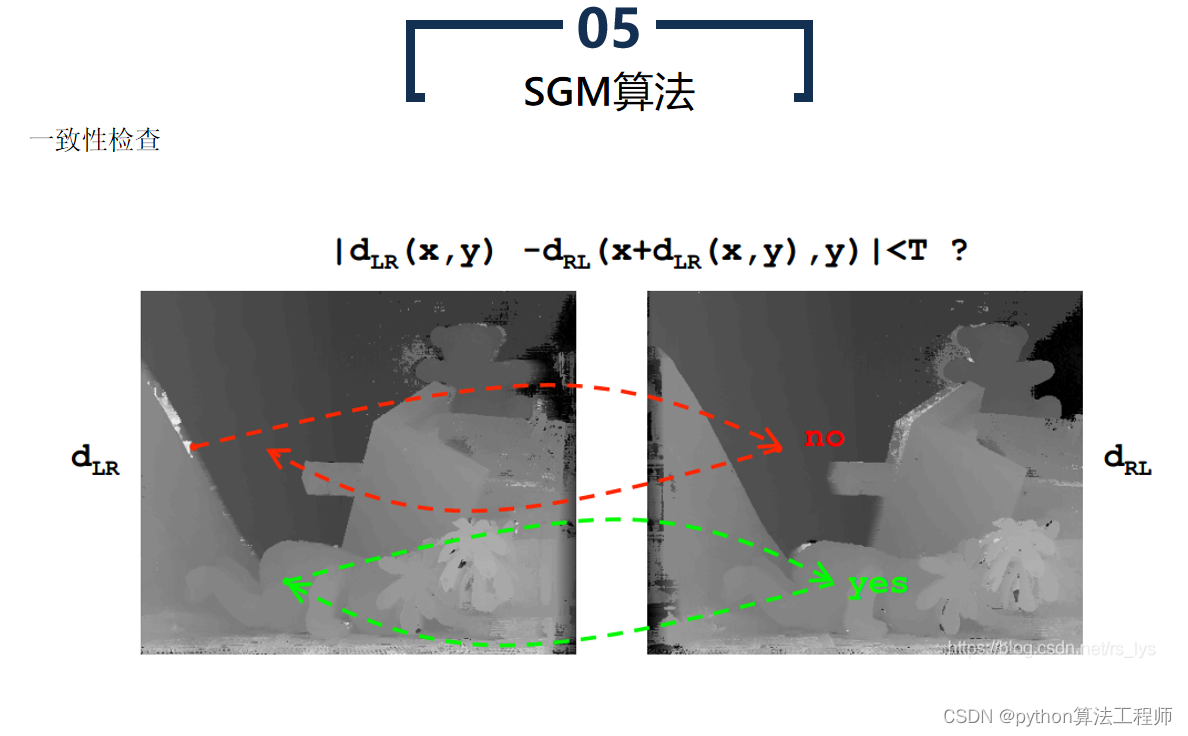
- 视差后处理
对视差图进行后处理,如去噪、填补空洞、边缘增强等,以获得更为准确的立体匹配结果。
SGBM算法相比于BM算法具有更高的精度和鲁棒性,但计算量较大,运行速度较慢。因此,SGBM算法常用于高精度的立体匹配场景,如机器人视觉、自动驾驶、工业检测等领域。




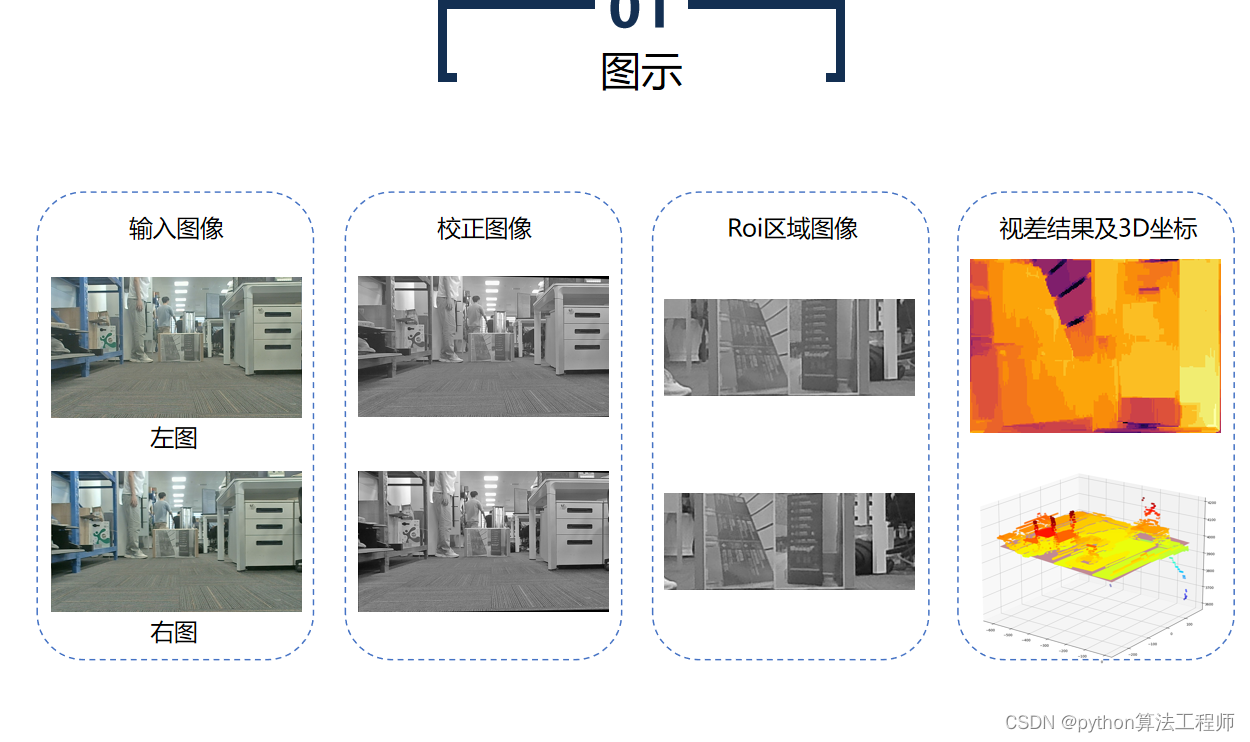
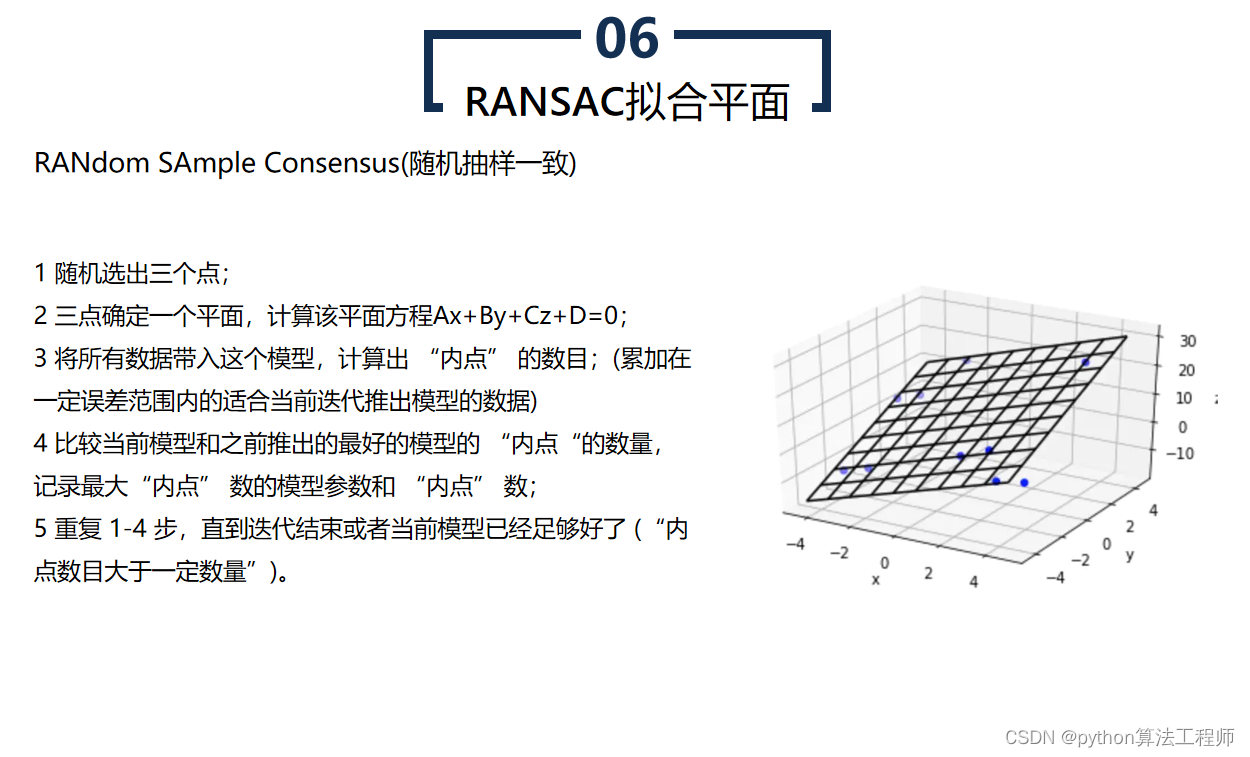
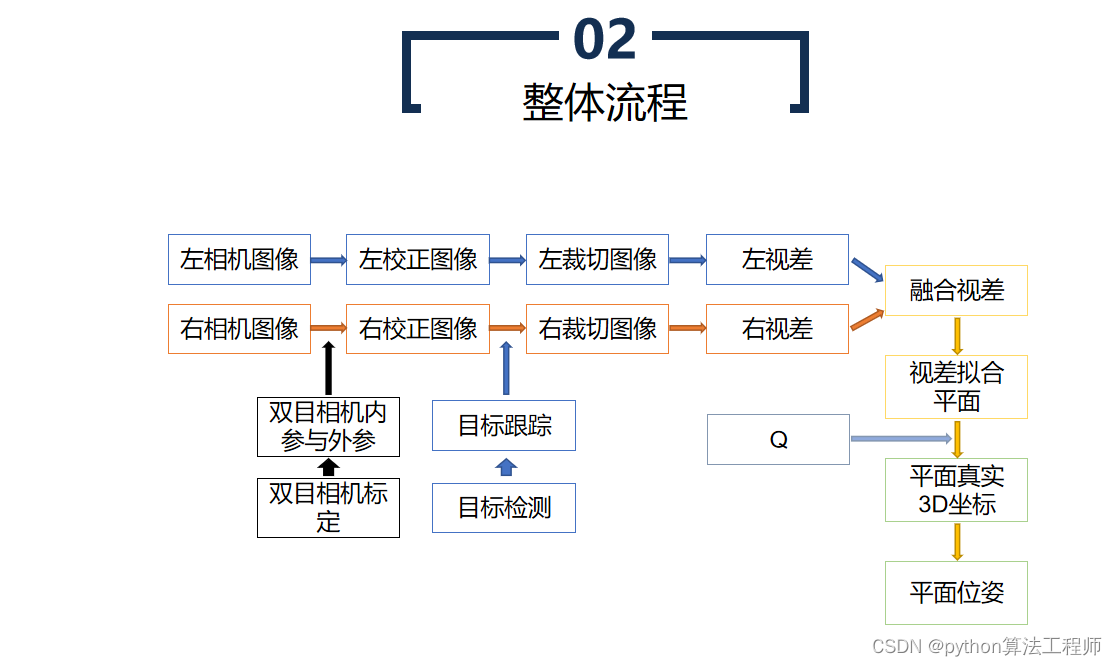 RANSAC是一种随机采样一致性算法,常用于拟合平面等模型。RANSAC算法可以在含有噪声和异常点的数据集中,从数据集中随机选择一个子集,通过拟合模型,寻找与模型一致的数据点,从而得到更为准确的模型参数。
RANSAC是一种随机采样一致性算法,常用于拟合平面等模型。RANSAC算法可以在含有噪声和异常点的数据集中,从数据集中随机选择一个子集,通过拟合模型,寻找与模型一致的数据点,从而得到更为准确的模型参数。
RANSAC拟合平面的具体步骤如下:
- 随机采样
从数据集中随机选择一小部分数据点,假设这些数据点能够拟合成一个平面模型。
- 模型拟合
基于选择的数据点,拟合一个平面模型,计算平面模型的参数,如平面法向量和平面方程。
- 点选择
对于未被选择的数据点,计算其到拟合平面的距离。如果距离小于阈值,将该点标记为内点。
- 估计模型
如果内点数大于一个阈值,则使用内点重新计算平面模型的参数。如果内点数不足,则返回第1步,重新随机选择数据点。
- 重复迭代
重复执行上述步骤,直到满足停止条件。停止条件可以是达到最大迭代次数、内点比例达到一定阈值等。
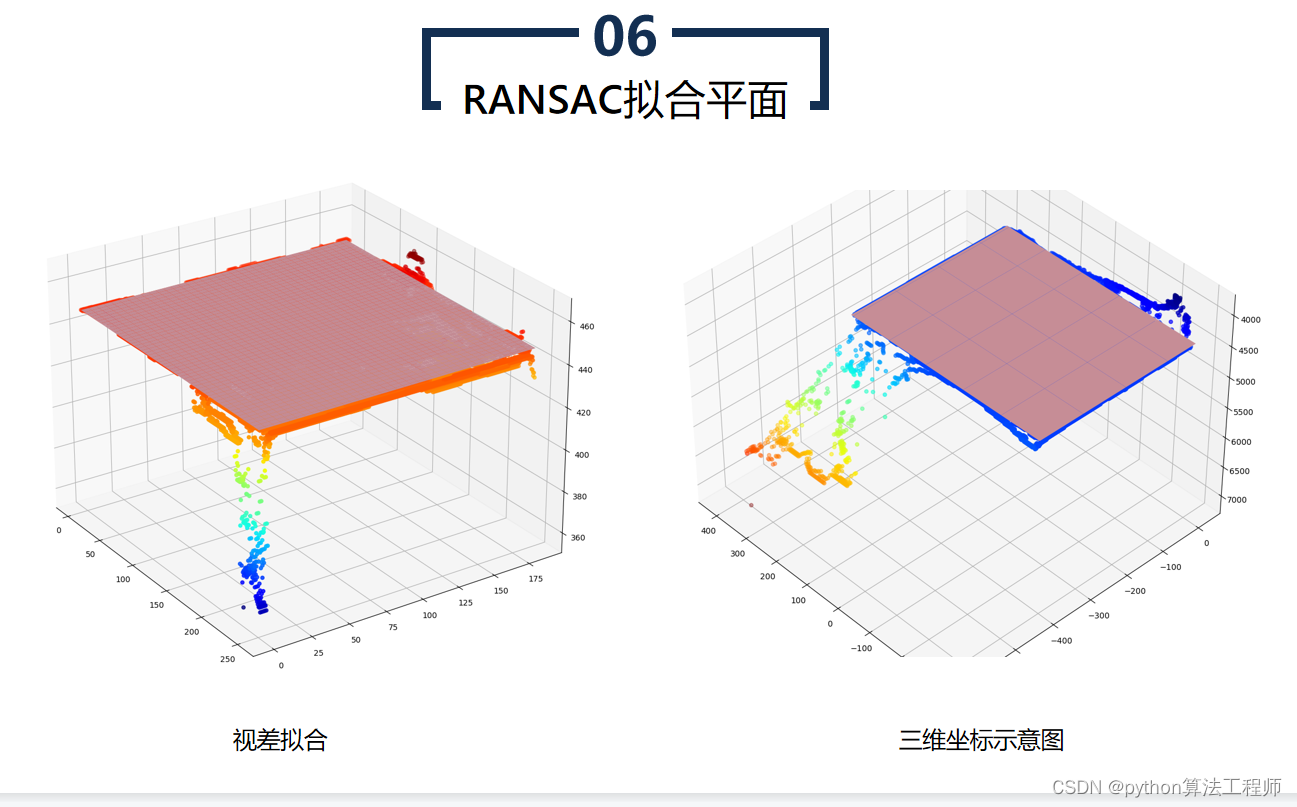
通过RANSAC算法拟合平面,可以有效地去除数据集中的异常点和噪声,得到更为准确的平面模型。RANSAC算法在计算机视觉、机器人视觉、图像处理等领域中得到广泛应用。
 目标检测与追踪是计算机视觉领域中的重要问题,目的是在图像或视频中检测和跟踪感兴趣的目标物体。目标检测和追踪对于自动驾驶、智能监控、机器人视觉等领域都具有重要的应用价值。
目标检测与追踪是计算机视觉领域中的重要问题,目的是在图像或视频中检测和跟踪感兴趣的目标物体。目标检测和追踪对于自动驾驶、智能监控、机器人视觉等领域都具有重要的应用价值。
目标检测主要包括以下步骤:
- 图像预处理
对输入的图像进行预处理,如图像去噪、灰度化、边缘检测等操作。
- 特征提取
通过特征提取算法,从图像中提取有用的特征,如颜色、纹理、形状等特征。
- 候选框生成
基于特征提取结果,使用候选框生成算法,生成可能包含目标的候选框。
- 候选框分类
对于生成的候选框,使用目标分类算法,判断该候选框是否包含目标。
- 目标定位
对于包含目标的候选框,使用目标定位算法,得到目标物体的位置和大小。
目标追踪主要包括以下步骤:
- 目标匹配
将当前帧中的目标与上一帧中的目标进行匹配,以确定目标的运动轨迹。
- 运动预测
基于目标的运动轨迹,预测目标在下一帧中的位置。
- 目标检测
在下一帧中,对目标进行检测,以确定目标的位置和大小。
- 目标跟踪
将当前帧中的目标与上一帧中的目标进行匹配,以确定目标的运动轨迹。
目标检测与追踪是计算机视觉领域中的重要问题,需要结合多种算法和技术,如深度学习、图像处理、运动估计等。目前,基于深度学习的目标检测和追踪算法已经成为主流,如YOLO、Faster R-CNN、SORT等算法,具有较高的检测和追踪精度和速度。
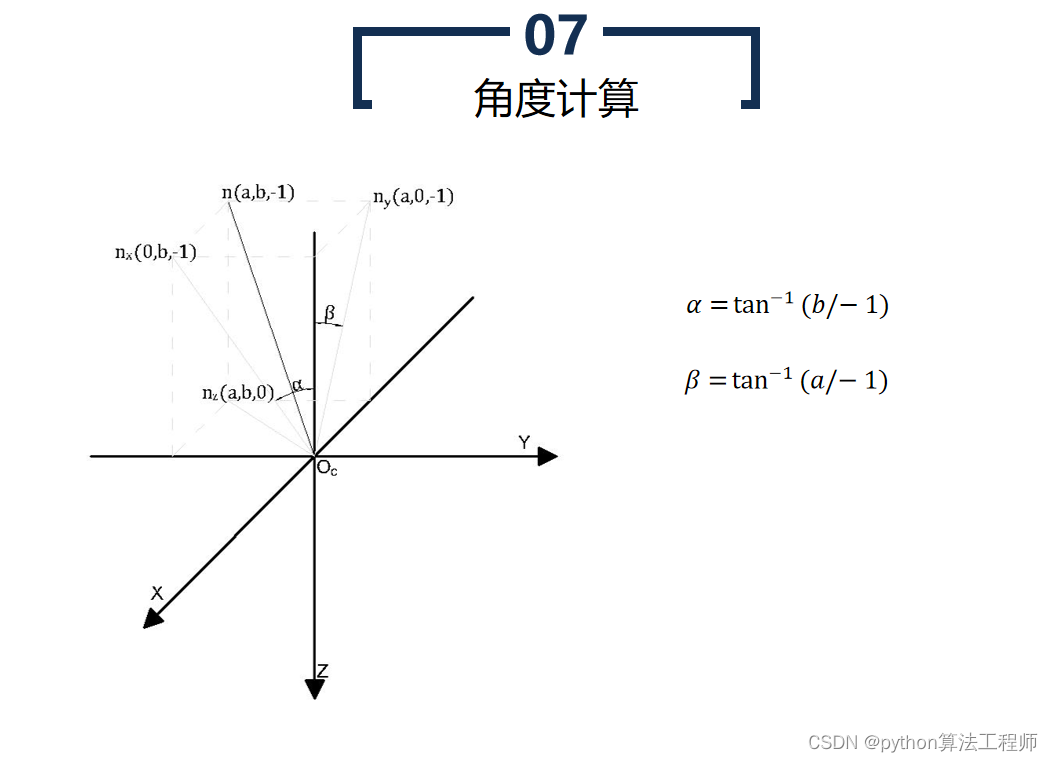
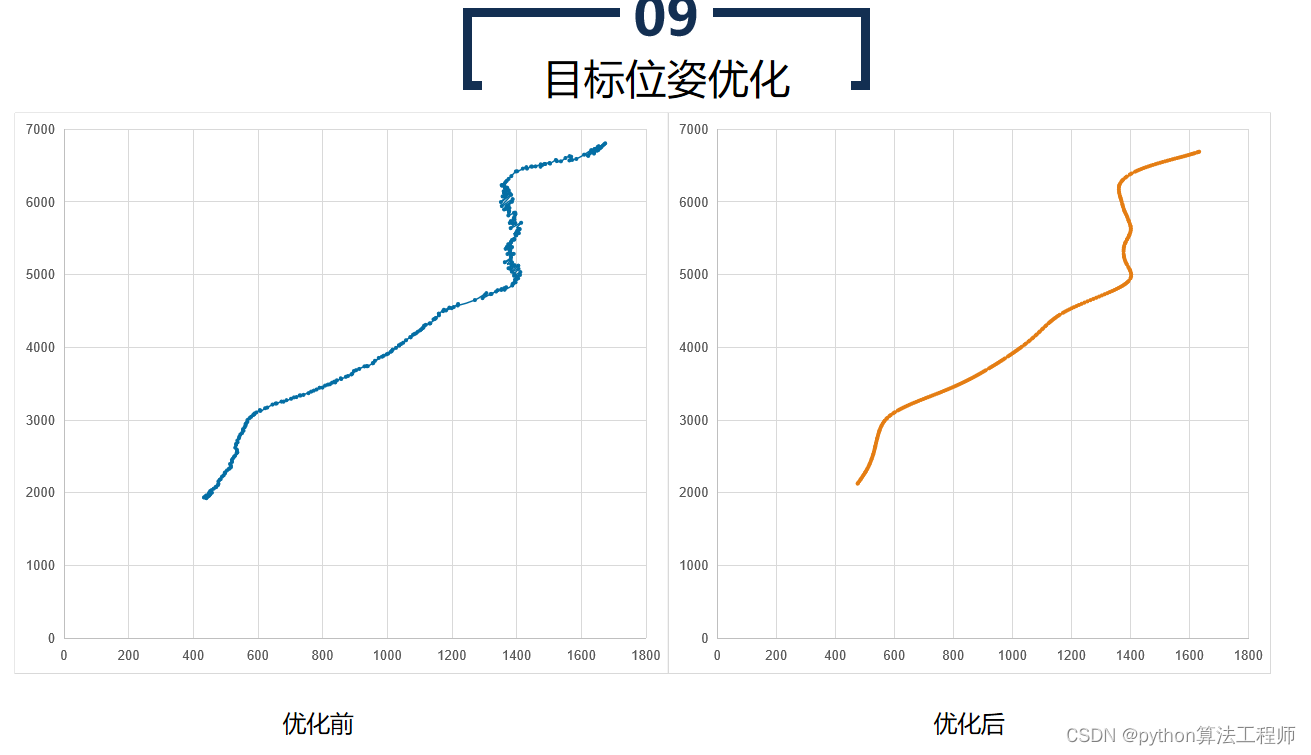
 目标位姿优化是指通过优化算法,寻找目标物体在三维空间中的位姿(位置和姿态),使其尽可能地与真实物体的位姿一致。目标位姿优化通常用于机器人视觉、自动驾驶、工业检测等领域,以实现精准的目标定位和姿态控制。
目标位姿优化是指通过优化算法,寻找目标物体在三维空间中的位姿(位置和姿态),使其尽可能地与真实物体的位姿一致。目标位姿优化通常用于机器人视觉、自动驾驶、工业检测等领域,以实现精准的目标定位和姿态控制。
目标位姿优化的具体步骤如下:
- 数据采集
通过相机或传感器采集目标物体的图像或点云数据,并进行预处理和特征提取。
- 初始位姿估计
根据预处理后的数据,使用初始位姿估计算法,估计目标物体的初始位姿。常用的初始位姿估计算法包括3D-3D、3D-2D、PnP等。
- 目标位姿优化
将初始位姿作为优化的初始状态,通过优化算法,寻找最优的目标位姿,使其尽可能地与真实物体的位姿一致。常用的优化算法包括非线性最小二乘法、Levenberg-Marquardt算法、高斯-牛顿算法等。
- 位姿反馈控制
根据优化得到的目标位姿,对机器人或其他设备进行反馈控制,使其移动到目标位置并调整姿态。
目标位姿优化可以提高目标定位和姿态控制的精度和鲁棒性,可以应用于机器人自主导航、机器人抓取、工业检测等领域,具有广泛的应用前景。
sgbm-video.py
import cv2
import numpy as np
import random
import math
# 左镜头的内参,如焦距
left_camera_matrix = np.array([[516.5066236,-1.444673028,320.2950423],[0,516.5816117,270.7881873],[0.,0.,1.]])
right_camera_matrix = np.array([[511.8428182,1.295112628,317.310253],[0,513.0748795,269.5885026],[0.,0.,1.]])
# 畸变系数,K1、K2、K3为径向畸变,P1、P2为切向畸变
# left_distortion = np.array([[-0.154511565,0.325173292, 0.006934081,0.017466934, -0.340007548]])
left_distortion = np.array([[-0.046645194,0.077595167, 0.012476819,-0.000711358,0]])
# right_distortion = np.array([[-0.192887524,0.706728768, 0.004233541,0.021340116,-1.175486913]])
right_distortion = np.array([[-0.061588946,0.122384376,0.011081232,-0.000750439,0]])
# 旋转矩阵
R = np.array([[0.999911333,-0.004351508,0.012585312],
[0.004184066,0.999902792,0.013300386],
[-0.012641965,-0.013246549,0.999832341]])
# 平移矩阵
T = np.array([-120.3559901,-0.188953775,-0.662073075])
size = (640, 480)
R1, R2, P1, P2, Q, validPixROI1, validPixROI2 = cv2.stereoRectify(left_camera_matrix, left_distortion,
right_camera_matrix, right_distortion, size, R,
T)
# 校正查找映射表,将原始图像和校正后的图像上的点一一对应起来
left_map1, left_map2 = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(left_camera_matrix, left_distortion, R1, P1, size, cv2.CV_16SC2)
right_map1, right_map2 = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(right_camera_matrix, right_distortion, R2, P2, size, cv2.CV_16SC2)
print(Q)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 鼠标回调函数
def onmouse_pick_points(event, x, y, flags, param):
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
threeD = param
print('\n像素坐标 x = %d, y = %d' % (x, y))
# print("世界坐标是:", threeD[y][x][0], threeD[y][x][1], threeD[y][x][2], "mm")
print("世界坐标xyz 是:", threeD[y][x][0] / 1000.0, threeD[y][x][1] / 1000.0, threeD[y][x][2] / 1000.0, "m")
distance = math.sqrt(threeD[y][x][0] ** 2 + threeD[y][x][1] ** 2 + threeD[y][x][2] ** 2)
distance = distance / 1000.0 # mm -> m
print("距离是:", distance, "m")
# 2 加载视频文件
# capture = cv2.VideoCapture("output.avi")
capture = cv2.VideoCapture(1)
WIN_NAME = 'Deep disp'
cv2.namedWindow(WIN_NAME, cv2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE)
# 3 读取视频
ret, frame = capture.read()
while ret:
# 4 ret 是否读取到了帧,读取到了则为True
cv2.imshow("video", frame)
ret, frame = capture.read()
img_color = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
frame1 = frame[0:480, 0:640]
frame2 = frame[0:480, 640:1280] # 割开双目图像
imgL = cv2.cvtColor(frame1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 将BGR格式转换成灰度图片
imgR = cv2.cvtColor(frame2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# cv2.remap 重映射,就是把一幅图像中某位置的像素放置到另一个图片指定位置的过程。
# 依据MATLAB测量数据重建无畸变图片
img1_rectified = cv2.remap(imgL, left_map1, left_map2, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
img2_rectified = cv2.remap(imgR, right_map1, right_map2, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
imageL = cv2.cvtColor(img1_rectified, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
imageR = cv2.cvtColor(img2_rectified, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
cv2.imshow("img-L", imageL)
cv2.imshow("img-R", imageR)
# SGBM-室外
blockSize = 8
img_channels = 3
stereo = cv2.StereoSGBM_create(minDisparity=1,
numDisparities=64,
blockSize=blockSize,
P1=8 * img_channels * blockSize * blockSize,
P2=32 * img_channels * blockSize * blockSize,
disp12MaxDiff=-1,
preFilterCap=1,
uniquenessRatio=10,
speckleWindowSize=100,
speckleRange=100,
mode=cv2.STEREO_SGBM_MODE_HH)
disparity = stereo.compute(img1_rectified, img2_rectified) # 计算视差
disp = cv2.normalize(disparity, disparity, alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U) # 归一化函数算法
threeD = cv2.reprojectImageTo3D(disparity, Q, handleMissingValues=True) # 计算三维坐标数据值
threeD = threeD * 16
# threeD[y][x] x:0~640; y:0~480; !!!!!!!!!!
cv2.setMouseCallback(WIN_NAME, onmouse_pick_points, threeD) # 鼠标回调事件
#
# # 三维重建代码
# import open3d as o3d
#
dis_color = disparity
dis_color = cv2.normalize(dis_color, None, alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U)
dis_color = cv2.applyColorMap(dis_color, 2)
cv2.imshow("depth", dis_color)
cv2.imshow("left", frame1)
cv2.imshow(WIN_NAME, disp) # 显示深度图的双目画面
# 5 若键盘按下q则退出播放
if cv2.waitKey(20) & 0xff == ord('q'):
break
# 4 释放资源
capture.release()
# 5 关闭所有窗口
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
sgbm_img.py
'''
Author: YeHanyu
Date: 2022-08-02 11:32:58
LastEditors: YeHanyu
LastEditTime: 2022-08-09 18:09:38
FilePath: /SGBM/sgbm_img.py
Description:
Copyright (c) 2022 by YeHanyu, All Rights Reserved.
'''
import cv2
import numpy as np
import random
import math
# import pcl
# import pcl.pcl_visualization
import time
from scipy.optimize import leastsq
# from scipy import io
# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
camera = '720p'
gt_pred = False
v_size = 5
Dst_mode = 'Z'
leastsq_mode = True
point_x = 0
point_y = 0
if camera=='kitti':
# 左镜头的内参,如焦距
left_camera_matrix = np.array([[718.856,0,607.1928], [0, 718.856, 185.2157],[0.,0.,1.]])
right_camera_matrix = np.array([[718.856,0,607.1928], [0, 718.856, 185.2157],[0.,0.,1.]])
# 畸变系数,K1、K2、K3为径向畸变,P1、P2为切向畸变
# left_distortion = np.array([[-0.154511565,0.325173292, 0.006934081,0.017466934, -0.340007548]])
left_distortion = np.array([[0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0]])
# right_distortion = np.array([[-0.192887524,0.706728768, 0.004233541,0.021340116,-1.175486913]])
right_distortion = np.array([[0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0]])
# 旋转矩阵
R = np.array([[1,0.0,0.0],
[0.0,1,0.0],
[0.0,0.0,1]])
# 平移矩阵
T = np.array([537.165719, 0, 0])
size = (1241, 376)
elif camera=='720p':
# 左镜头的内参,如焦距
left_camera_matrix = np.array([[730.207611356134, 0, 617.761835197854],
[0, 729.722484488817, 356.281832636247],
[0., 0., 1.]])
right_camera_matrix = np.array([[726.617693292221, 0, 615.126833857842],
[0, 726.598401621709, 355.079105280920],
[0.,0.,1.]])
# 畸变系数,K1、K2、K3为径向畸变,P1、P2为切向畸变
# left_distortion=[K1,K2,P1,P2,K3]
# left_distortion = np.array([[-0.154511565,0.325173292, 0.006934081,0.017466934, -0.340007548]])
left_distortion = np.array([[0.114254497790507,-0.153178688236797,0,0,0]])
# right_distortion = np.array([[-0.192887524,0.706728768, 0.004233541,0.021340116,-1.175486913]])
right_distortion = np.array([[0.101619261365358,-0.128310783815266, 0, 0,0]])
# 旋转矩阵
R = np.array([[1,0.000117007865065619,0.000551464061148515],
[-0.000116357622553170,1,-0.00117900500140576],
[-0.000551601626991256,0.00117894064701274,1]])
# 平移矩阵
T = np.array([-59.9695960974267,-0.00773947743447085,0.298781994352248])
size = (1280, 720)
R1, R2, P1, P2, Q, validPixROI1, validPixROI2 = cv2.stereoRectify(left_camera_matrix, left_distortion,
right_camera_matrix, right_distortion, size, R,
T)
# 校正查找映射表,将原始图像和校正后的图像上的点一一对应起来
left_map1, left_map2 = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(left_camera_matrix, left_distortion, R1, P1, size, cv2.CV_16SC2)
right_map1, right_map2 = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(right_camera_matrix, right_distortion, R2, P2, size, cv2.CV_16SC2)
def pcl_show(three, rgbimg):
color = rgbimg.reshape(720*1280,3)
three[np.isinf(three)]=0
three[three > 10000] = 10000
three[three < -10000] = -10000
temp = np.zeros((720, 1280, 4))
temp[:,:,0:3] = three
temp=temp.reshape(720*1280,4)
temp=temp/1000
temp = temp.astype(np.float32)
for i in range(color.shape[0]):
rgb = np.left_shift(color[i,2], 16) + np.left_shift(color[i,1],8) + np.left_shift(color[i,0], 0)
# c = (color[i,2]<<16)|(color[i,1]<<8)|color[i,0]
temp[i,3] = rgb
# temp[:,3] = 1.6777215
cloud0 = pcl.PointCloud_PointXYZRGBA()
cloud0.from_array(temp)
# color_cloud = pcl.PointCloud_PointXYZRGB(temp)
# pcl.savePCD('scen.pcd', color_cloud)
visual = pcl.pcl_visualization.CloudViewing()
visual.ShowColorACloud(cloud0)
v = True
while v:
v = not(visual.WasStopped())
def bm(rimg1, rimg2):
# rimg1 = cv2.cvtColor(rimg1, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
# rimg2 = cv2.cvtColor(rimg2, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
left_matcher = cv2.StereoBM_create(numDisparities=16, blockSize=9)
left_matcher.setROI1(validPixROI1)
left_matcher.setROI2(validPixROI2)
left_matcher.setPreFilterCap(31)
left_matcher.setBlockSize(15)
left_matcher.setMinDisparity(0)
left_matcher.setNumDisparities(128)
left_matcher.setTextureThreshold(10)
left_matcher.setUniquenessRatio(15)
left_matcher.setSpeckleWindowSize(100)
left_matcher.setSpeckleRange(1)
left_matcher.setDisp12MaxDiff(1)
right_matcher = cv2.ximgproc.createRightMatcher(left_matcher)
lmbda = 8000
sigma = 1.5
wls_filter = cv2.ximgproc.createDisparityWLSFilter(matcher_left=left_matcher)
wls_filter.setLambda(lmbda)
wls_filter.setSigmaColor(sigma)
t0 = time.time()
displ = left_matcher.compute(rimg1, rimg2)
dispr = right_matcher.compute(rimg2, rimg1)
t1 = time.time()
print('BM计算时间',t1-t0)
# displ_show = cv2.normalize(displ,displ,alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U)
# dispr_show = cv2.normalize(dispr,dispr,alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U)
# cv2.imshow('L', displ_show)
# cv2.imshow('R', dispr_show)
displ = np.int16(displ)
dispr = np.int16(dispr)
t0 = time.time()
disparity = wls_filter.filter(displ, rimg1, None, dispr)
t1 = time.time()
print('BM融合时间',t1-t0)
return disparity
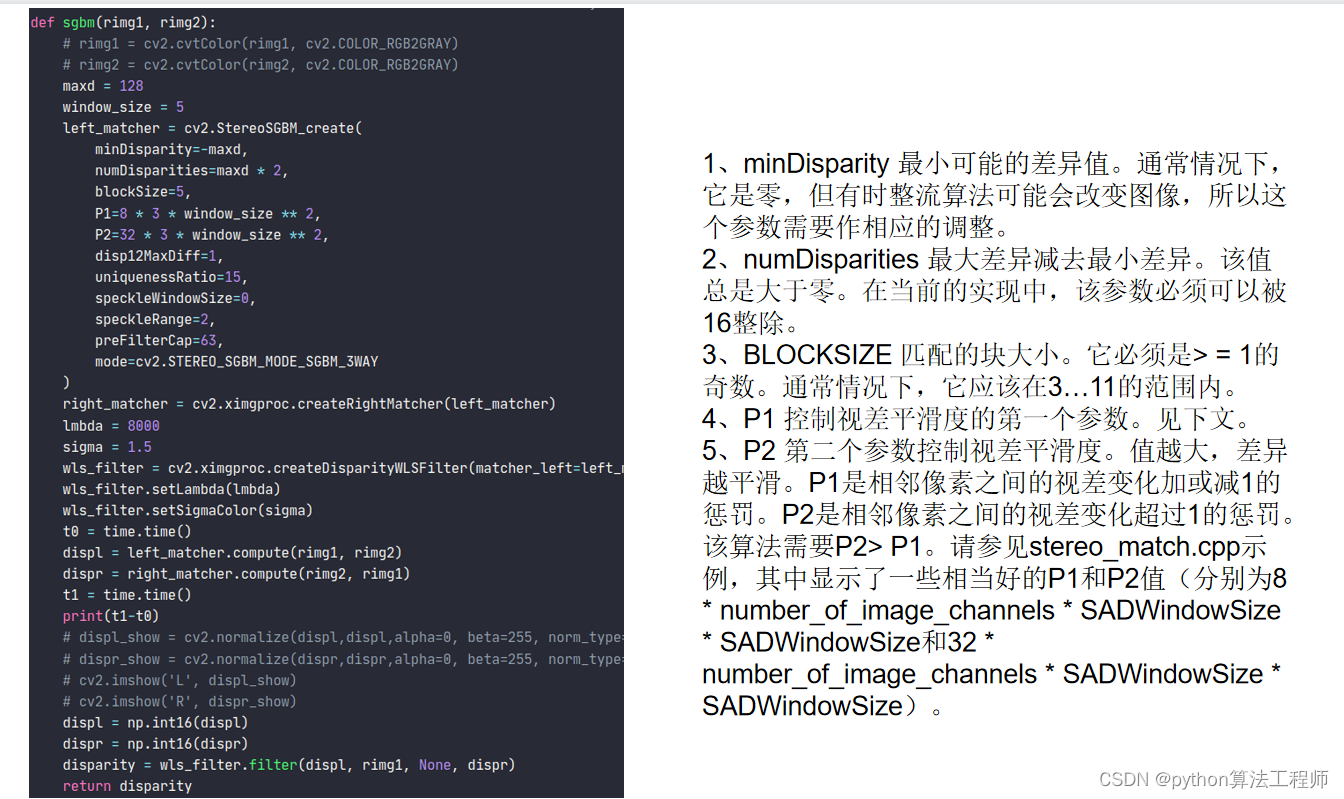
def sgbm(rimg1, rimg2):
# rimg1 = cv2.cvtColor(rimg1, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
# rimg2 = cv2.cvtColor(rimg2, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
maxd = 128
window_size = 5
left_matcher = cv2.StereoSGBM_create(
minDisparity=-maxd,
numDisparities=maxd * 2,
blockSize=5,
P1=8 * 3 * window_size ** 2,
P2=32 * 3 * window_size ** 2,
disp12MaxDiff=1,
uniquenessRatio=15,
speckleWindowSize=100,
speckleRange=2,
preFilterCap=31,
mode=cv2.STEREO_SGBM_MODE_SGBM_3WAY
)
right_matcher = cv2.ximgproc.createRightMatcher(left_matcher)
lmbda = 8000
sigma = 1.5
wls_filter = cv2.ximgproc.createDisparityWLSFilter(matcher_left=left_matcher)
wls_filter.setLambda(lmbda)
wls_filter.setSigmaColor(sigma)
t0 = time.time()
displ = left_matcher.compute(rimg1, rimg2)
dispr = right_matcher.compute(rimg2, rimg1)
t1 = time.time()
print('SGBM计算时间',t1-t0)
# displ_show = cv2.normalize(displ,displ,alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U)
# dispr_show = cv2.normalize(dispr,dispr,alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U)
# cv2.imshow('L', displ_show)
# cv2.imshow('R', dispr_show)
displ = np.int16(displ)
dispr = np.int16(dispr)
t0 = time.time()
disparity = wls_filter.filter(displ, rimg1, None, dispr)
t1 = time.time()
print('SGBM融合时间',t1-t0)
return disparity
def dist(threeD,x,y):
out=[]
for i in range(v_size):
for j in range(v_size):
if Dst_mode == 'Z':
temp = threeD[y-v_size//2+i][x-v_size//2+j][2]/1000
out.append(temp)
else:
temp = math.sqrt(threeD[y-v_size//2+i][x-v_size//2+j][0] ** 2 + threeD[y-v_size//2+i][x-v_size//2+j][1] ** 2 + threeD[y-v_size//2+i][x-v_size//2+j][2] ** 2)/1000
out.append(temp)
return sum(out)/len(out)
def augment(xyzs):
axyz = np.ones((len(xyzs), 4))
axyz[:, :3] = xyzs
return axyz
def estimate(xyzs):
axyz = augment(xyzs[:3])
return np.linalg.svd(axyz)[-1][-1, :]
def is_inlier(coeffs, xyz, threshold):
return np.abs(coeffs.dot(augment([xyz]).T)) < threshold
def run_ransac(data, estimate, is_inlier, sample_size, goal_inliers, max_iterations, stop_at_goal=True, random_seed=None):
best_ic = 0
best_model = None
random.seed(random_seed)
# random.sample cannot deal with "data" being a numpy array
data = list(data)
for i in range(max_iterations):
s = random.sample(data, int(sample_size))
m = estimate(s)
ic = 0
for j in range(len(data)):
if is_inlier(m, data[j]):
ic += 1
print(s)
print('estimate:', m,)
print('# inliers:', ic)
if ic > best_ic:
best_ic = ic
best_model = m
if ic > goal_inliers and stop_at_goal:
break
print('took iterations:', i+1, 'best model:', best_model, 'explains:', best_ic)
return best_model, best_ic
# 鼠标回调函数
def onmouse_pick_points(event, x, y, flags, param):
global flag_mouse_lbutton_down, point_x, point_y
if leastsq_mode:
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
point_x = x
point_y = y
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONUP:
threeD = param
threeD = threeD[point_y:y,point_x:x,:]
threeD = threeD.reshape(threeD.shape[0]*threeD.shape[1],threeD.shape[2])
mean = np.mean(threeD[:,2])
std = np.std(threeD[:,2])
temp_three = threeD[:,2]
list = np.where((temp_three>mean+2*std)|(temp_three<mean-2*std))
threeD_1 = np.delete(threeD, list, axis = 0)
test_tr = threeD_1[:,2]
goal_inliers = threeD_1.shape[0] * 0.5
max_iterations = 20
m, b = run_ransac(threeD_1, estimate, lambda x, y: is_inlier(x, y, 0.01), 3, goal_inliers, max_iterations)
a, b, c, d = m
# z = p[0]*np.mean(threeD[:,0])+p[1]*np.mean(threeD[:,1])+p[2]
z = (-d - a * threeD_1[:,0] - b * threeD_1[:,1]) / c
print(point_x,x,point_y,y,-d/c)
print("中心的距离为:%.3f, %.3f"%(np.median(z),np.mean(z)), "m")
a= 1
else:
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
for i in range(len(param)):
threeD = param[i]
# threeD2 = param[1]
print('\n%d 像素坐标 x = %d, y = %d' % (i, x, y))
print("世界坐标xyz 是:(%.3f,%.3f,%.3f)"%(threeD[y][x][0] / 1000.0, threeD[y][x][1] / 1000.0, threeD[y][x][2] / 1000.0), "m")
distance = dist(threeD, x, y)
print("%dx%d平均距离是:%.3f"%(v_size,v_size,distance),"m")
WIN_NAME = 'RGB'
cv2.namedWindow(WIN_NAME, cv2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE)
if camera=='kitti':
imgL = cv2.imread('/media/ye/File/KITTI/data_stereo_flow/testing/image_0/000000_10.png')
imgR = cv2.imread('/media/ye/File/KITTI/data_stereo_flow/testing/image_1/000000_10.png')
else:
frame = cv2.imread("/media/ye/File/Stereo/SGBM/data/8-4/test2/8000.jpg")
img_color = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
w = frame.shape[1]
frame1 = frame[:, :int(w/2)]
frame2 = frame[:, int(w/2):] # 割开双目图像
imgL = cv2.cvtColor(frame1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 将BGR格式转换成灰度图片
imgR = cv2.cvtColor(frame2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# cv2.imshow('L', imgL)
# cv2.imshow('R', imgR)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# cv2.remap 重映射,就是把一幅图像中某位置的像素放置到另一个图片指定位置的过程。
# 依据MATLAB测量数据重建无畸变图片
img1_rectified = cv2.remap(imgL, left_map1, left_map2, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
img2_rectified = cv2.remap(imgR, right_map1, right_map2, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
# cv2.imshow('L', img1_rectified)
# cv2.imshow('R', img2_rectified)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
imgL_rectified = cv2.remap(frame1, left_map1, left_map2, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
# cv2.imwrite('data/8-4/imgL.png', imgL_rectified)
# t0 = time.time()
for i in range(1):
disparity2 = bm(img1_rectified, img2_rectified)
disparity2 = np.where(disparity2 > 0, disparity2, 0)
# t1 = time.time()
# disp = cv2.normalize(disparity, disparity, alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U) # 归一化函数算法
disp2 = cv2.normalize(disparity2, disparity2, alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U) # 归一化函数算法
# cv2.imwrite('data/8-4/bm.png', disp2)
for i in range(1):
disparity3 = sgbm(img1_rectified, img2_rectified)
disparity3 = np.where(disparity3 > 0, disparity3, 0)
disp3 = cv2.normalize(disparity3, disparity3, alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U) # 归一化函数算法
# cv2.imwrite('sbbm.png', disp3)
# print('2: ', t1-t0)
disparity_crop = sgbm(img1_rectified[120:600,320:960], img2_rectified[120:600,320:960])
disparity_crop = np.where(disparity_crop > 0, disparity_crop, 0)
disparity_crop = np.pad(disparity_crop, [[120,120], [320,320]])
disp_crop = cv2.normalize(disparity_crop, disparity_crop, alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U) # 归一化函数算法
# cv2.imwrite('sbbm_crop.png', disp_crop)
threeD2 = cv2.reprojectImageTo3D(disparity2, Q, handleMissingValues=False) # 计算三维坐标数据值
threeD2 = threeD2 * 16
np.save('three_bm.npy', threeD2[379:629,435:863,:])
threeD3 = cv2.reprojectImageTo3D(disparity3, Q, handleMissingValues=True) # 计算三维坐标数据值
threeD3 = threeD3 * 16
np.save('three_sgbm.npy', threeD3[379:629,435:863,:])
if gt_pred:
if camera=='kitti':
disparity3 = cv2.imread('/media/ye/File/LEAStereo/predict/kitti2012/images/000000_10.png', cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)
elif camera=='720p':
disparity3 = cv2.imread('/media/ye/File/LEAStereo/predict/test_15/4.png', cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)
disparity3 = np.pad(disparity3, [[72,72], [160,160]])
disparity3 = (disparity3/16).astype(np.int16)
disp3 = cv2.normalize(disparity3, disparity3, alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U) # 归一化函数算法
threeD3 = cv2.reprojectImageTo3D(disparity3, Q, handleMissingValues=True) # 计算三维坐标数据值
threeD3 = threeD3 * 16
threeD4 = (threeD2,threeD3)
cv2.imshow('Ref', disp3)
else:
threeD4 = threeD2
# threeD[y][x] x:0~640; y:0~480; !!!!!!!!!!
cv2.setMouseCallback(WIN_NAME, onmouse_pick_points, threeD4) # 鼠标回调事件
dis_color = threeD2[...,2]
dis_color[np.isinf(dis_color)]=0
dis_color[dis_color > 9000] =9000
dis_color = cv2.normalize(dis_color, None, alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U)
# dis_color = cv2.applyColorMap(dis_color, 2)
# cv2.imshow("depth", dis_color)
# cv2.imshow("left", frame1)
# cv2.imshow('single', disp)
cv2.imshow(WIN_NAME, imgL_rectified)
# cv2.imshow('sgbm', disp3)
cv2.imshow('bm', disp2)# 显示深度图的双目画面
cv2.waitKey()
# 销毁内存
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
pcl_show(threeD3, imgL_rectified)
sgbm_crop.py
'''
Author: YeHanyu
Date: 2022-08-02 11:32:58
LastEditors: YeHanyu
LastEditTime: 2022-08-18 16:42:16
FilePath: /undefined/media/ye/File/Stereo/SGBM/sgbm_crop.py
Description:
Copyright (c) 2022 by YeHanyu, All Rights Reserved.
'''
import cv2
import numpy as np
import time
from sklearn.linear_model import RANSACRegressor, LinearRegression
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits import mplot3d
global numDisp
numDisp = 80
# 相机参数读取
class cam_cfg:
def __init__(self, config_path):
self.config_path = config_path
camera_config = cv2.FileStorage(config_path, cv2.FILE_STORAGE_READ)
self.size = camera_config.getNode("Size").mat().astype(int)[0]
self.left_matrix = camera_config.getNode("KL").mat()
self.right_matrix = camera_config.getNode("KR").mat()
self.left_distortion = camera_config.getNode("DL").mat()
self.right_distortion = camera_config.getNode("DR").mat()
self.R = camera_config.getNode("R").mat()
self.T = camera_config.getNode("T").mat()
def bm(l_img, r_img):
# l_img = cv2.cvtColor(l_img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
# r_img = cv2.cvtColor(r_img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
numDisp = 80
l_img = np.pad(l_img, [[0, 0], [numDisp, numDisp]]) # pad防止crop溢出
r_img = np.pad(r_img, [[0, 0], [numDisp, numDisp]])
left_matcher = cv2.StereoBM_create(numDisparities=16, blockSize=9)
left_matcher.setROI1(validPixROI1)
left_matcher.setROI2(validPixROI2)
left_matcher.setPreFilterCap(31)
left_matcher.setBlockSize(15)
left_matcher.setMinDisparity(0)
left_matcher.setNumDisparities(numDisp - 22)
left_matcher.setTextureThreshold(10)
left_matcher.setUniquenessRatio(15)
left_matcher.setSpeckleWindowSize(100)
left_matcher.setSpeckleRange(1)
left_matcher.setDisp12MaxDiff(1)
right_matcher = cv2.ximgproc.createRightMatcher(left_matcher)
lmbda = 8000
sigma = 1.5
wls_filter = cv2.ximgproc.createDisparityWLSFilter(matcher_left=left_matcher)
wls_filter.setLambda(lmbda)
wls_filter.setSigmaColor(sigma)
t0 = time.time()
displ = left_matcher.compute(l_img[:, 0:-numDisp], r_img[:, 0:-numDisp])
dispr = right_matcher.compute(r_img[:, numDisp:], l_img[:, numDisp:])
t1 = time.time()
print('BM计算时间: %.2f ms' % ((t1 - t0) * 1000))
# displ_show = cv2.normalize(displ,displ,alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U)
# dispr_show = cv2.normalize(dispr,dispr,alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U)
# cv2.imshow('L', displ_show)
# cv2.imshow('R', dispr_show)
displ = np.int16(displ)
dispr = np.int16(dispr)
t0 = time.time()
dispr = np.pad(dispr[:, :-numDisp], [[0, 0], [numDisp, 0]])
disparity = wls_filter.filter(displ, l_img[:, :-numDisp], None, dispr)
disparity = np.where(disparity > 0, disparity, 0)
disp_out = disparity[:, numDisp:]
t1 = time.time()
print('BM融合时间: %.2f ms' % ((t1 - t0) * 1000))
return disp_out
def sgbm(l_img, r_img):
if l_img.shape[1]==1920:
l_img = np.pad(l_img, [[0, 0], [numDisp, numDisp]]) # 去除匹配时的黑边
r_img = np.pad(r_img, [[0, 0], [numDisp, numDisp]])
left_matcher = cv2.StereoSGBM_create(
minDisparity=1,
numDisparities=int(numDisp/1.25),
blockSize=15,
P1=8 * 3 * 5 ** 2,
P2=32 * 3 * 5 ** 2,
disp12MaxDiff=1,
uniquenessRatio=10,
speckleWindowSize=100,
speckleRange=10,
preFilterCap=31,
mode=cv2.STEREO_SGBM_MODE_SGBM_3WAY
)
right_matcher = cv2.ximgproc.createRightMatcher(left_matcher)
lmbda = 8000
sigma = 1.5
wls_filter = cv2.ximgproc.createDisparityWLSFilter(matcher_left=left_matcher)
wls_filter.setLambda(lmbda)
wls_filter.setSigmaColor(sigma)
wls_filter2 = cv2.ximgproc.createDisparityWLSFilter(matcher_left=right_matcher)
wls_filter2.setLambda(lmbda)
wls_filter2.setSigmaColor(sigma)
t0 = time.time()
displ = left_matcher.compute(l_img, r_img)
dispr = right_matcher.compute(r_img, l_img)
# displ = left_matcher.compute(l_img, r_img)
# dispr = right_matcher.compute(r_img, l_img)
t1 = time.time()
print('SGBM计算时间: %.2f ms' % ((t1 - t0) * 1000))
# displ_show = cv2.normalize(displ,displ,alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U)
# dispr_show = cv2.normalize(dispr,dispr,alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U)
# cv2.imshow('L', displ_show)
# cv2.imshow('R', dispr_show)
displ = np.int16(displ)
# cv2.imshow('displ', norm_disp(displ))
dispr = np.int16(dispr)
# cv2.imshow('dispr', norm_disp(-dispr))
t0 = time.time()
disparity = wls_filter.filter(displ, l_img, None, dispr)
disparity2 = -wls_filter2.filter(dispr, r_img, None, displ)
disparity = np.where(disparity > 0, disparity, 0)
disparity2 = np.where(disparity2 > 0, disparity2, 0)
# cv2.imshow('disparity', norm_disp(disparity))
t1 = time.time()
print('SGBM融合时间: %.2f ms' % ((t1 - t0) * 1000))
disp_out = disparity[:, numDisp:-numDisp]
disp_out2 = disparity2[:, numDisp:-numDisp]
return disp_out, disp_out2
'''
description: 计算ROI区域视差,并使用RANSAC进行平面拟合,再计算3D坐标
'''
def calc_dist(x_L, y_L, x_R, y_R):
l_img = np.pad(img1_rectified, [[0, 0], [numDisp, numDisp]]) # 防止索引为空,放大图像
r_img = np.pad(img2_rectified, [[0, 0], [numDisp, numDisp]])
disp_crop, disp_crop2 = sgbm(l_img[y_L:y_R, x_L:x_R + 2 * numDisp], r_img[y_L:y_R, x_L:x_R + 2 * numDisp]) # 使用更大的ROI区域进行计算
cv2.namedWindow("DISP-CROP", 0)
cv2.resizeWindow("DISP-CROP", 640, 640)
cv2.imshow('DISP-CROP', norm_disp(disp_crop))
cv2.namedWindow("DISP-CROP2", 0)
cv2.resizeWindow("DISP-CROP2", 640, 640)
cv2.imshow('DISP-CROP2', norm_disp(disp_crop2))
cv2.waitKey(0)
# 提取ROI区域
# 为disp添加x,y坐标
h = disp_crop.shape[0]
w = disp_crop.shape[1]
x = np.arange(0, w)
y = np.arange(0, h)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
disp_3d = np.stack((X, Y, disp_crop), axis=2)
disp_3d_o = np.stack((X, Y, disp_crop), axis=2)
# 去除异常点
disp_3d = disp_3d.reshape(disp_3d.shape[0] * disp_3d.shape[1], disp_3d.shape[2])
mean = np.mean(disp_3d[:, 2])
std = np.std(disp_3d[:, 2])
temp_three = disp_3d[:, 2]
list = np.where((temp_three > mean + std) | (temp_three < mean - std))
disp_3d_tmp = np.delete(disp_3d, list, axis=0)
# 原始的disp点查看
fig = plt.figure()
ax = mplot3d.Axes3D(fig, auto_add_to_figure=False)
fig.add_axes(ax)
# color_map = plt.get_cmap('jet')
# ax.scatter3D(disp_3d[:,0], disp_3d[:,1], disp_3d[:,2], c=disp_3d[:,2],cmap = color_map)
# plt.show()
# RANSAC拟合平面
ransac_disp = RANSACRegressor(LinearRegression(), max_trials=50)
t0 = time.time()
ransac_disp.fit(disp_3d_tmp[:, 0:2], disp_3d_tmp[:, -1])
t1 = time.time()
print('RANSAC计算时间: %.2f ms' % ((t1 - t0) * 1000))
z_disp = ransac_disp.predict(disp_3d[:, 0:2])
z_disp = z_disp.reshape(h, w).astype(np.float32)
disp_gt_sub = disp_gt[y_L:y_R, x_L:x_R]
disp_diff = z_disp / 16 - disp_gt_sub
disp_diff = np.delete(disp_diff, np.where(np.isinf(disp_diff[:, :]))[0])
disp_diff = np.delete(disp_diff, np.where(np.isneginf(disp_diff[:]))[0])
print(disp_diff.mean(), disp_diff.std())
# cv2.imshow('DISP2', norm_disp(disp_diff))
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# disp_ref = disp[y_L:y_R,x_L:x_R] # 参考用,对比裁切后disp和原disp
# diff = disp_ref - disp_crop
# ax.plot_surface(disp_3d_o[:,:,0], disp_3d_o[:,:,1], z_disp, rstride=5, cstride=5, color ='lightpink')
# plt.show()
# 计算3D坐标
T = np.eye(4, dtype=float) # 用于将ROI区域映射回原图所在位置,计算3D坐标
T[0, 3] = x_L
T[1, 3] = y_L
xyz_d = cv2.reprojectImageTo3D(z_disp, Q @ T, handleMissingValues=False)
xyz_d = xyz_d * 16
# 输出结果 ref为原始完整disp计算的全图3D坐标
xyz_ref = xyz[y_L:y_R, x_L:x_R, :]
print("距离中位数:%.1f mm, 距离平均数:%.1f mm" % (np.median(xyz_d[:, :, 2]), np.mean(xyz_d[:, :, 2])))
print('左上真实坐标: ', xyz_d[0, 0], '右下真实坐标: ', xyz_d[-1, -1])
print("预测对角线距离: ", np.sqrt(np.sum((xyz_d[0, 0] - xyz_d[-1, -1]) ** 2)))
# 显示点云与拟合后的点云
color_map = plt.get_cmap('jet')
ax.plot_surface(xyz_d[:, :, 0], xyz_d[:, :, 1], xyz_d[:, :, 2], rstride=50, cstride=50, color='lightpink')
# ax.scatter3D(xyz_d[:,:,0], xyz_d[:,:,1], xyz_d[:,:,2], c='b')
ax.scatter3D(xyz_ref[:, :, 0], xyz_ref[:, :, 1], xyz_ref[:, :, 2], c=xyz_ref[:, :, 2], cmap=color_map)
plt.show()
# 鼠标回调函数
def onmouse_pick_points(event, x, y, flags, param):
global x_L, y_L
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
# t0 = time.time()
# temp= np.argwhere((left_map1[:,:,0]==x)&(left_map1[:,:,1]==y)) # 提取remap后检测框的坐标
# i = 1
# while temp.size == 0: # remap后坑可能存在空映射,向右下方寻找寻找最近的映射点
# temp = np.argwhere((left_map1[:,:,0]<=x+i)&(left_map1[:,:,0]>=x)&(left_map1[:,:,1]<=y+i)&(left_map1[:,:,1]>=y))
# i+=1
# y_L,x_L = temp[0]
# t1 = time.time()
# print('Remap坐标时间: %.2f ms'%((t1-t0)*1000))
x_L, y_L = x, y # 直到找到一个最近的有效点。操作在原图上,因此需要借助map_rev得到在校正之后的坐标
# x_L, y_L = map_rev[y, x] # 直到找到一个最近的有效点。操作在原图上,因此需要借助map_rev得到在校正之后的坐标
# num = 1
# while x_L == -1:
# x_L, y_L = map_rev[y + num, x + num]
# num += 1
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONUP:
# temp= np.argwhere((left_map1[:,:,0]==x)&(left_map1[:,:,1]==y))
# i = 1
# while temp.size == 0: # remap后坑可能存在空映射,向左上方寻找寻找最近的映射点
# temp = np.argwhere((left_map1[:,:,0]<=x)&(left_map1[:,:,0]>=x-i)&(left_map1[:,:,1]<=y)&(left_map1[:,:,1]>=y-i))
# i+=1
# y_R,x_R = temp[0]
x_R, y_R = x, y
# x_R, y_R = map_rev[y, x]
# num = 1
# while x_R == -1:
# x_R, y_R = map_rev[y - num, x - num]
# num += 1
# print('左上像素坐标: ', x_L, y_L, ' 右下像素坐标: ', x_R, y_R)
calc_dist(x_L, y_L, x_R, y_R) # 计算视差等数据
# RANSAC 3D点云代码
def calc_3d_dist(x_L, y_L, x_R, y_R):
disp_ref = disp
T = np.eye(4, dtype=float)
T[0, 3] = x_L
T[1, 3] = y_L
t0 = time.time()
xyz = cv2.reprojectImageTo3D(disp_ref, Q @ T, handleMissingValues=False) # 计算三维坐标数据值
t1 = time.time()
print('3D坐标计算时间: %.2f ms' % ((t1 - t0) * 1000))
xyz = xyz * 16
xyz = xyz.reshape(xyz.shape[0] * xyz.shape[1], xyz.shape[2])
tmp = xyz[:, 2]
inf_list = np.where(tmp == np.inf)
xyz = np.delete(xyz, inf_list, axis=0)
mean = np.mean(xyz[:, 2])
std = np.std(xyz[:, 2])
temp_three = xyz[:, 2]
list = np.where((temp_three > mean + std) | (temp_three < mean - std))
xyz = np.delete(xyz, list, axis=0)
test_tr = xyz[:, 2]
# goal_inliers = xyz.shape[0] * 0.4
# max_iterations = 5
# t0 = time.time()
# m, b = run_ransac(xyz, estimate, lambda x, y: is_inlier(x, y, 0.01), 3, goal_inliers, max_iterations)
# t1 = time.time()
t0 = time.time()
lr = LinearRegression().fit(xyz[:, 0:2], xyz[:, -1])
t1 = time.time()
print('最小二乘计算时间: %.2f ms' % ((t1 - t0) * 1000))
z = lr.predict(xyz[:, 0:2])
print("距离中位数:%.1f mm, 距离平均数:%.1f mm, 原平均数:%.1f mm" % (np.median(z), np.mean(z), mean))
stride = xyz.shape[0] // 10000 + 1
xyz_s = xyz[::stride, :]
ransac = RANSACRegressor(LinearRegression(), max_trials=100, residual_threshold=mean * 0.01,
stop_n_inliers=xyz_s.shape[0] // 1.1, stop_probability=1)
t0 = time.time()
ransac.fit(xyz_s[:, 0:2], xyz_s[:, -1])
t1 = time.time()
print('RANSAC计算时间: %.2f ms' % ((t1 - t0) * 1000))
# 获取内点和异常点集合
inlier_mask = ransac.inlier_mask_
# a, b, c, d = m
# z = p[0]*np.mean(xyz[:,0])+p[1]*np.mean(xyz[:,1])+p[2]
# z = (-d - a * xyz[:,0] - b * xyz[:,1]) / c
list = np.where(inlier_mask == 0)
xyz_ss = np.delete(xyz_s, list, axis=0)
z = ransac.predict(xyz_ss[:, 0:2])
dif = xyz_ss[:, -1] - z
# xyz_ss[:,-1] = z
x_median = np.median(xyz_ss[:, 0])
y_median = np.median(xyz_ss[:, 1])
z_median = ransac.predict(((x_median, y_median), (0, 0)))
print("距离中位数:%.1f mm, 距离平均数:%.1f mm, 原平均数:%.1f mm" % (np.median(z), np.mean(z), z_median[0]))
def norm_disp(disp):
# 归一化显示视差
disp[np.isinf(disp)] = 0
disp = np.where(disp < 0, 0, disp)
disp = np.where(disp > 200, 200, disp)
mean = np.mean(disp)
std = np.std(disp)
disp_norm = np.where(disp < mean + 2 * std, disp, mean + 2 * std)
disp_norm = cv2.normalize(disp_norm, disp_norm, alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX,
dtype=cv2.CV_8U) # 归一化函数算法
disp_norm = cv2.applyColorMap(disp_norm, 14)
return disp_norm
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 读取相机参数
camera_cfg = cam_cfg('/mnt/sda1/Stereo/data/config/cam25/camera24.yml')
# 双目极线校正
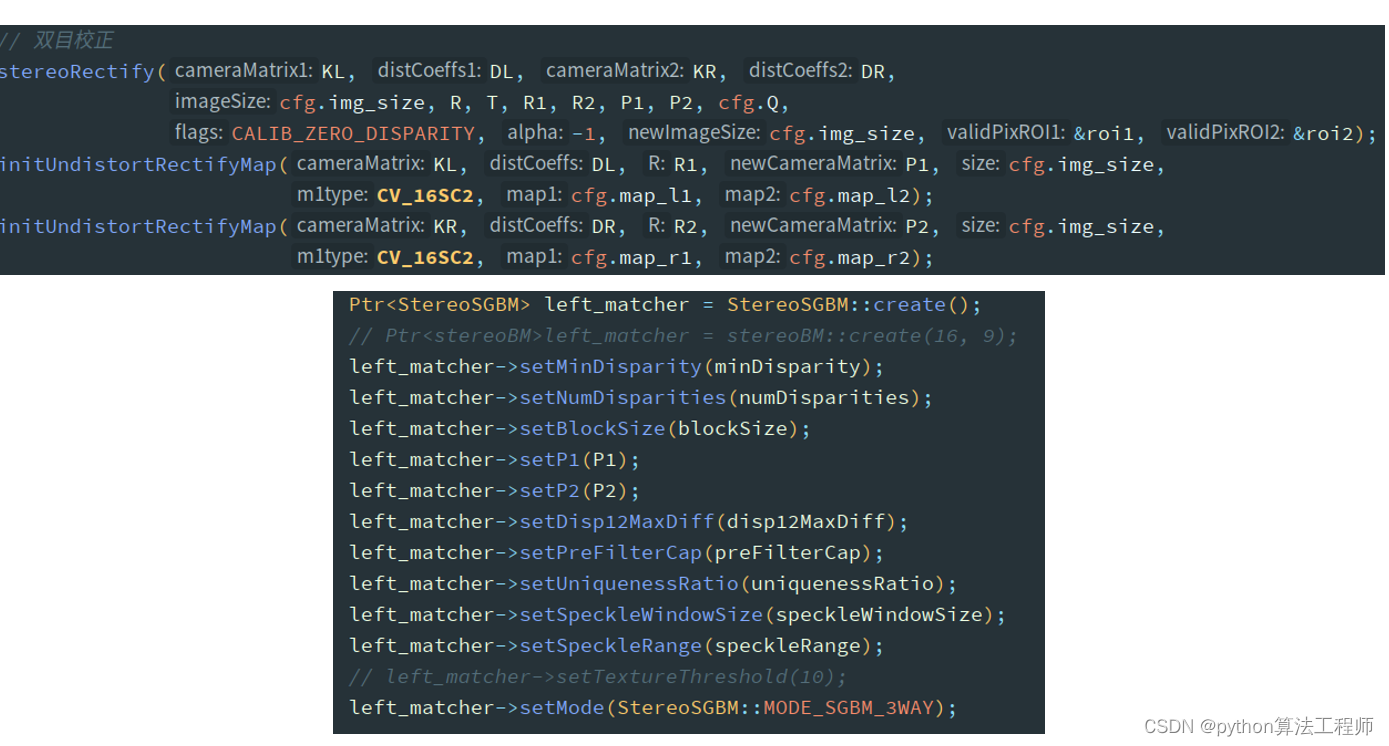
R1, R2, P1, P2, Q, validPixROI1, validPixROI2 = cv2.stereoRectify(camera_cfg.left_matrix,
camera_cfg.left_distortion,
camera_cfg.right_matrix,
camera_cfg.right_distortion, camera_cfg.size,
camera_cfg.R,
camera_cfg.T,
flags=cv2.CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY,
alpha=-1)
# 校正查找映射表,将原始图像和校正后的图像上的点一一对应起来
left_map1, left_map2 = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(camera_cfg.left_matrix, camera_cfg.left_distortion, R1, P1,
camera_cfg.size, cv2.CV_16SC2)
right_map1, right_map2 = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(camera_cfg.right_matrix, camera_cfg.right_distortion, R2, P2,
camera_cfg.size, cv2.CV_16SC2)
map_rev = -np.ones(left_map1.shape, dtype=np.int16)
t0 = time.time()
for y, list in enumerate(left_map1): # 每一行
for x, point in enumerate(list): # 每个点
if point[1] < left_map1.shape[0] and point[0] < left_map1.shape[1]: # 有效区域映射回去
map_rev[point[1], point[0]] = (x, y)
# print('1')
t1 = time.time()
print('remap_rev', (t1 - t0) * 1000)
WIN_NAME = 'RGB'
cv2.namedWindow(WIN_NAME, cv2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE)
img = cv2.imread('/mnt/sda1/Stereo/data/imgs/00.jpg')
w = img.shape[1]
img_R = img[:, :int(w / 2)]
img_L = img[:, int(w / 2):] # 割开双目图像
# cv2.imshow('RGB_L', img_L)
imgL = cv2.cvtColor(img_L, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 将BGR格式转换成灰度图片
imgR = cv2.cvtColor(img_R, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# cv2.imshow('L', imgL)
# cv2.imshow('R', imgR)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# l_tmp = left_map1[400:800, 400:800, :]-(400, 400)
# r_tmp = right_map1[400:800, 400:800, :]-(400, 400)
# l_tmp2 = left_map2[400:800, 400:800]
# r_tmp2 = right_map2[400:800, 400:800]
# l_tmpimg = imgL[400:800, 400:800]
# r_tmpimg = imgR[400:800, 400:800]
# img1_re = cv2.remap(l_tmpimg, l_tmp.astype(np.int16), l_tmp2, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
# img2_re = cv2.remap(r_tmpimg, r_tmp.astype(np.int16), r_tmp2, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
# cv2.remap 重映射,就是把一幅图像中某位置的像素放置到另一个图片指定位置的过程。
# 依据MATLAB测量数据重建无畸变图片
t0 = time.time()
img1_rectified = cv2.remap(imgL, left_map1, left_map2, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
img2_rectified = cv2.remap(imgR, right_map1, right_map2, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
# cv2.imwrite('/mnt/sda1/CREStereo/img/left.png', img1_rectified)
# cv2.imwrite('/mnt/sda1/CREStereo/img/right.png', img2_rectified)
t1 = time.time()
print('remap', (t1 - t0) * 1000)
# cv2.imshow('L', img1_rectified)
# cv2.imshow('R', img1_re)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# mlimg1 = cv2.imread('/mnt/sda1/Stereo/data/cam-test/cam1-1920-1080-2.1mm/image0/04.png')
# mlimg2 = cv2.imread('/mnt/sda1/Stereo/data/cam-test/cam1-1920-1080-2.1mm/image1/04.png')
# disp2 = sgbm(mlimg1, mlimg2)
# 原始图计算视差,参考用
# img1_rectified = cv2.imread("/media/hx/datav/data/octogons2/im0.png", 0)
#
# img2_rectified = cv2.imread("/media/hx/datav/data/octogons2/im1.png", 0)
# disp = (sgbm(img1_rectified, img2_rectified) / 16).astype(np.float32)
# import readpfm
# disp_gt, scale = readpfm.readPFM("/media/hx/datav/data/octogons2/disp0.pfm")
# cv2.imwrite("disp_gt.png", norm_disp(disp_gt))
# cv2.imwrite("disp_sgbm.png", norm_disp(disp))
# disp_diff = disp - disp_gt
# disp_diff = np.delete(disp_diff, np.where(np.isinf(disp_diff[:, :]))[0])
# disp_diff = np.delete(disp_diff, np.where(np.isneginf(disp_diff[:]))[0])
# np.save('/mnt/sda1/CREStereo/ref.npy', disp)
# np.save('ref.npy', disp)
# 3D坐标计算
# xyz = cv2.reprojectImageTo3D(disp, Q, handleMissingValues=True) # 计算三维坐标数据值
# xyz = xyz * 16
cv2.setMouseCallback(WIN_NAME, onmouse_pick_points, 0) # 鼠标回调事件
cv2.imshow(WIN_NAME, img1_rectified)
# cv2.imshow('DISP', norm_disp(disp)) # 显示深度图的双目画面
# cv2.imshow('DISP2', norm_disp(disp2)) # 显示深度图的双目画面
cv2.waitKey()
# 销毁内存
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
calib.yaml
%YAML:1.0
---
Size: !!opencv-matrix
rows: 1
cols: 2
dt: d
data: [ 1280., 720. ]
KL: !!opencv-matrix
rows: 3
cols: 3
dt: d
data: [1.031166048190102e+03,0,6.397823165430833e+02,
0,1.030609520117754e+03,3.593594070175213e+02,
0,0,1]
DL: !!opencv-matrix
rows: 1
cols: 5
dt: d
data: [7.578583011535487e-04,0.011344482472558,
4.941192721917284e-04,-8.099662583730570e-04, 0. ]
KR: !!opencv-matrix
rows: 3
cols: 3
dt: d
data: [1.028352854986099e+03,0,6.073814839692546e+02,
0,1.028170084680186e+03,3.529749353040706e+02,
0,0,1]
DR: !!opencv-matrix
rows: 1
cols: 5
dt: d
data: [0.002326846567408,-0.00269445169779,
-6.700566986846144e-05,-0.001008664981002, 0. ]
R: !!opencv-matrix
rows: 3
cols: 3
dt: d
data: [0.999955307511155,0.001114669387009,-0.009388316804935,
-0.001207328658961,0.999950563891670,-0.009869758367851,
0.009376851165579,0.009880652047723,0.999907219384544]
T: !!opencv-matrix
rows: 3
cols: 1
dt: d
data: [-63.384113887029390,-0.059003868331137,-0.191187441950284]
标签:
相关文章
最新发布
- 光流法结合深度学习神经网络的原理及应用(完整代码都有Python opencv)
- Python 图像处理进阶:特征提取与图像分类
- 大数据可视化分析-基于python的电影数据分析及可视化系统_9532dr50
- 【Python】入门(运算、输出、数据类型)
- 【Python】第一弹---解锁编程新世界:深入理解计算机基础与Python入门指南
- 华为OD机试E卷 --第k个排列 --24年OD统一考试(Java & JS & Python & C & C++)
- Python已安装包在import时报错未找到的解决方法
- 【Python】自动化神器PyAutoGUI —告别手动操作,一键模拟鼠标键盘,玩转微信及各种软件自动化
- Pycharm连接SQL Sever(详细教程)
- Python编程练习题及解析(49题)
点击排行
- 版本匹配指南:Numpy版本和Python版本的对应关系
- 版本匹配指南:PyTorch版本、torchvision 版本和Python版本的对应关系
- Anaconda版本和Python版本对应关系(持续更新...)
- 相关性分析——Pearson相关系数+热力图(附data和Python完整代码)
- Python 可视化 web 神器:streamlit、Gradio、dash、nicegui;低代码 Python Web 框架:PyWebIO
- Windows上安装 Python 环境并配置环境变量 (超详细教程)
- Python与PyTorch的版本对应
- 安装spacy+zh_core_web_sm避坑指南

