首页 > Python资料 博客日记
Java-----String类
2024-07-01 14:00:03Python资料围观107次
1.String类的重要性
经过了C语言的学习,我们认识了字符串,但在C语言中,我们表示字符串进行操作的话需要通过字符指针或者字符数组,可以使用标准库中提供的一系列方法对字符串的内容进行操作,但这种表达和操作数据的方法不太符合面向对象的思想,所以在Java中提供了String类。
2. 认识String类
在Java中,String类是一种存储字符串数据类型的类。在Java中,String类属于引用数据类型,由String类创建的对象里面存的是引用。
2.1 字符串构造
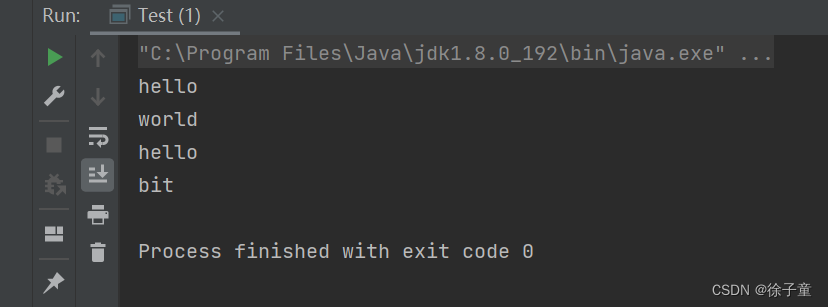
在Java中,字符串的构造有很多种方式,常用的就以下三种。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用常量直接构造
String s1="haha";
System.out.println(s1);
//直接new String对象
String s2=new String("man");
System.out.println(s2);
//使用字符数组进行构造
char[] array={'w','c','I','s'};
String s3=new String(array);
System.out.println(s3);
}
}运行代码
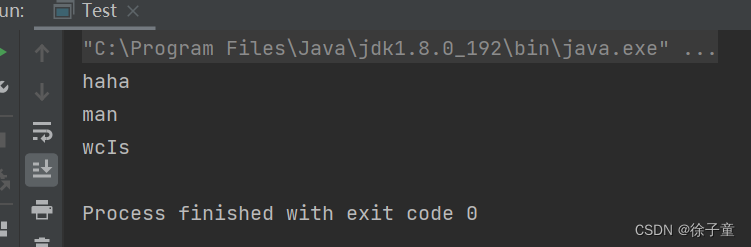
2.2 深刻认识String类
我们知道String类的对象里面存的是引用,那字符串的内容具体是存在哪里的呢?
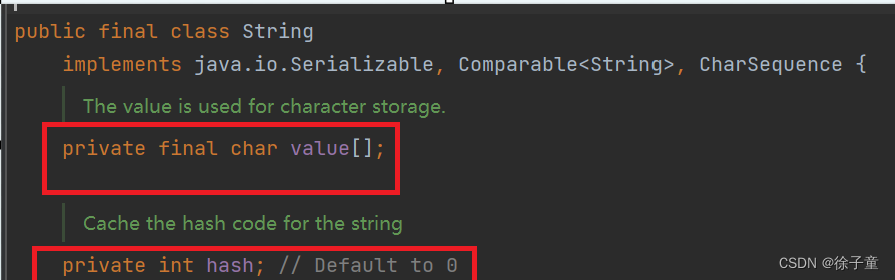
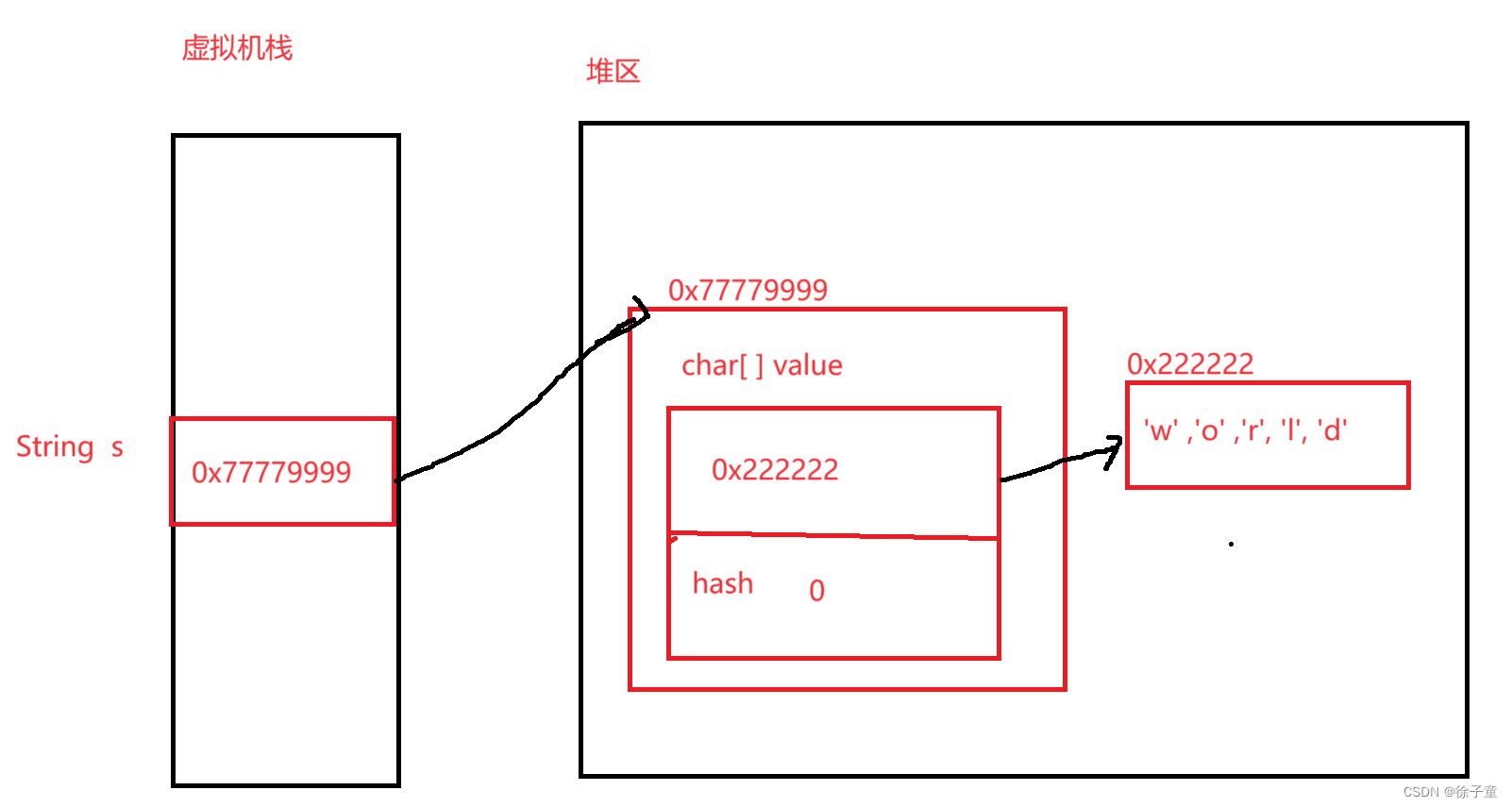
上图是String类里面的一些具体细节,发现里面有一个char[ ] value数组,所以字符串就是存储在这个数组中。
String类的堆栈图
2.3 String类的比较
1. 用 == 比较
当我们用 == 进行String类的对象进行比较时,是比较对象里面存的引用的值。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1="man";
String s2=new String("man");
String s3=s1;
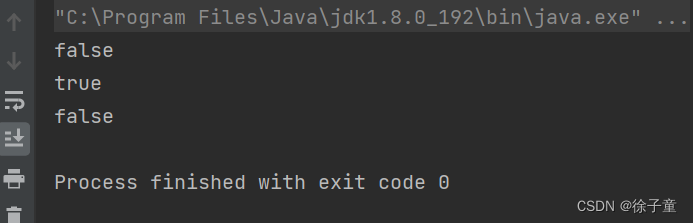
System.out.println(s1==s2);
System.out.println(s1==s3);
System.out.println(s2==s3);
}
}
2. equal()方法比较
用equal方法比较String类的对象时,比较的是对象的字符串的内容是否相同。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1="haha";
String s2=new String("man");
String s3=s1;
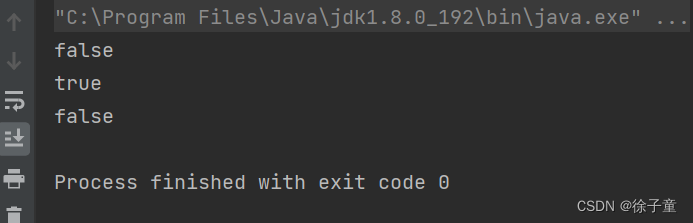
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));
System.out.println(s2.equals(s3));
}
}
3.int compareTo(String s)方法比较
1.当我们使用 int compareTo(String s) 方法比较时,比较的规则是:两个字符串对应位置上的的字母比较,直到比到对应的字母不同时,看哪个字母的ASCII值大,对应的那个字符串就长。就直接放回对应两个字母的ASCII值的差值。
2.当比较的两个字符串的长度不一样,一个长,一个短,假设短的字符串的长度为k,如果短的字符串的k个字符的内容与长字符串前k个字符相同,则放回两个字符串的差值。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = new String("ac");
String s3 = new String("abc");
String s4 = new String("abcdef");
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); // 不同输出字符差值-1
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s3)); // 相同输出 0
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s4)); // 前k个字符完全相同,输出长度差值 -3
}4. int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) 方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = new String("ac");
String s3 = new String("ABc");
String s4 = new String("abcdef");
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2)); // 不同输出字符差值-1
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s3)); // 相同输出 0
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s4)); // 前k个字符完全相同,输出长度差值 -3
}5.易错点(超级重点)
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1="hhh";
String s2="hhh";
System.out.println(s1==s2);//结果为true
}这时候因为s1和s2都是直接赋值,且内容一样,这时编译器会默认s1和s2指向同一块空间。
3.String类的常用方法
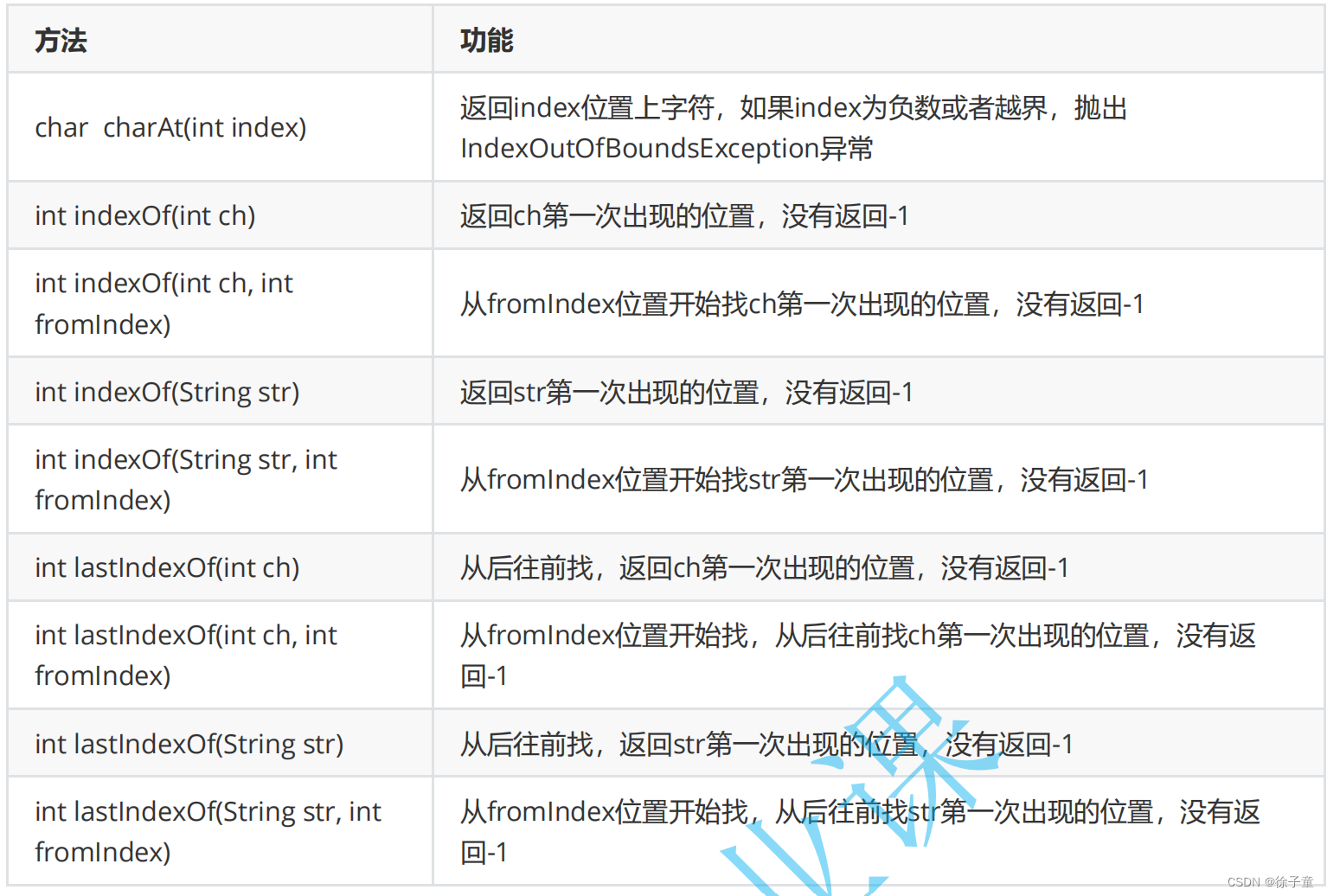
3.1 字符串查找
下图是一些Java中常用的字符串查找功能的方法。
charAt(int index) 方法
用来查找字符串中指定位置上的字符
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="manlebron";
System.out.println(str.charAt(4));
//输出e
}
}以上代码是查找字符串中下标为4的字符,是e。
int indexOf(int ch)方法
用来查找指定字符第一次出现的位置
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="manlebron";
System.out.println(str.indexOf('n'));
}
}
int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)方法
用来在字符串中从fromIndex位置开始寻找第一次出现字符ch的位置
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="manlebron";
System.out.println(str.indexOf('l',2));
}
}int indexOf(String str) 方法
用来查找str第一次在字符串中出现的位置
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="manlebron";
System.out.println(str.indexOf("le"));
}
}由于剩下的方法用法差不多,就不 一 一 介绍了。
3.2 字符串转换
1. 数值和字符串之间的转换
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 数字转字符
String s1 = String.valueOf(1234);
String s2 = String.valueOf(12.34);
String s3 = String.valueOf(true);
String s4 = String.valueOf(new Student("Hanmeimei", 18));
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
System.out.println(s4);
System.out.println("=================================");
// 字符串转数字
// 注意:Integer、Double等是Java中的包装类型,这个后面会讲到
int data1 = Integer.parseInt("1234");
double data2 = Double.parseDouble("12.34");
System.out.println(data1);
System.out.println(data2);
}2. 大小写转换
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "HELLO";
// 小写转大写
System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase());
// 大写转小写
System.out.println(s2.toLowerCase());
}3.字符串和数组之间的转换
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
// 字符串转数组
char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++) {
System.out.print(ch[i]);
}
System.out.println();
// 数组转字符串
String s2 = new String(ch);
System.out.println(s2);
}4. 格式化
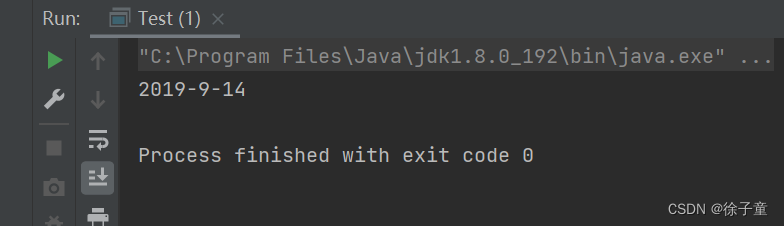
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = String.format("%d-%d-%d", 2019, 9,14);
System.out.println(s);
}
4.字符串替换
用来将一个字符串替换原有字符串中指定的一部分。
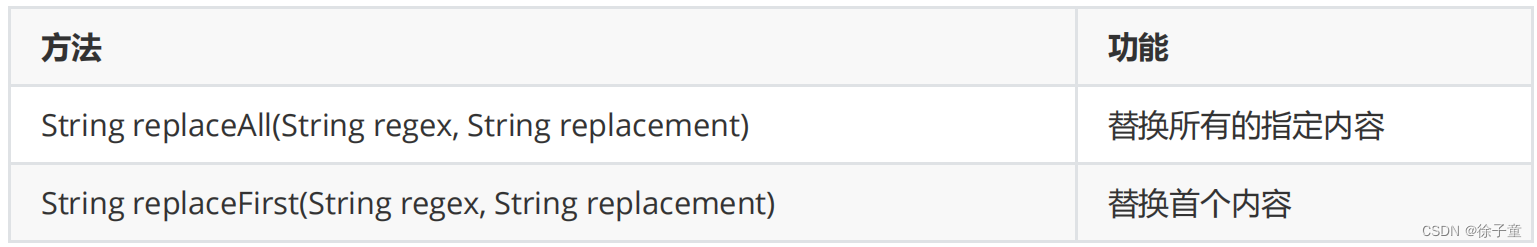
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld" ;
System.out.println(str.replaceAll("l", "_"));
System.out.println(str.replaceFirst("l", "_"));
}
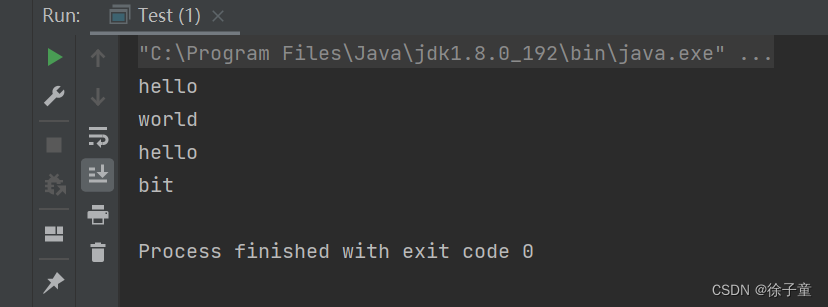
5. 字符串拆分------split方法
用来将一个字符串按指定的分割符将原来的字符串分割成多个字符串。

public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello world hello bit" ;
String[] result = str.split(" ") ; // 按照空格拆分
for(String s: result) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
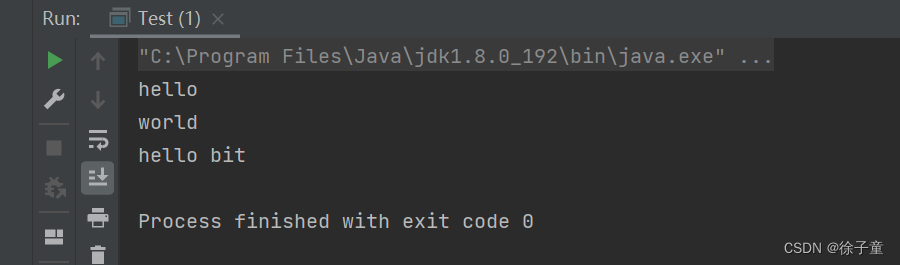
部分拆分
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello world hello bit" ;
String[] result = str.split(" ",3) ; // 按照空格拆分,分为3组
for(String s: result) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
注意事项:拆分是常用的操作,一定要重点掌握。另外,有些特殊的字符无法直接进行拆分,需要加上转移符号 ' \\ ' 。
如拆分IP地址
如以下代码
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String IP="192.168.1.1";
String s[]=IP.split(".");
for(String tmp:s){
System.out.println(tmp);
}
}
}
运行代码
5.1 特殊字符的拆分
1.点字符
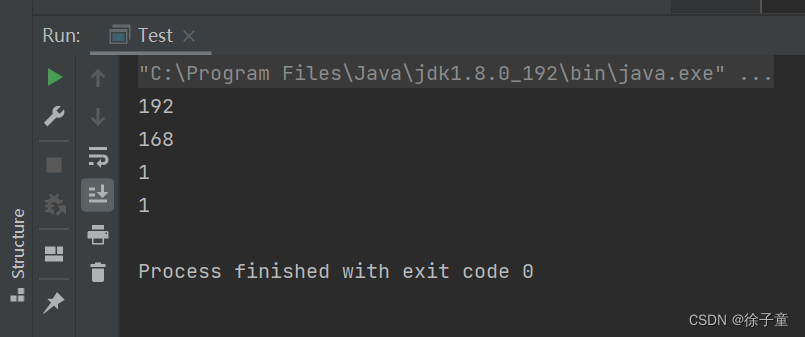
我们发现什么输出都没有,这也就意味这分割没成功,因为 " . "是一个特殊的操作符,需要加上转义符号 " \\ " 。
修改如下
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String IP="192.168.1.1";
String s[]=IP.split("\\."); //在 " . " 前加\\
for(String tmp:s){
System.out.println(tmp);
}
}
}
运行代码
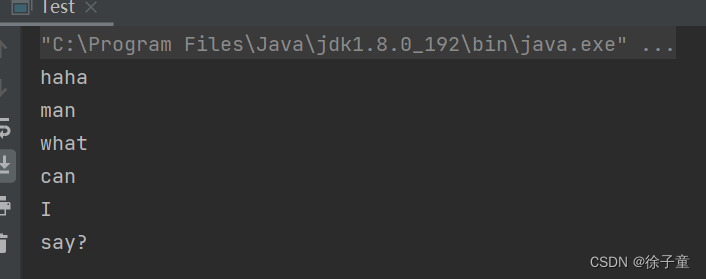
2. " \ " 字符
由于 \ 是一个整除符号,想要在表示 \ 是一个普通的斜杆,就必须在前面再加一个 \ 。
所以将其作为分割符时,要写成 "\\\\".
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="haha\\man\\what\\can\\I\\say?";
for(String tmp:str.split("\\\\")){
System.out.println(tmp);
}
}
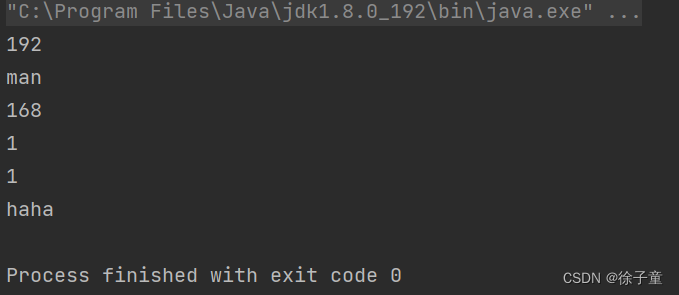
5.2 多次拆分
当一个字符串中有多个字符时,我们可以进行多次拆分。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String IP="192&man.168.1.1&haha";
String s[]=IP.split("\\."); //在 " . " 前加\\
for(String tmp:s){
for(String tmp2:tmp.split("&")){
System.out.println(tmp2);
}
}
}
运行代码:z
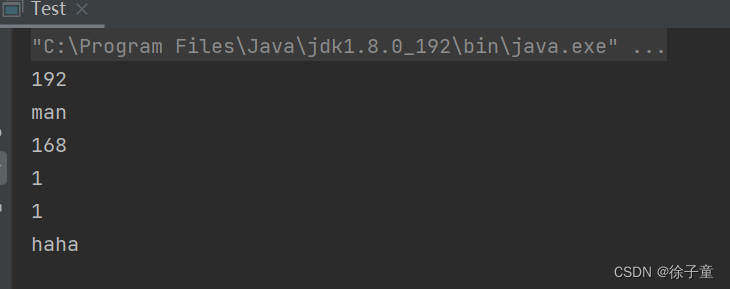
我们也可以用 “ | ” 作为连字符,进行有多个字符的字符串进行拆分。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String IP="192&man.168.1.1&haha";
for(String tmp:IP.split("&|\\.")){
System.out.println(tmp);
}
}
注意:不能在指定的分隔符前加上一个空格,因为空格也算一个字符。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String IP="192&man.168.1.1&haha";
for(String tmp:IP.split("\\. | &")){
System.out.println(tmp);
}
}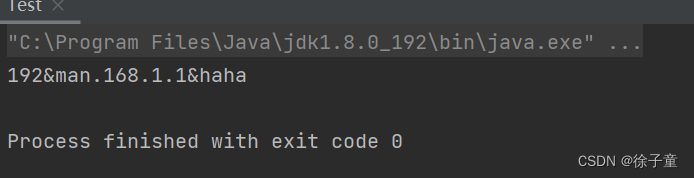
如上图所示,在分隔符前加一个空格,效果就变得不一样了。因为加了空格之后,分隔符就变成了“分隔符+空格”。
5.3 小总结
1.字符 " | " , " * " , " + "都得加上转义字符,前面加上 " \\ " 。
2. 而如果是 " \ " ,那么就得写成 " \\\\ " 。
3. 如果一个字符串中有多个分隔符,可以用"|"作为连字符。
6. 字符串截取-----substring方法
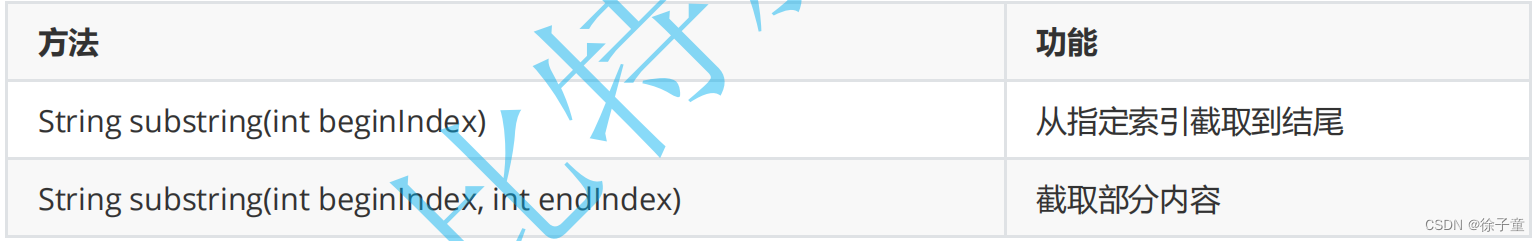
以上的substring方法是用来截取字符串中的一部分内容的。
代码演示
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld" ;
System.out.println(str.substring(5));
System.out.println(str.substring(0, 5));//左开右闭 [0,5)
}
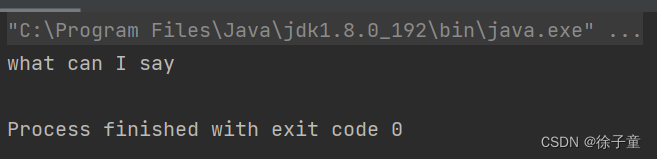
7.其他方法---trim( )方法
trim( ) 方法是用来除去字符串两边的空格的,但并不会出去字符串里面的空格。
代码演示
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str=" what can I say ";
String s=str.trim();
System.out.println(s);
}
8. 字符串的不可变性
首先,我们要清楚,只要涉及到String类型的转变都不是在原字符串上进行的修改,原理是产生一个新的对象。
1.string类在设计时就是被设计为无法改变的,在String类中已经具体描述了,如下图:

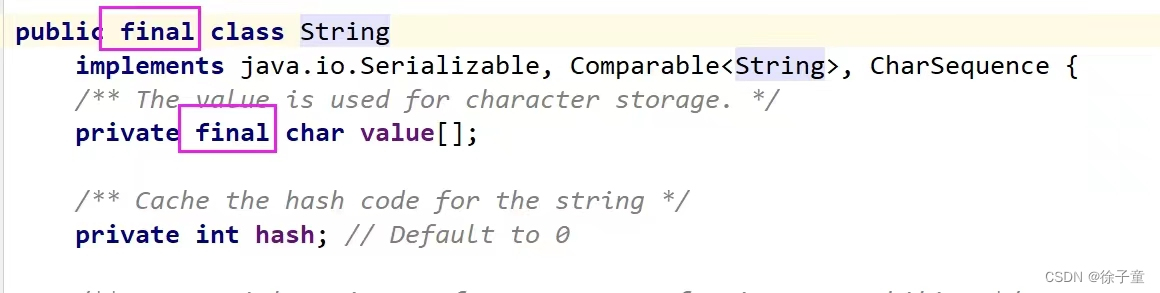
从该图中还可以看出,字符串的内容是保存在char[ ] value 数组中的。
String类是如何设计成无法改变的呢?
一直有人误认为String类之所以无法被改变是因为String类被final修饰或者string类中的那个数组被final修饰,其实这些都是错误的。
因为一个类被final修饰只能表明这个类无法被继承,一个数组被final修饰,表示数组名存的引用无法被改变。这些都与String类无法被改变有联系。
真正的原因是,存放字符串的那个数组被private修饰了,且String类内没有提供任何方法来让外界去访问和使用该数组,所以就造成了字符串的不可变性。
10.字符串的修改
注意:我们要尽量避开对字符串的直接修改,因为String类是无法被改变的,所有的修改都会创建新的对象,会导致效率非常底下。
如以下代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
s += " world";
System.out.println(s); // 输出:hello world
}这段代码看似很简单,有看起来像直接对String类进行了修改。其实不然,
在这段代码的背后做了很多工作,先是创建了一个StringBuilder对象,在原来s中字符串的内容存到StringBuilder对象里面,然后在对StringBuilder对象进行了修改,然后再通过toString()方法转换为String类型,最后再放回一个新的String类的对象。
如下图
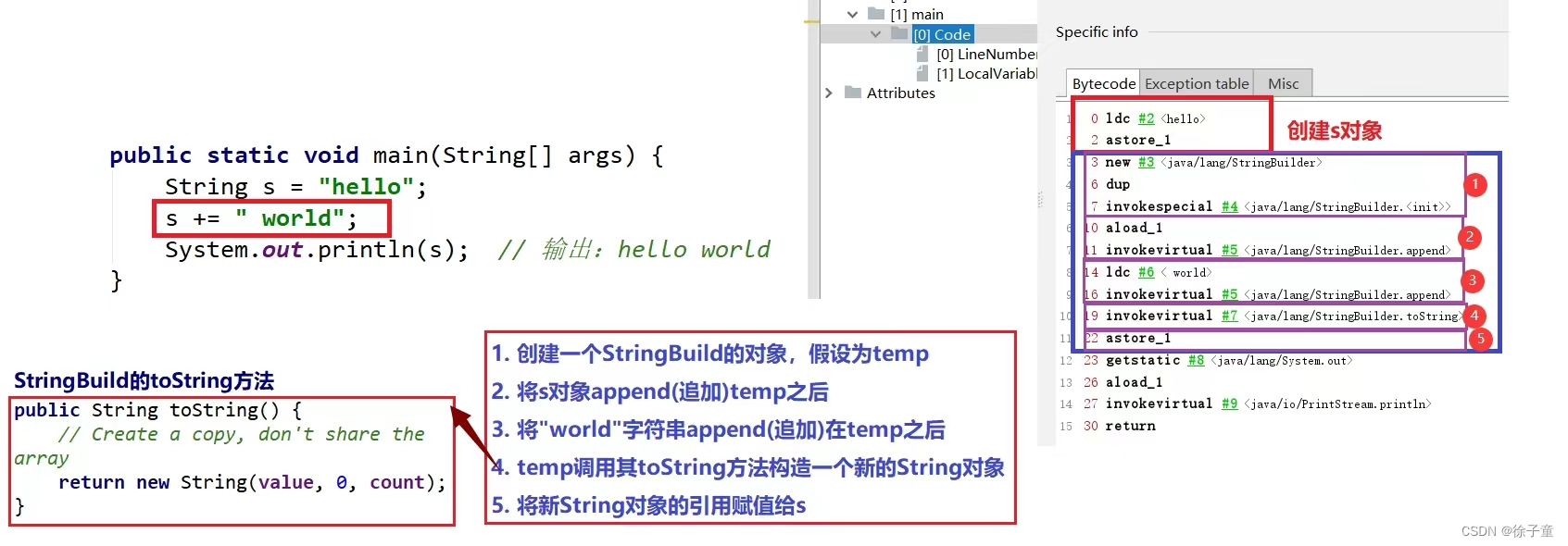
这里创建了很多临时变量,就导致了效率低下。
因此我们要尽量避免对String类的直接改变,如果要修改建议尽量 使用StringBuffer或者StringBuilder。
11.StringBuilder和StringBuffer
由于String类型无法直接被改变,再Java中提供了StringBuilder和StringBuffer类,这两个类也是可以存储字符串的,但可以直接对字符串修改的。
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder=new StringBuilder("haha ");
System.out.println(stringBuilder.append("man"));
StringBuffer stringBuffer=new StringBuffer("what can I say");
stringBuffer.append("?");
System.out.println(stringBuffer);
}
其实 StringBuilder和StringBuffer的用法很相似,就一个区别。
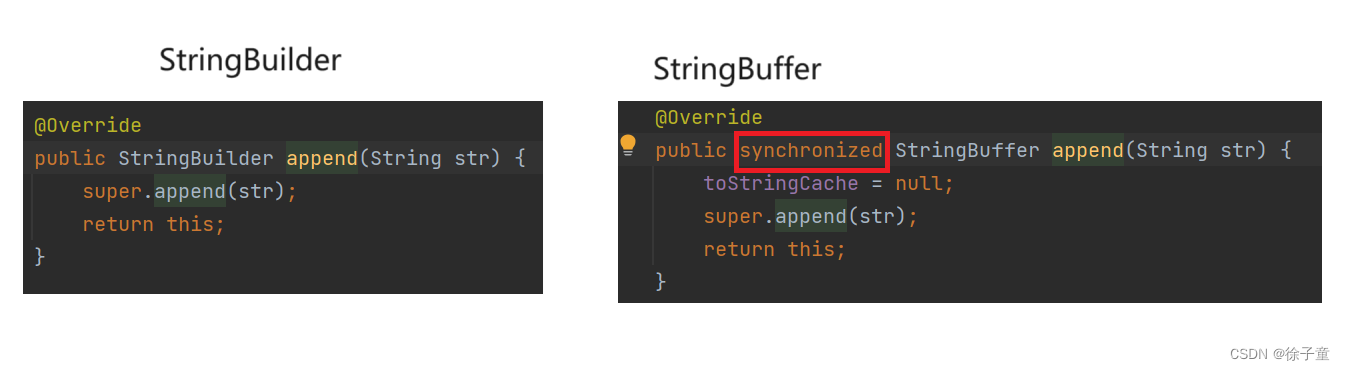
如上图StringBuffer中多了一个synchronized,这个可以理解为一把锁,在多线程的情况下可以保证安全。
而StringBuilder主要是在单线程情况下使用。
StringBuilder和StringBuffer和String的区别
1. String的内容不可修改,StringBuffer与StringBuilder的内容可以修改.
标签:
相关文章
最新发布
- 【Python】selenium安装+Microsoft Edge驱动器下载配置流程
- Python 中自动打开网页并点击[自动化脚本],Selenium
- Anaconda基础使用
- 【Python】成功解决 TypeError: ‘<‘ not supported between instances of ‘str’ and ‘int’
- manim边学边做--三维的点和线
- CPython是最常用的Python解释器之一,也是Python官方实现。它是用C语言编写的,旨在提供一个高效且易于使用的Python解释器。
- Anaconda安装配置Jupyter(2024最新版)
- Python中读取Excel最快的几种方法!
- Python某城市美食商家爬虫数据可视化分析和推荐查询系统毕业设计论文开题报告
- 如何使用 Python 批量检测和转换 JSONL 文件编码为 UTF-8
点击排行
- 版本匹配指南:Numpy版本和Python版本的对应关系
- 版本匹配指南:PyTorch版本、torchvision 版本和Python版本的对应关系
- Python 可视化 web 神器:streamlit、Gradio、dash、nicegui;低代码 Python Web 框架:PyWebIO
- 相关性分析——Pearson相关系数+热力图(附data和Python完整代码)
- Anaconda版本和Python版本对应关系(持续更新...)
- Python与PyTorch的版本对应
- Windows上安装 Python 环境并配置环境变量 (超详细教程)
- Python pyinstaller打包exe最完整教程

